Summary
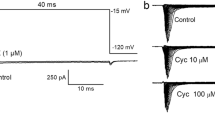
The actions of the insecticide avermectin (AVM) were studied in rat cultured hippocampal neurons with patch-clamp techniques. Application of micromolar concentrations of AVM to voltage-clamped cells gave rise to whole-cell currents, which showed a slow time-course of activation in the order of 10 s, and wash-out periods of typically 20 min. Dose-response curves revealed a half-maximally activating AVM concentration (EC50) of 2.0±0.6 μM and a Hill coefficent of 1.5±0.9. The current activated by AVM was carried predominantly by Cl− ions, as demonstrated by ion-substitution experiments. The Cl− channel blocker picrotoxinin (100 μM) substantially but transiently reduced the AVM response. Outsideout patch recording showed that AVM opened Cl− channels with a conductance of 40±12 pS. The open-time distribution was characterized by two time constants of 11 ms and 259 ms. It is suggested that AVM directly activates Cl− channels in mammalian central neurons, which resemble the channels activated by the physiological transmitters GABA and glycine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalis IM, Eldefrawi AT, Eldefrawi ME (1986) Actions of avermectin B1a on the γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor and chloride channels in rat brain. J Biochem Toxicol 1:69–82
Akaike N, Hattori K, Oomura Y, Carpenter DO (1985) Bicuculline and picrotoxinin block γ-aminobutyric acid-gated Cl− conductance by different mechanisms. Experientia 41:70–71
Arena JP, Liu KK, Paress PS, Cully DF (1991) Avermectin-sensitive chloride currents induced by Caenorhabditis elegans RNA in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol 40:368–374
Banker GA, Cowan MW (1979) Further observations on hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. J Comp Neurol 187:469–494
Bokisch AJ, Walker RJ (1986) The action of avermectin (MK 936) on identified central neurones from Helix and its interaction with acetylcholine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) responses. Comp Biochem Physiol 84C119–125
Bormann J (1988) Electrophysiology of GABAA and GABAB receptor subtypes. Trends Neurosci 11:112–116
Bormann J (1992) U-tube drug application. In: Kettenmann H, Grantyn R (eds) Practical electrophysiological methods. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 136–140
Bormann J, Hamill OP, Sakmann B (1987) Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and γ-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol 385:243–286
Bormann J, Rundström N, Betz H, Langosch D (1993) Residues within transmembrane segment M2 determine chloride conductance of glycine receptor homo- and heterooligomers. EMBO J 12: 3729–3737
Duce IR, Scott RH (1985) Actions of dihydroavermectin B1a on insect muscle. Br J Pharmacol 85:395–401
Fenwick EM, Marty A, Neher E (1982) A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol 331:577–597
Fisher MH, Mrozik H (1992) The chemistry and pharmacology of avermectins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 32:537–553
Gähwiler BH (1984) Development of the hippocampus in vitro: Cell types, synapses and receptors. Neuroscience 11:751–760
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hamill OP, Bormann J, Sakmann B (1983) Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. Nature 305:805–808
Jackson MB, Lecar H, Mathers DA, Barker JL (1982) Single channel currents activated by γ-aminobutyric acid, muscimol, and (−)pentobarbital in cultured mouse spinal neurons. J Neurosci 7: 889–894
Lees G, Beadle DJ (1986) Dihydroavermectin B1a: actions on cultured neurones from the insect central nervous system. Brain Res 366: 369–372
Macdonald RL, Rogers CJ, Twyman RE (1989) Kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol 410:479–499
Martin RJ, Pennington AJ (1989) A patch clamp study of effects of dihydroavermectin on Ascaris muscle. Br J Pharmacol 98:747–765
Matsumoto K, Yamazaki J, Fukuda H (1986) The actions of ivermectin on cultured chick spinal cord neurons. Neurosci Lett 69:279–284
Pribilla I, Takagi T, Langosch D, Bormann J, Betz H (1992) The atypical M2 segment of the β subunit confers picrotoxinin resisitance to inhibitory glycine receptor channels. EMBO J 11:4305–4311
Payne GT, Soderlund DM (1991) Activation of γ-aminobutyric acid insensitive chloride channels in mouse brain synaptic vesicles by avermectin B1a. J Biochem Toxicol 6:283–292
Robertson B (1989) Actions of anaesthetics and avermectin on GABAA chloride channels in mammalian dorsal root ganglion neurones. Br J Pharmacol 98:167–176
Sakmann B, Hamill OP, Bormann J (1983) Patch-clamp measurements of elementary chloride currents activated by the putative inhibitory transmitters GABA and glycine in mammalian spinal neurons. J Neural Transm [Suppl] 18:83–95
Schönrock B, Bormann J (1993) Functional heterogeneity of hippocampal GABAA receptors. Eur J Neurosci 5:1042–1049
Sigel E, Baur R (1987) Effect of avermectin B1a on chick neuronal γ-aminobutyric receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol 32:749–752
Sigworth FJ (1983) An example of analysis. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) Single-channel recording. Plenum Press, New York, pp 301–321
Sigworth FJ, Sine SM (1987) Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys J 52:1047–1054
Sutherland IH, Campbell WC (1990) Development, pharmacokinetics and mode of action of ivermectin. Acta Leiden 59:161–168
Verdoorn TA, Draguhn A, Ymer S, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B (1990) Functional properties of recombinant rat GABA receptors depend upon subunit composition. Neuron 4:919–928
Weiss DS, Magleby KL (1989) Gating scheme for single GABA-activated Cl− channels determined from stability plots, dwell-time distributions and adjacent-interval durations. J Neurosci 9:1314–1324
Zufall F, Franke C, Hatt H (1989) The inseticide avermectin B1a activates a chloride channel in crayfish muscle membrane. J Exp Biol 142:191–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: J. Bormann at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schönrock, B., Bormann, J. Activation of Cl− channels by avermectin in rat cultured hippocampal neurons. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 348, 628–632 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167239
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167239