Summary
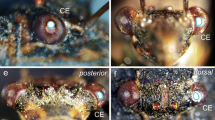
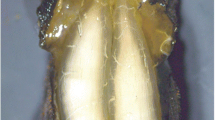
Evidence is presented that neurons in the adult Colorado potato beetle contain a proctolin-like substance. By use of immunocytochemical methods the location of immunoreactive neurons in the central and stomatogastric nervous systems is described. No such neurons were found in the proto- and deutocerebrum or optic lobe. Few immunoreactive neurons are present in the tritocerebrum and numerous proctolin-immunoreactive neurons occur in all ventral ganglia and in the frontal ganglion. Two groups of neurosecretory cells in the suboesophageal ganglion contain a proctolin-immunoreactive substance. In these cells this material is co-localized with a bovine pancreatic polypeptide/FMRF amide-like substance and with a vasopressin/vasotocin/oxytocin-like substance. Proctolin-immunoreactive axon terminals were found on the musculature of the fore- and hindgut and of the vas deferens, and on some segmental muscles. Furthermore, proctolin-immunoreactive neurosecretory axon terminals were found in the corpus cardiacum. The proctolin-like substance may therefore function both as a neurotransmitter/neuromodulator and as a neurohormone. The presence of a proctolin-like substance was also demonstrated with a sensitive bioassay. On fractionation of extracts of the nervous systems of Leptinotarsa decemlineata with high performance liquid chromatography most of the proctolin-like bioactive material comigrated with authentic proctolin. This shows that a proctolin-like substance in this insect is very similar to, if not identical with, the known pentapeptide proctolin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams ME, O'Shea M (1983) Peptide co-transmitter at a neuromuscular junction. Science 221:286–289
Aubele E, Klemm N (1977) Origin, destination and mapping of tritocerebral neurons of locust. Cell Tissue Res 178:199–219
Benson JA, Sullivan RE, Watson WH, Augustine GJ (1981 a) The neuropeptide proctolin acts directly on Limulus cardiac muscle to increase the amplitude of contraction. Brain Res 213:449–454
Benson J, Watson W, Augustine G, Sullivan R (1981 b) A proctolin-like peptide from cardiac ganglion increases heart muscle contraction in Limulus. Experientia 37:606
Bernstein H-G, Eckert M, Penzlin H, Dorn A (1984) Proctolinrelated material in the mouse brain as revealed by immunohistochemistry. Neurosci Lett 45:229–232
Bishop CA, O'Shea M (1982) Neuropeptide proctolin (H-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr-OH): immunocytochemical mapping of neurons in the central nervous system of the cockroach. J Comp Neurol 207:223–238
Bishop CA, O'Shea M, Miller RJ (1981) Neuropeptide proctolin (H-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr-OH): immunological detection and neuronal localization in insect central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 78:5899–5902
Boer HH, Schot LPC, Roubos EW, Maat A ter, Lodder JC, Reichelt D (1979) ACTH-like immunoreactivity in two electronically coupled giant neurones in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 202:231–240
Brown BE (1975) Proctolin: a peptide transmitter candidate in insects. Life Sci 17:1241–1252
Brown BE (1977) Occurrence of proctolin in six orders of insects. J Insect Physiol 23:861–864
Brown BE, Starratt AN (1975) Isolation of proctolin, a myotropic peptide, from Periplaneta americana. J Insect Physiol 21:1879–1881
Cook BJ, Meola S (1978) The oviduct musculature of the horsefly, Tabanus sulcifrons, and its response to 5-hydroxytryptamine and proctolin. Physiol Entomol 3:273–280
Eckert M, Ude J (1983) Immunocytochemical techniques for the identification of peptidergic neurons. In: Strausfeld NJ (ed) Functional neuroanatomy. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo, pp 267–301
Eckert M, Agricola H, Penzlin H (1981) Immunocytochemical identification of proctolin-like immunoreactivity in the terminal ganglion and hindgut of the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 217:633–645
Kingan TG, Titmus M (1980) Proctolin radioimmunoassay in arthropod nervous system. Soc Neurosci Abstr 6:619
Kingan T, Titmus M (1983) Radioimmunological detection of proctolin in arthropods. Comp Biochem Physiol 74C:75–78
Miller T (1979) Nervous versus humoral control of insect heartbeat. Am Zool 19:77–86
Mordue W (1981) Adipokinetic hormone and related peptides. In: Farner DS, Lederis K (eds) Neurosecretion, molecules, cells, systems. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 391–401
Nakane PK (1968) Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using peroxidase labeled antibody method: A study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 16:560–577
O'Shea M, Adams ME (1981) Pentapeptide (proctolin) associated with an identified neuron. Science 213:567–569
O'Shea M, Bishop CA (1982) Neuropeptide proctolin associated with an identified skeletal motoneuron. J Neurosci 2:1242–1251
O'Shea M, Witten J, Schaffer M (1984) Isolation and characterization of two myoactive neuropeptides: further evidence of an invertebrate peptide family. J Neurosci 4:521–529
Piek T, Mantel P (1977) Myogenic contractions in locust muscle induced by proctolin and by wasp Philanthus triangulum venom. J Insect Physiol 23:321–325
Starratt AN, Brown BE (1975) Structure of the pentapeptide proctolin, a proposed neurotransmitter in insects. Life Sci 17:1253–1256
Sternberger LA (1974) Immunocytochemistry. Prentice-Hall Inc, New Yersey
Sullivan RE (1979) A proctolin-like peptide in crab pericardial organs. J Exp Zool 210:543–552
Swaab DF, Pool CW, Leeuwen FW van (1977) Can specificity ever be proved in immunocytochemical staining? J Histochem Cytochem 25:388–391
Veenstra JA (1984) Immunocytochemical demonstration of a homology in peptidergic neurosecretory cells in the suboesophageal ganglion of a beetle and a locust with antisera to bovine pancreatic polypeptide, FMRFamide, vasopressin and α-MSH. Neurosci Lett 48:185–190
Veenstra JA, Schooneveld H (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of peptidergic neurons in the nervous system of the Colorado potato beetle with antisera against FMRFamide and bovine pancreatic polypeptide. Cell Tissue Res 235:303–308
Veenstra JA, Yanaihara N (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of gastrin-releasing peptide/bombesin-like immunoreactive neurons in insects. Histochemistry 81:133–138
Veenstra JA, Romberg-Privee HM, Schooneveld H (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of peptidergic cells in the neuroendocrine system of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, with antisera against vasopressin, vasotocin and oxytocin. Histochemistry 81:29–34
Veenstra JA, Romberg-Privee HM, Schooneveld H, Polak JM (1985) Immunocytochemical localization of peptidergic neurons and neurosecretory cells in the neuro-endocrine system of the Colorado potato beetle with antisera to vertebrate regulatory peptides. Histochemistry 82:9–18
Walker RJ, James VA, Roberts CJ, Kerkut GA (1980) Neurotransmitter receptors in invertebrates. In: Satelle DB, Hall LM (eds) Receptors for neurotransmitters, hormones and pheromones in insects. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 41–57
Watson WH, Augustine GJ, Benson JA, Sullivan RE (1983) Proctolin and an endogenous proctolin-like peptide enhance the contractility of the Limulus heart. J Exp Biol 103:55–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veenstra, J.A., Romberg-Privee, H.M. & Schooneveld, H. A proctolin-like peptide and its immunocytochemical localization in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata . Cell Tissue Res. 240, 535–540 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216342
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216342