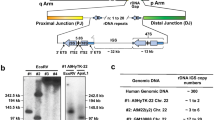
Summary
Friedreich ataxia (FA) is a severe autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease. The defective gene has been previously assigned to chromosome 9q13-q21 by demonstration of tight linkage to the two independent loci D9S15 and D9S5. Linkage data indicate that FRDA is at less than 1 cM from both markers. Previous physical mapping has shown that probes defining D9S15 (MCT112) and D9S5 (26P) are less than 260kb apart and are surrounded by at least six CpG clusters within 450 kb, which might indicate the presence of “candidate” genes for FA. We isolated and characterized a 530 kb YAC (yeast artificial chromosome) contig that contains five of the CpG clusters. The YACs were used to search for new polymorphic markers needed to map FRDA precisely with respect to the cloned segment. In particular, we found a (CA)n microsatellite polymorphism, GS4, that detects 13 alleles with a PIC value of 0.83 and allows the definition of haplotypes extending over 310kb when used in combination with polymorphic markers at D9S5 and D9S15.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertsen HM, Le Paslier D, Abderrahim H, Dausset J, Cann H, Cohen D (1989) Improved control of partial DNA restriction in agarose using limiting concentrations of Mg++. Nucleic Acids Res 17:808
Albertsen HM, Abderahim H, Cann H, Dausset J, Le Paslier D, Cohen D (1990) Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library containing seven haploid human genome equivalents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:456–460
Anand R, Villasante A, Tyler-Smith C (1989) Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulse-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3425–3433
Bellis M, Pages M, Royzes G (1987) A simple method for preparing yeast chromosomes for pulse field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res 15:6749
Breukel C, Wijnen J, Tops C, Klift H vd, Dauwerse H, Khan M (1990) Vector-Alu PCR: a rapid step in mapping cosmids and YACs. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3097
Brownstein BH, Silverman GA, Little RD, Burke DT, Korsmeyer SJ, Schlessinger D, Olson MV (1989) Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science 236:806–812
Burke DT, Carle GF, Olson MV (1987) Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science 236:806–812
Carlson M, Nakamura Y, Krapcho K, Fujimoto E, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, White R (1987) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pMCT112 on chromosome 9q (D9S15). Nucleic Acids Res 15:10614
Chamberlain S, Shaw J, Rowland A, Wallis J, South S, Nakamura Y, von Gabain AS, Farral M, Williamson R (1988) Mapping of mutation causing Friedreich ataxia to human chromosome 9. Nature 334:248–250
Chamberlain S, Shaw J, Wallis J, Rowland A, Chow L, Farral M, Keats B, Richter A, Roy M, Melançon S, Deufel T, Berciano J, Williamson R (1989) Genetic homogeneity at the Friedreich ataxia locus on chromosome 9. Am J Hum Genet 44:518–521
Feinberg A, Vogelstein B (1984) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 137:266–267
Fujita R, Agid Y, Trouillas P, Seck A, Tommasi-Davenas C, Driesel AJ, Olek K, Grzeschik KH, Nakamura Y, Mandel JL, Hanauer A (1989) Confirmation of linkage of Friedreich Ataxia to chromosome 9 and identification of a new closely linked marker. Genomics 4:110–111
Fujita R, Hanauer A, Sirugo G, Heilig R, Mandel JL (1990) Additional polymorphisms at marker loci D9S5 and D9S15 generate extended haplotypes in linkage disequilibrium with Friedreich ataxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1796–1800
Fujita R, Hanauer A, Vincent A, Mandel JL, Kœig M (1991) Physical mapping of two loci (D9S5 and D9S15) tightly linked to Friedreich ataxia locus (FRDA) and identification of nearby CpG islands by pulse field gel electrophoresis. Genomics 10:915–920
Hanauer A, Chery M, Fujita R, Driesel AJ, Gilgenkrantz S, Mandel JL (1990) The Friedreich ataxia gene is assigned to chromosome 9q13–q21 by mapping of tightly linked markers and shows linkage disequilibrium with D9S15. Am J Hum Genet 46:133–137
Heilig R, Lemaire C, Mandel JL (1987). A 230kb cosmid walk in Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene: detection of a conserved sequence and a possible deletion prone region. Nucleic Acids Res 15:9129–9142
Hsu LC, Yoshida A, Mohandas T (1986) Chromosomal assignment of the genes for human aldehyde dehydrogenase-1 and aldehyde dehydrogenase-2. Am J Hum Genet 38:641–648
Nizetic DB, Zehetner G, Monaco AP, Gellen L, Young BD, Lehrach H (1991) Construction, arraying and high density screening of large insert libraries of the human X and 21 chromosomes, their potential use as reference libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3233–3237
Orita M, Sekiya T, Hayashi K (1990) DNA sequence polymorphisms in Alu repeats. Genomics 8:271–278
Orzechowski HD, Henning J, Winter P, Grzeschik KH, Olek K, Driesel AJ (1987) A human single copy DNA probe (DR47) detects a TaqI RFLP on chromosome 9 (D9S5). Nucleic Acids Res 15:6310
Pandolfo M, Sirugo G, Antonelli A, Weitnauer L, Ferretti L, Leone M, Dones I, Cerino A, Fujita R, Hanauer A, Mandel JL, diDonato S (1990) Friedreich ataxia in Italian families: genetic homogeneity and linkage disequilibrium with the marker loci D9S5 and D9S15. Am J Hum Genet 47:228–235
Sirugo G, Keats B, Fujita R, Duclos F, Purohit K, Kœnig M, Mandel JL (1991) Friedreich ataxia in Louisiana-Acadians: demonstration of a founder effect by analysis of microsatellite generated extended haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 50:559–566
Southern EM, Anand R, Brown WRA, Fletscher DS (1987) A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res 15:5925–5943
Wilkes D, Shaw J, Anand R, Riley J, Winter P, Wallis J, Driesel AG, Williamson R, Chamberlain S (1991) Identification of CpG islands in a physical map encompassing the Friedreich's ataxia locus. Genomics 9:90–95
Zonana J, Roberts SH, Thomas NST, Harper PS (1988) Recognition and reanalysis of a cell line from a manifesting female with linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and an X: autosome balanced translocation. J Med Genet 25:383–386
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, R., Sirugo, G., Duclos, F. et al. A 530kb YAC contig tightly linked to the Friedreich ataxia locus contains five CpG clusters and a new highly polymorphic microsatellite. Hum Genet 89, 531–538 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219179
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219179