Abstract
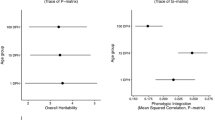
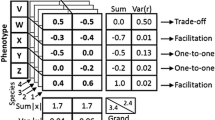
Paradise fish exhibit complex, environment-specific behavioral responses which consist of behavioral elements (motor and posture patterns) appearing in a typical, correlated manner. The genetic and environmental components underlying these phenotypical correlations have not been comprehensively investigated. Therefore, we have analyzed the behavioral elements of paradise fish from the nine populations of a 3×3 full diallel cross by employing a bivariate extension of the Hayman-Jinks variance-covariance analysis, demonstrating the presence of significant environmental and genetic correlations. To investigate the multivariate structure of the correlation matrices obtained, we subjected the phenotypical, environmental, additive genetic, and dominance correlations to principal-component analyses (PCAs). After rotation, the phenotypical principal factor pattern found was similar to previously obtained ones, suggesting stable underlying biological mechanisms. The environmental PCA extracted several environmental principal factors that were highly situation-specific. PCAs of the matrices of genetic correlations extracted only a small number of genetic principal factors which were not situation-specific, suggesting a relatively simple underlying genetic structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benno, R. H. (1990) Development of the nervous system: Genetics, epigenetics, and phylogenetics. In Hahn, M. E., Hewitt, J. K., Henderson, N. D., and Benno, R. H. (eds.),Developmental Behavior Genetics: Neural, Biometrical, and Evolutionary Approaches, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 113–143.
Crusio, W. E. (1992) Quantitative genetics. In Goldowitz, D., Wahlsten, D., and Wimer, R. (eds.),Techniques for the Genetic Analysis of Brain and Behavior: Focus on the Mouse, Techniques in the Behavioral and Neural Sciences, Vol. 8, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 231–250.
Crusio, W. E. (1993). Bi- and multivariate analyses of diallel crosses: A tool for the genetic dissection of neurobehavioral phenotypes.Behav. Genet. 23:59–67.
Crusio, W. E., Kerbusch, J. M. L., and van Abeelen, J. H. F. (1984). The replicated diallel cross: A generalized method of analysis.Behav. Genet. 14:81–104.
Csányi, V., and Gerlai, R. (1988) Open-field behavior and the behavior-genetic analysis of the paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis).J. Comp. Psychol. 102:326–336.
Csányi, V., Tóth, P., Altbäcker, V., Dóka, A., and Gervai, J. (1985a). Behavioural elements of the paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis). I. Regularities of defensive behaviour.Acta Biol. Hung. 36:93–114.
Csányi, V., Tóth, P., Altbäcker, V., Dóka, A., and Gervai, J. (1985b). Behavioural elements of the paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis). II. A functional analysis.Acta Biol. Hung. 36:115–130.
Fuller, J. L. (1979) The taxonomy of psychophenes. In Royce, J. R., and Mos, L. P. (eds.),Theoretical Advances in Behavior Genetics, Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, pp. 483–504.
Gerlai, R., and Csányi, V. (1990). Genotype-environment interaction and the correlation structure of behavioral elements in paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis).Physiol. Behav. 47:343–356.
Gerlai, R., and Csányi, V. (1994). Artificial bidirectional selection for a species-specific behavioural element, staccato movement, in paradise fish,Macropodus opercularis.Anim. Behav. 48:1293–1300.
Gerlai, R., and Hogan, J. A. (1992). Learning to find the opponent: An ethological analysis of the behavior of paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis, Anabantidae) in intra- and inter-specific encounters.J. Comp. Psychol. 106:306–315.
Gerlai, R., Crusio, W. E., and Csányi, V. (1990). Inheritance of species-specific behaviors in the paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis): A diallel study.Behav. Genet. 20: 487–498.
Gervai, J., and Csányi, V. (1985). Behavior genetic analysis of the paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis). I. Characterization of the behavioral responses of inbred strains in novel environments: A factor analysis.Behav. Genet. 15:503–519.
Hayman, B. I. (1954). The theory and analysis of diallel crosses.Genetics 39:789–809.
Huntingford, F. (1984).The Study of Animal Behaviour, Chapman and Hall, London.
Jinks, J. L., and Hayman, B. I. (1953). The analysis of diallel crosses.Maize Genet. News Lett.27:48–54.
Ray, A. A. (ed.) (1982)SAS User's Guide: Statistics, SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
van Abeelen, J. H. F. (1963). Mouse mutants studied by means of ethological methods. I. Ethogram.Genetica 34:79–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerlai, R., Crusio, W.E. Organization of motor and posture patterns in paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis): Environmental and genetic components of phenotypical correlation structures. Behav Genet 25, 385–396 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02197289
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02197289