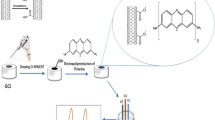
Abstract
The pollution generated by the metallurgical industry effluents represents a serious issue for human health and the environment where the presence of cyanide species is particularly dangerous even at low concentration. In this context, we have developed an electrochemical sensor based on a glassy carbon (GC) electrode modified with 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (HNFQ) for the detection of the \({[\text{Ni}({\text{CN})}_{4}]}_{(\text{aq})}^{2-}\) complex ion from galvanic wastewater. It was characterized by physicochemical techniques such as Raman spectroscopy, electrochemical spectroscopy impedance, and UV–Visible spectroscopy. The electrochemical detection of the complex ion \({[\text{Ni}({\text{CN})}_{4}]}_{(\text{aq})}^{2-}\) was carried out by the square-wave voltammetry electrochemical technique. The GC/HNFQ electrochemical sensor features a wide linear range of 1.28 × 10–5–1.63 × 10–3 mol L−1 with a determination coefficient R2 of 0.9993, a limit of detection (LOD) of 3.31 ± 2.21 µmol L−1, and a limit of quantification (LOQ) of 10.93 ± 7.31 µmol L−1. Moreover, the proposed sensor displays excellent selectivity to the interfering ions (\({\text{K}}^{+}\), \({\text{Na}}^{+}\), \({\text{Cl}}^{-}\), \({\text{NO}}_{3}^{-}\), \({\text{SO}}_{4}^{2-},\) and \({\text{HCO}}_{3}^{-}\)). Finally, in order to investigate the molecular interplay between the involved species at the electrode-solution interface, a computational study in the framework of DFT has been conducted, which suggests a parallel orientation of a formed Ni(II)-bis(2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinonate) complex and a graphitic domain of the glassy carbon surface.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabeen AH, Kamaruddin SNB, Noor ZZ (2019) Environmental impacts assessment of industrial wastewater treatment system using electroless nickel plating and life cycle assessment approaches. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:3171–3182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1974-6
Gorokhovsky A, Vikulova M, Escalante-Garcia JI et al (2020) Utilization of nickel-electroplating wastewaters in manufacturing of photocatalysts for water purification. Process Saf Environ Prot 134:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.11.040
Chen M, Lu W, Hou Z et al (2017) Heavy metal pollution in soil associated with a large-scale cyanidation gold mining region in southeast of Jilin, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3084–3096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7968-3
GracePavithra K, Jaikumar V, Kumar PS, SundarRajan PS (2019) A review on cleaner strategies for chromium industrial wastewater: present research and future perspective. J Clean Prod 228:580–593
Moscatello N, Swayambhu G, Jones CH et al (2018) Continuous removal of copper, magnesium, and nickel from industrial wastewater utilizing the natural product yersiniabactin immobilized within a packed-bed column. Chem Eng J 343:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.093
Al-Saydeh SA, El-Naas MH, Zaidi SJ (2017) Copper removal from industrial wastewater: a comprehensive review. J Ind Eng Chem 56:35–44
Benvenuti T, Siqueira Rodrigues MA, Bernardes AM, Zoppas-Ferreira J (2017) Closing the loop in the electroplating industry by electrodialysis. J Clean Prod 155:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.139
Sivakumar D, Nouri J, Modhini TM, Deepalakshmi K (2018) Nickel removal from electroplating industry wastewater: a bamboo activated carbon. Glob J Environ Sci Manag 4:325–338. https://doi.org/10.22034/GJESM.2018.03.006
Dermentzis KI, Marmanis DI, Christoforidis AK, et al Recovery of metallic nickel from waste sludge produced by electrocoagulation of nickel bearing electroplating effluents
Pertile TS, Birriel EJ (2017) Treatment of hydrocyanic galvanic effluent by electrocoagulation: optimization of operating parameters using statistical techniques and a coupled polarity inverter. Korean J Chem Eng 34:2631–2640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0178-y
Kumar Meher A, Labhsetwar N, Bansiwal A (2018) An improved method for direct estimation of free cyanide in drinking water by ion chromatography-pulsed amperometry detection (IC-PAD) on gold working electrode. Food Chem 240:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.041
Betancourt-Buitrago LA, Hernandez-Ramirez A, Colina-Marquez JA et al (2019) Recent developments in the photocatalytic treatment of cyanide wastewater: an approach to remediation and recovery of metals. Processes 7:225. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040225
Song Y, Lei S, Zhou J, Tian Y (2016) Removal of heavy metals and cyanide from gold mine waste-water by adsorption and electric adsorption. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:2539–2544. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4859
Sengan M, Veerappan A (2019) N-myristoyltaurine capped copper nanoparticles for selective colorimetric detection of Hg 2+ in wastewater and as effective chemocatalyst for organic dye degradation. Microchem J 148:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.049
Sasaki Y, Minamiki T, Tokito S, Minami T (2017) A molecular self-assembled colourimetric chemosensor array for simultaneous detection of metal ions in water. Chem Commun 53:6561–6564. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc03218h
Azhari S, Sathishkumar P, Ahamad R et al (2016) Fabrication of a composite modified glassy carbon electrode: a highly selective, sensitive and rapid electrochemical sensor for silver ion detection in river water samples. Anal Methods 8:5712–5721. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay01336h
Nisar A, Shah A, Zahid A et al (2018) Sensitive and selective detection of multiple metal ions using amino acids modified glassy carbon electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 165:B67–B73. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0151803jes
Huang SS, Liu L, Mei LP et al (2016) Electrochemical sensor for nitrite using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold-copper nanochain networks. Microchim Acta 183:791–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1717-z
Rodrigues JA, Rodrigues CM, Almeida PJ et al (2011) Increased sensitivity of anodic stripping voltammetry at the hanging mercury drop electrode by ultracathodic deposition. Anal Chim Acta 701:152–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2011.05.031
Xu K, Pérez-Ràfols C, Marchoud A (2021) Anodic stripping voltammetry with the hanging mercury drop electrode for trace metal detection in soil samples. Chemosens 9:107 https://doi.org/10.3390/CHEMOSENSORS9050107
El Tall O, Jaffrezic-Renault N, Sigaud M, Vittori O (2007) Anodic stripping voltammetry of heavy metals at nanocrystalline boron-doped diamond electrode. Electroanalysis 19:1152–1159. https://doi.org/10.1002/ELAN.200603834
Barvin RKB, Prakash P, Ganesh V, Jeyaprabha B (2019) Highly selective and sensitive sensing of toxic mercury ions utilizing carbon quantum dot-modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Environ Res 13:1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00236-2
Vimala A, Vedhi C (2019) Electrochemical sensors for heavy metals detection in gracilaria corticata using multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. J Anal Chem 74:276–285. https://doi.org/10.1134/S106193481903002X
Hassan KM, Elhaddad GM, AbdelAzzem M (2019) Voltammetric determination of cadmium(II), lead(II) and copper(II) with a glassy carbon electrode modified with silver nanoparticles deposited on poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene). Microchim Acta 186:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3552-0
Kokab T, Shah A, Iftikhar FJ et al (2019) Amino acid-fabricated glassy carbon electrode for efficient simultaneous sensing of Zinc(II), Cadmium(II), Copper(II), and Mercury(II) ions. ACS Omega 4:22057–22068. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03189
Zheng Y, Luo R, Xu Y et al (2020) Adsorbate-mediated deposition of noble-metal nanoparticles on carbon substrates for electrocatalysis. ACS Appl Energy Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.0c00706
Xu Y, Zheng Y, Wang C, Chen Q (2019) An all-organic aqueous battery powered by adsorbed quinone. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:23222–23228. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b05159
Kim HJ, Han YK (2016) How can we describe the adsorption of quinones on activated carbon surfaces? Curr Appl Phys 16:1437–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2016.08.009
Parthiban C, Ciattini S, Chelazzi L, Elango KP (2016) Colorimetric sensing of anions by Cu(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes of naphthoquinone-imidazole hybrid—influence of complex formation on selectivity and sensing medium. Sens Actuators B 231:768–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.03.106
Shalini Devi KS, Senthil Kumar A (2018) A blood-serum sulfide selective electrochemical sensor based on a 9,10-phenanthrenequinone-tethered graphene oxide modified electrode. Analyst 143:3114–3123. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an00756j
Jayasudha P, Manivannan R, Ciattini S et al (2017) Selective sensing of cyanide in aqueous solution by quinone-indole ensembles—quantitative effect of substituents on the HBD property of the receptor moiety. Sens Actuators B 242:736–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.117
Jayasudha P, Manivannan R, Elango KP (2017) Benzoquinone based chemodosimeters for selective and sensitive colorimetric and turn-on fluorescent sensing of cyanide in water. Sens Actuators B 251:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.105
Kasumov VT, Taş E, Kartal I et al (2006) Complexation of metal ions with 3,5-di-tert-butyl-1,2-benzoquinone-1-monooxime. ESR Studies of Radical Intermediates. 52:207–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970108022588
Jali BR (2021) A mini-review: Quinones and their derivatives for selective and specific detection of specific cations. 11:11679–11699. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC114.1167911699
Yuasa J, Suenobu T, Fukuzumi S (2006) Binding modes in metal ion complexes of Quinones and semiquinone radical anions: electron-transfer reactivity. ChemPhysChem 7:942–954. https://doi.org/10.1002/CPHC.200500640
Kelsall GH (1991) Cyanide oxidation at nickel anodes: I. Thermodynamics of and Systems at 298 K. J Electrochem Soc 138:108. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2085519
Cukman D, Pravdic V (1978) Croatica Chemica Acta. An Investigation of the electrochemical reactions of a nickel cyanide complex at mercury electrode by cyclic voltammetry 51(3):243–247
Orlik M, Galus Z (1988) Electrochemistry of the nickel-cyanide system at mercury electrodes. Part III. The role of intermediate products in the mechanism of ni(cn)42- electroreduction at mercury electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 248:139–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(88)85157-X
Orlik M, Galus Z (1990) Electrochemistry of the nickel-cyanide system at mercury electrodes: Part VI. On the decrease in the Ni(CN)2–4 electroreduction wave caused by repulsive double-layer effects. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 296:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(90)87236-D
Ferreira MA, Barros AA (2002) Determination of As(III) and arsenic(V) in natural waters by cathodic stripping voltammetry at a hanging mercury drop electrode. Anal Chim Acta 459:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(02)00086-7
Katz E, Schlereth DD, Schmidt HL (1994) Electrochemical study of pyrroloquinoline quinone covalently immobilized as a monolayer onto a cystamine-modified gold electrode. J Electroanal Chem 367:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(93)03010-M
Sedenho GC, De Porcellinis D, Jing Y et al (2020) Effect of molecular structure of quinones and carbon electrode surfaces on the interfacial electron transfer process. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:1933–1943. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAEM.9B02357/SUPPL_FILE/AE9B02357_SI_001.PDF
Roy S, Sarkar B, Bubrin D et al (2008) Stabilizing the elusive ortho-quinone/copper (I) oxidation state combination through π/π interaction in an isolated complex. J Am Chem Soc 130:15230–15231
Frisch M, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, et al (2009) Gaussian 09, revision a. 02, gaussian. Inc, Wallingford, CT 200:28
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG (2008) The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other function. Theor Chem Acc 120:215–241
Tomasi J, Mennucci B, Cammi R (2005) Quantum mechanical continuum solvation models. Chem Rev 105:2999–3094
Mennucci B, Tomasi J, Cammi R et al (2002) Polarizable continuum model (PCM) calculations of solvent effects on optical rotations of chiral molecules. J Phys Chem A 106:6102–6113
Wen X, Zhang D, Shi L et al (2012) Three-dimensional hierarchical porous carbon with a bimodal pore arrangement for capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem 22:23835–23844. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm35138b
Heo JY, Cho CH, Jeon HS et al (2011) Enhanced Raman spectrum of lawsone on Ag surface: vibrational analyses, frequency shifts, and molecular geometry. Spectrochim Acta A 83:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.08.057
Kathawate L, Shinde Y, Yadav R, et al Thermal and spectral properties of alkali metal complexes of 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3204-2
Cárdenas Riojas AA, Wong A, Planes GA et al (2019) Development of a new electrochemical sensor based on silver sulfide nanoparticles and hierarchical porous carbon modified carbon paste electrode for determination of cyanide in river water samples. Sens Actuators B 287:544–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2019.02.053
Cardenas-Riojas AA, Cornejo-Herrera AF, Muedas-Taipe G et al (2021) Electrochemical sensor based on 1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone adsorbed on a glassy carbon electrode for the detection of [Cu(CN)3]2-(aq) in alkaline cyanide copper plating baths waste. J Electroanal Chem 880:114909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114909
Lin Q, Li Q, Batchelor-McAuley C, Compton RG (2015) Two-electron, two-proton oxidation of catechol: kinetics and apparent catalysis. J Phys Chem C 119:1489–1495
Zhang Y, Hu L, Liu X et al (2015) Highly-sensitive and rapid detection of ponceau 4R and tartrazine in drinks using alumina microfibers-based electrochemical sensor. Food Chem 166:352–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2014.06.048
Hijji YM, Barare B, Zhang Y (2012) Lawsone (2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) as a sensitive cyanide and acetate sensor. Sens Actuators B 169:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2012.03.067
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2000) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Vivek JP, Monsur A, Burgess IJ (2013) Differential capacity and chronocoulometry studies of a quaternary ammonium surfactant adsorbed on Au(111). Surf Interface Anal 45:1402–1409. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.5300
Inzelt G (2010) Chronocoulometry. Electroanalytical methods: guide to experiments and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 147–158
Pérez Domínguez JC, Higuera Cobos ÓF (2011) Comportamiento electroquímico del cianuro. Rev Científica Ing y Desarro 24
Seghiouer A, Chevalet J, Barhoun A, Lantelme F (1998) Electrochemical oxidation of nickel in alkaline solutions: a voltammetric study and modelling. J Electroanal Chem 442:113–123
Casella IG, Gatta M (2000) Electrochemical and XPS characterization of composite modified electrodes obtained by nickel deposition on noble metals. Anal Chem 72:2969–2975. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9913863
Dai J, Deng D, Yuan Y et al (2016) Amperometric nitrite sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and poly(toluidine blue). Microchim Acta 183:1553–1561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1773-z
Wang J (1994) Selectivity coefficients for amperometric sensors. Talanta 41:857–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(94)E0079-7
Sebroski JR, Ode RH (1997) Method comparison and evaluation for the analysis of weak acid-dissociable cyanide. Environ Sci Technol 31:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/es960016i
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank CONCYTEC/FONDECYT (Contract 210-2015) for the funding granted for carrying out the research and FONDECYT (Contract 237-2015-FONDECYT) for the provision of a doctoral scholarship. The authors acknowledge the MaSCA (Maison de la Simulation de Champagne-Ardenne, France) for computing facilities (http://romeo.univ-reims.fr) and gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the project FC-MF-10-2019 provided by the Vicerrectorado de Investigación of the Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería (National University of Engineering), Lima – Perú.
Funding
Funding was provided by FONDECYT (Contract 210-2015, Contract 237-2015-FONDECYT) and Vicerrectorado de Investigación of the Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería (FC-MF-10-2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardenas-Riojas, A.A., Muedas-Taipe, G., La Rosa-Toro, A. et al. Simple and highly sensitive 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone/glassy carbon sensor for the electrochemical detection of [Ni(CN)4]2− in metallurgical industry wastewater. J Appl Electrochem 52, 1053–1065 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01691-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01691-0