Summary
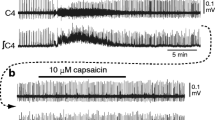
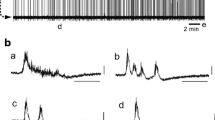
Previous experiments performed in the in vitro newborn rat brainstem-spinal cord preparation reported that the addition of serotonin (5-HT, 30–50 μM) to the bathing medium induced increases in the respiratory frequency and a large tonic discharge on all the cervical ventral roots. The aim of the present work was to define whether the 5-HT-induced tonic discharge involved respiratory or non-respiratory motoneurones. Intracellular recordings demonstrated that cervical (C2) motoneurones (n = 27) were depolarized by 5-HT but that the 5-HT-induced tonic discharge was mainly due to recruitment of silent motoneurones (n = 18) which fired permanently (15/18; 17 ±3 Hz) under 5-HT. The respiratory motoneurones (n = 9) retained a phasic inspiratory discharge (5/9), even if some (4/9) occasionally exhibited a few spikes during expiration. Therefore, it is concluded that the 5-HT-induced tonic discharge is unlikely to have functional significance in respiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams L, Datta AK, Guz A (1988) Short-term synchronization of motor unit discharge in human sterno-cleidomastoid muscle during different respiratory and postural tasks. J Physiol (Lond)399:34P
Adams L, Datta AK, Guz A (1989) Synchronization of motor firing during different respiratory and postural tasks in human sternocleidomastoid muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 413:213–231
Berger AJ (1979) Phrenic motoneurons in the cat: subpopulations and nature of respiratory drive potentials. J Neurophysiol 42:76–90
Campbell EJM (1974) Muscular activity in normal and abnormal ventilation. In: Wyke B (ed) Ventilatory and phonatory control systems. Oxford University Press, London, pp 3–11
Harada Y, Wang YZ, Kuno M (1985) Central chemosensitivity to H+ and CO2 in the rat respiratory centre in vitro. Brain Res 333:336–339
Hebel R, Stromberg MW (1986) Anatomy and embryology of the laboratory rat. BioMed Verlag, Wörthsee, p 271
Hilaire G, Monteau R, Gauthier P, Rega P, Morin D (1990) Functional significance of the dorsal respiratory group in adult and newborn rats: in vivo and in vitro studies. Neurosci Lett 111:133–138
Lalley PM (1986) Serotoninergic and non serotoninergic responses of phrenic motoneurones to raphe stimulation in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 380:373–385
Monteau R, Errchidi S, Gauthier P, Hilaire G, Rega P (1989) Pneumotaxic centre and apneustic breathing: interspecies differences between rat and cat. Neurosci Lett 99:311–316
Monteau R, Gauthier P, Rega P, Hilaire G (1990a) Effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist MK-801 on breathing pattern in rats. Neurosci Lett 109:134–139
Monteau R, Morin D, Hennequin S, Hilaire G (1990b) Differential effects of serotonin on respiratory activity of hypoglossal and cervical motoneurons: an in vitro study on the newborn rat. Neurosci Lett 111:127–132
Monteau R, Morin D, Hilaire G (1990c) Acetylcholine and central chemosensitivity: in vitro study in the newborn rat. Respir Physiol 81:241–254
Morin D, Hennequin S, Monteau R, Hilaire G (1990) Serotonergic influences on central respiratory activity: an in vitro study in the newborn rat. Brain Res 535:281–287
Murakami Y, Kirchner JA (1974) Respiratory activity of the external laryngeal muscles: an electromyographic study in the cat. In: Wyke B (ed) Ventilatory and phonatory control systems. Oxford University Press, London, pp 430–448
Murakoshi T, Otsuka M (1985) Respiratory reflexes in an isolated brainstem-lung preparation of the newborn rat: possible involvement of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glycine. Neurosci Lett 62:63–68
Richmond FJR, Scott DA, Abrahams VC (1978) Distribution of motoneurones to the neck muscles, biventer cervicis, splenius and complexus in the cat. J Comp Neurol 181:451–464
Rose PK (1977) Morphology of motoneurones in the upper cervical cord of the adult cat. J Physiol (Lond) 272:37P
Smith JC, Feldman JL (1987) In vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparation for study of motor systems for mammalian respiration and locomotion. J Neurosci Meth 21:321–333
Smith JC, Liu G, Feldman JL (1988) Intracellular recording from phrenic motoneurons receiving respiratory drive in vitro. Neurosci Lett 88:27–32
Stella G (1938) On the mechanisms of production and the physiological significance of ‘apneusis’. J Physiol (Lond) 93:10–23
Suzue T (1984) Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain-stem-spinal cord preparation of neonatal rat. J Physiol (Lond) 93:173–183
Takahashi T, Berger AJ (1990) Direct excitation of rat spinal motoneurones by serotonin. J Physiol (Lond) 423:63–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morin, D., Monteau, R. & Hilaire, G. Serotonin and cervical respiratory motoneurones: intracellular study in the newborn rat brainstem-spinal cord preparation. Exp Brain Res 84, 229–232 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231779
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231779