Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether reversal of DWI lesions (DWIr) on the DWI-ASPECTS (diffusion weighted imaging Alberta Stroke Program CT Score) template should serve as a predictor of 90-day clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients with pretreatment diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI)-ASPECTS 0–5 treated with thrombectomy, and to determine its predictors in current practice.
Methods
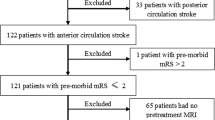
We analyzed data of all consecutive patients included in the prospective multicenter national Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke Registry between 1 January 2015 and 31 December 2020 with a premorbid mRS ≤ 2, who presented with a pretreatment DWI-ASPECTS 0–5 score, underwent thrombectomy and had an available 24 h post-interventional MRI follow-up. Multivariable analyses were performed to evaluate the clinical impact of DWIr on early neurological improvement (ENI), 3‑month modified Rankin scale (mRS) score distribution (shift analysis) and to define independent predictors of DWIr.
Results
Early neurological improvement was detected in 82/211 (41.7%) of patients while 3‑month functional independence was achieved by 75 (35.5%) patients. The DWI reversal (39/211, 18.9%) resulted an independent predictor of both ENI (aOR 3.6, 95% CI 1.2–7.7; p 0.018) and 3‑month clinical outcome (aOR for mRS shift: 2.2, 95% CI 1–4.6; p 0.030). Only successful recanalization (mTICI 2c–3) independently predicted DWIr in the studied population (aOR 3.3, 95% CI 1.3–7.9; p 0.009).
Conclusion
The DWI reversal occurs in a non-negligible proportion of DWI-ASPECTS 0–5 patients subjected to thrombectomy and significantly influences clinical outcome. The mTICI 2c–3 recanalization emerged as an independent DWIr predictor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Román LS, Menon BK, Blasco J, Hernández-Pérez M, Dávalos A, Majoie CBLM, Campbell BCV, Guillemin F, Lingsma H, Anxionnat R, Epstein J, Saver JL, Marquering H, Wong JH, Lopes D, Reimann G, Desal H, Dippel DWJ, Coutts S, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Yavagal D, Ferre JC, Roos YBWEM, Liebeskind DS, Lenthall R, Molina C, Al Ajlan FS, Reddy V, Dowlatshahi D, Sourour NA, Oppenheim C, Mitha AP, Davis SM, Weimar C, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Cobo E, Kleinig TJ, Donnan GA, van der Lugt A, Demchuk AM, Berkhemer OA, Boers AMM, Ford GA, Muir KW, Brown BS, Jovin T, van Zwam WH, Mitchell PJ, Hill MD, White P, Bracard S, Goyal M; HERMES collaborators. Imaging features and safety and efficacy of endovascular stroke treatment: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:895–904. Erratum in: Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:e2–3.
Kaesmacher J, Chaloulos-Iakovidis P, Panos L, Mordasini P, Michel P, Hajdu SD, Ribo M, Requena M, Maegerlein C, Friedrich B, Costalat V, Benali A, Pierot L, Gawlitza M, Schaafsma J, Mendes Pereira V, Gralla J, Fischer U. Mechanical Thrombectomy in Ischemic Stroke Patients With Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score 0-5. Stroke. 2019;50:880–8.
Panni P, Gory B, Xie Y, Consoli A, Desilles JP, Mazighi M, Labreuche J, Piotin M, Turjman F, Eker OF, Bracard S, Anxionnat R, Richard S, Hossu G, Blanc R, Lapergue B; ETIS (Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke) Investigators. Acute Stroke With Large Ischemic Core Treated by Thrombectomy. Stroke. 2019;50:1164–71.
Cagnazzo F, Derraz I, Dargazanli C, Lefevre PH, Gascou G, Riquelme C, Bonafe A, Costalat V. Mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke and ASPECTS ≤6: a meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020;12:350–5.
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ, Wu TY, Brooks M, Simpson MA, Miteff F, Levi CR, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Priglinger M, Ang T, Scroop R, Barber PA, McGuinness B, Wijeratne T, Phan TG, Chong W, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM; EXTEND-IA Investigators. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1009–18.
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O, Jovin TG, Mattle HP, Nogueira RG, Siddiqui AH, Yavagal DR, Baxter BW, Devlin TG, Lopes DK, Reddy VK, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Singer OC, Jahan R; SWIFT PRIME Investigators. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2285–95.
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, San Román L, Serena J, Abilleira S, Ribó M, Millán M, Urra X, Cardona P, López-Cancio E, Tomasello A, Castaño C, Blasco J, Aja L, Dorado L, Quesada H, Rubiera M, Hernandez-Pérez M, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, von Kummer R, Gallofré M, Dávalos A; REVASCAT Trial Investigators. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2296–306.
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD; ESCAPE Trial Investigators. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1019–30.
Broocks G, Hanning U, Flottmann F, Schönfeld M, Faizy TD, Sporns P, Baumgart M, Leischner H, Schön G, Minnerup J, Thomalla G, Fiehler J, Kemmling A. Clinical benefit of thrombectomy in stroke patients with low ASPECTS is mediated by oedema reduction. Brain. 2019;142:1399–407. Erratum in: Brain. 2019;142:e26.
Broocks G, Fiehler J, Kemmling A. Collateral scoring in acute stroke patients with low ASPECTS: an unnecessary or underestimated tool for treatment selection? Brain. 2019;142:e36.
Desilles JP, Consoli A, Redjem H, Coskun O, Ciccio G, Smajda S, Labreuche J, Preda C, Ruiz Guerrero C, Decroix JP, Rodesch G, Mazighi M, Blanc R, Piotin M, Lapergue B; ETIS (Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke) Research Investigators. Successful Reperfusion With Mechanical Thrombectomy Is Associated With Reduced Disability and Mortality in Patients With Pretreatment Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score ≤6. Stroke. 2017;48:963–9. Erratum in: Stroke. 2017;48:e120. Erratum in: Stroke. 2017;48:e138.
Panni P, Michelozzi C, Blanc R, Chen B, Consoli A, Mazighi M, Piotin M, Dargazanli C, Arquizan C, Marnat G, Sibon I, Anxionnat R, Richard S, Hossu G, Bourcier R, Lapergue B, Gory B; ETIS (Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke) Investigators. The role of infarct location in patients with DWI-ASPECTS 0-5 acute stroke treated with thrombectomy. Neurology. 2020;95:e3344–54.
Tisserand M, Turc G, Charron S, Legrand L, Edjlali M, Seners P, Roca P, Lion S, Naggara O, Mas JL, Méder JF, Baron JC, Oppenheim C. Does Diffusion Lesion Volume Above 70 mL Preclude Favorable Outcome Despite Post-Thrombolysis Recanalization? Stroke. 2016;47:1005–11.
Labeyrie MA, Turc G, Hess A, Hervo P, Mas JL, Meder JF, Baron JC, Touzé E, Oppenheim C. Diffusion lesion reversal after thrombolysis: a MR correlate of early neurological improvement. Stroke. 2012;43:2986–91.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–7.
Yoo J, Choi JW, Lee SJ, Hong JM, Hong JH, Kim CH, Kim YW, Kang DH, Kim YS, Hwang YH, Ovbiagele B, Demchuk AM, Lee JS, Sohn SI. Ischemic Diffusion Lesion Reversal After Endovascular Treatment. Stroke. 2019;50:1504–9.
Campbell BC, Purushotham A, Christensen S, Desmond PM, Nagakane Y, Parsons MW, Lansberg MG, Mlynash M, Straka M, De Silva DA, Olivot JM, Bammer R, Albers GW, Donnan GA, Davis SM; EPITHET–DEFUSE Investigators. The infarct core is well represented by the acute diffusion lesion: sustained reversal is infrequent. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:50–6.
Sakamoto Y, Kimura K, Shibazaki K, Inoue T, Uemura J, Aoki J, Sakai K, Iguchi Y. Early ischaemic diffusion lesion reduction in patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator: infrequent, but significantly associated with recanalization. Int J Stroke. 2013;8:321–6.
Simpkins AN, Dias C, Norato G, Kim E, Leigh R; NIH Natural History of Stroke Investigators. Early Change in Stroke Size Performs Best in Predicting Response to Therapy. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;44:141–9.
Inoue M, Olivot JM, Labreuche J, Mlynash M, Tai W, Albucher JF, Meseguer E, Amarenco P, Mazighi M. Impact of diffusion-weighted imaging Alberta stroke program early computed tomography score on the success of endovascular reperfusion therapy. Stroke. 2014;45:1992–8.
Kim SK, Yoon W, Park MS, Heo TW, Baek BH, Lee YY. Outcomes Are Not Different between Patients with Intermediate and High DWI-ASPECTS after Stent-Retriever Embolectomy for Acute Anterior Circulation Stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37:1080–5.
Manceau PF, Soize S, Gawlitza M, Fabre G, Bakchine S, Durot C, Serre I, Metaxas GE, Pierot L. Is there a benefit of mechanical thrombectomy in patients with large stroke (DWI-ASPECTS ≤ 5)? Eur J Neurol. 2018;25:105–10.
Mourand I, Abergel E, Mantilla D, Ayrignac X, Sacagiu T, Eker OF, Gascou G, Dargazanli C, Riquelme C, Moynier M, Bonafé A, Arquizan C, Costalat V. Favorable revascularization therapy in patients with ASPECTS ≤ 5 on DWI in anterior circulation stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018;10:5–9.
Song K, Guan M, Li W, Jing Z, Xie X, Shi C, Liang J, Qiao H, Huang L. Acute ischemic stroke patients with diffusion-weighted imaging-Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score ≤ 5 can benefit from endovascular treatment: a single-center experience and literature review. Neuroradiology. 2019;61:451–9.
Yoo AJ, Berkhemer OA, Fransen PSS, van den Berg LA, Beumer D, Lingsma HF, Schonewille WJ, Sprengers MES, van den Berg R, van Walderveen MAA, Beenen LFM, Wermer MJH, Nijeholt GJLÀ, Boiten J, Jenniskens SFM, Bot JCJ, Boers AMM, Marquering HA, Roos YBWEM, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Dippel DWJ, van der Lugt A, van Zwam WH, Majoie CBLM; MR CLEAN investigators. Effect of baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score on safety and efficacy of intra-arterial treatment: a subgroup analysis of a randomised phase 3 trial (MR CLEAN). Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:685–94.
Yoshimoto T, Inoue M, Tanaka K, Kanemaru K, Koge J, Shiozawa M, Kamogawa N, Kimura S, Chiba T, Satow T, Takahashi JC, Toyoda K, Koga M, Ihara M. Identifying large ischemic core volume ranges in acute stroke that can benefit from mechanical thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021;13:1081–7.
Yoshimura S, Sakai N, Yamagami H, Uchida K, Beppu M, Toyoda K, Matsumaru Y, Matsumoto Y, Kimura K, Takeuchi M, Yazawa Y, Kimura N, Shigeta K, Imamura H, Suzuki I, Enomoto Y, Tokunaga S, Morita K, Sakakibara F, Kinjo N, Saito T, Ishikura R, Inoue M, Morimoto T. Endovascular Therapy for Acute Stroke with a Large Ischemic Region. N Engl J Med. 2022; doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118191. Epub ahead of print.
Kidwell CS, Saver JL, Mattiello J, Starkman S, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Vespa P, Kalafut M, Alger JR. Thrombolytic reversal of acute human cerebral ischemic injury shown by diffusion/perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:462–9.
Fiehler J, Foth M, Kucinski T, Knab R, von Bezold M, Weiller C, Zeumer H, Röther J. Severe ADC decreases do not predict irreversible tissue damage in humans. Stroke. 2002;33:79–86.
Fiehler J, Knudsen K, Kucinski T, Kidwell CS, Alger JR, Thomalla G, Eckert B, Wittkugel O, Weiller C, Zeumer H, Röther J. Predictors of apparent diffusion coefficient normalization in stroke patients. Stroke. 2004;35:514–9.
Dargazanli C, Fahed R, Blanc R, Gory B, Labreuche J, Duhamel A, Marnat G, Saleme S, Costalat V, Bracard S, Desal H, Mazighi M, Consoli A, Piotin M, Lapergue B; ASTER Trial Investigators. Modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction 2C/Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction 3 Reperfusion Should Be the Aim of Mechanical Thrombectomy: Insights From the ASTER Trial (Contact Aspiration Versus Stent Retriever for Successful Revascularization). Stroke. 2018;49:1189–96.
Inoue M, Mlynash M, Christensen S, Wheeler HM, Straka M, Tipirneni A, Kemp SM, Zaharchuk G, Olivot JM, Bammer R, Lansberg MG, Albers GW; DEFUSE 2 Investigators. Early diffusion-weighted imaging reversal after endovascular reperfusion is typically transient in patients imaged 3 to 6 hours after onset. Stroke. 2014;45:1024–8.
Marks MP, Tong DC, Beaulieu C, Albers GW, de Crespigny A, Moseley ME. Evaluation of early reperfusion and i.v. tPA therapy using diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI. Neurology. 1999;52:1792–8.
Soize S, Tisserand M, Charron S, Turc G, Ben Hassen W, Labeyrie MA, Legrand L, Mas JL, Pierot L, Meder JF, Baron JC, Oppenheim C. How sustained is 24-hour diffusion-weighted imaging lesion reversal? Serial magnetic resonance imaging in a patient cohort thrombolyzed within 4.5 hours of stroke onset. Stroke. 2015;46:704–10.
Nagaraja N, Forder JR, Warach S, Merino JG. Reversible diffusion-weighted imaging lesions in acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review. Neurology. 2020;94:571–87.
Zaidat OO, Liebeskind DS, Jadhav AP, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Nguyen TN, Haussen DC, Yavagal DR, Froehler MT, Jahan R, Nogueira RG, Yao TL, Alenzi BA, Bushnaq S, Mueller-Kronast NH. Impact of Age and Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score 0 to 5 on Mechanical Thrombectomy Outcomes: Analysis From the STRATIS Registry. Stroke. 2021;52:2220–8.
de Margerie-Mellon C, Turc G, Tisserand M, Naggara O, Calvet D, Legrand L, Meder JF, Mas JL, Baron JC, Oppenheim C. Can DWI-ASPECTS substitute for lesion volume in acute stroke? Stroke. 2013;44:3565–7.
Members of the Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke (ETIS) Investigators
Rothschild Foundation: Michel Piotin; Raphael Blanc; Hocine Redjem; Simon Escalard; Jean-Philippe Dessilles; François Delvoye; Stanislas Smajda; Benjamin Maier; Hebert Solène; Mikael Mazighi; Mikael Obadia; Candice Sabben; Pierre Seners; Igor Raynouard; Ovide Corabianu; Thomas de Broucker; Eric Manchon; Guillaume Taylor; Malek Ben Maacha; Laurie-Anne Thion; Augustin Lecler; Julien Savatovsky. Foch Hospital: Adrien Wang; Serge Evrard; Maya Tchikviladze; Nadia Ajili; Bertrand Lapergue; David Weisenburger-Lile; Lucas Gorza; Géraldine Buard; Oguzhan Coskun; Arturo Consoli; Federico Di Maria; Georges Rodesch; Sergio Zimatore; Morgan Leguen; Julie Gratieux; Fernando Pico; Haja Rakotoharinandrasana; Philippe Tassan; Roxanna Poll; Sylvie Marinier. CHU Bordeaux: Gaultier Marnat; Florent Gariel; Xavier Barreau; Jérôme Berge; Patrice Menegon; Igor Sibon; Ludovic Lucas; Stéphane Olindo; Pauline Renou; Sharmila Sagnier; Mathilde Poli; Sabrina Debruxelles; François Rouanet; Thomas Tourdias; Jean-Sebastien Liegey; Pierre Briau; Nicolas Pangon. CHU Nantes: Romain Bourcier; Lili Detraz; Benjamin Daumas-Duport; Pierre-Louis Alexandre; Monica Roy; Cédric Lenoble; Hubert Desal; Benoît Guillon; Solène de Gaalon; Cécile Preterre. CHRU-Nancy: Benjamin Gory; Serge Bracard; René Anxionnat; Marc Braun; Anne-Laure Derelle; Romain Tonnelet; Liang Liao; François Zhu; Emmanuelle Schmitt; Sophie Planel; Sébastien Richard; Lisa Humbertjean; Gioia Mione; Jean-Christophe Lacour; Gérard Audibert; Marcela Voicu; Lionel Alb; Marie Reitter; Madalina Brezeanu; Agnès Masson; Adriana Tabarna; Iona Podar; Pauline Bourst; Sarah Guy; Fatiha Bechiri. CHU Limoges: Francisco Macian-Montoro; Suzanna Saleme; Charbel Mounayer; Aymeric Rouchaud; Laetitia Gimenez; Alexandre Cosnard. CHRU Gui de Chauliac: Vincent Costalat; Caroline Arquizan; Cyril Dargazanli; Grégory Gascou; Pierre-Henri Lefèvre; Imad Derraz; Carlos Riquelme; Nicolas Gaillard; Isabelle Mourand; Lucas Corti; Federico Cagnazzo; Adrien ter Schiphorst. CHU Rennes: Francois Eugene; Stéphane Vannier; Jean-Christophe Ferre; Hélène Raoult; Thomas Ronziere; Maria Lassale; Christophe Paya; Jean-Yves Gauvrit; Clément Tracol; Sophie Langnier-Lemercier; Axelle Maurice; Sabrina Cochennec; Mélanie Pinault. CHU Pitié-Salpétrière: Frédéric Clarençon; Eimad Shotar; Nader Sourour; Stéphanie Lenck; Kévin Premat; Yves Samson; Anne Léger; Sophie Crozier; Flore Baronnet; Sonia Alamowitch; Laure Bottin; Mathon Yger; Vincent Degos. CHU Kremlin-Bicêtre: Laurent Spelle; Christian Denier; Olivier Chassin; Vanessa Chalumeau; Jildaz Caroff; Olivier Chassin; Laura Venditti; Mariana Sarov; Nicolas Legris. Hôpital Saint-Anne: Olivier Naggara; Wagih Ben Hassen; Grégoire Boulouis; Christine Rodriguez-Régent; Denis Trystram; Basile Kerleroux; Guillaume Turc; Valérie Domigo; Catherine Lamy; Julia Birchenall; Clothilde Isabel; François Lun. CHU Toulouse: Alain Viguier; Christophe Cognard; Anne-Christine Januel; Jean-Marc Olivot; Louis Fontaine; Nicolas Raposo; Fabrice Bonneville; Jean-François Albucher; Lionel Calviere; Jean Darcourt; Guillaume Bellanger; Philippe Tall. CHU Caen: Emmanuel Touze; Charlotte Barbier; Romain Schneckenburger; Marion Boulanger; Julien Cogez; Sophie Guettier; Maxime Gauberti. CHU Brest: Serge Timsit; Jean-Christophe Gentric; Julien Ognard; Francois Mathias Merrien. CHU Rouen: Ozlem Ozku Wermester; Evelyne Massardier; Chrisanthi Papagiannaki; Aude Triquenot; Margeaux Lefebvre. CH Bayonne: Frédéric Bourdain; Patricia Bernady; Laurent Lagoarde-Segot; Hélène Cailliez; Louis Veunac; David Higue. CHU Strasbourg: Valérie Wolff; Veronique Quenardelle; Valerie Lauer; Roxana Gheoca; Irene Pierre-Paul; Raoul Pop; Remy Beaujeux; Dan Mihoc; Monica Manisor; Julien Pottecher; Alain Meyer; Thiên-Nga Chamaraux-Tran. CH Vannes: Anthony Le Bras; Sarah Evain; Arnaud Le Guen.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mary Osborne-Pellegrin for her help in editing the final draft of the article
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
P. Panni, B. Lapergue, B. Maïer, S. Finitsis, F. Clarençon, S. Richard, G. Marnat, R. Bourcier, I. Sibon, C. Dargazanli, R. Blanc, A. Consoli, F. Eugène, S. Vannier, L. Spelle, C. Denier, M. Boulanger, M. Gauberti, S. Saleme, F. Macian, C. Rosso, O. Naggara, G. Turc, O. Ozkul-Wermester, C. Papagiannaki, J.-F. Albucher, J. Darcourt, A. Le Bras, S. Evain, V. Wolff, R. Pop, S. Timsit, J.‑C. Gentric, F. Bourdain, L. Veunac, C. Arquizan and B. Gory declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
This article is published by all authors on behalf of Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke (ETIS) investigators. A list of ETIS Investigators is given at the end of the article.
Supplementary Information
62_2022_1156_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary Table 1: Outcome predictors: bivariate comparison of factors associated with 3-months functional independence (mRS 0‑2 VS 3‑6)
62_2022_1156_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
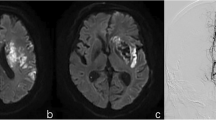
Online Resource Figure 1: Panel a represents baseline DWI showing involvement of both M3 and posterior limb of internal capsule region. Panel b shows partial but incomplete reversal of baseline DWI lesion. This patient was not classified as having DWIr
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panni, P., Lapergue, B., Maïer, B. et al. Clinical Impact and Predictors of Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) Reversal in Stroke Patients with Diffusion Weighted Imaging Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score 0–5 Treated by Thrombectomy. Clin Neuroradiol 32, 939–950 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-022-01156-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-022-01156-z