Abstract
Purpose
Human anatomy learning confronts many difficulties, including the lack of anatomical specimens and limitations in anatomical dissection techniques that can destroy and change the shape and position of anatomic structures. A Virtual Anatomy System can help to overcome these difficulties.
Methods
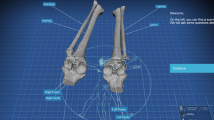
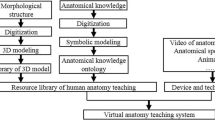
Based on the high-resolution thin-sectional anatomical images of the Chinese Visible Human data set, we created a Virtual Anatomical System, including nearly all male and female anatomical structures.
Results
With this system, medical students can freely observe the detailed anatomical information of the coronal, sagittal, and transverse sections through a 3D-reconstructed realistic model on a personal computer in the local network.
Conclusions
This Virtual Anatomy System is an easy and direct way for students to learn and understand the shape and the relationship of anatomic structures, which can also make the anatomy learning more interesting. Furthermore, it can help students synthetically master the anatomical knowledge.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burmester E, Leineweber T, Hacker S, Tiede U, Hutteroth TH, Hohne KH (2004) EUS Meets Voxel-Man: three-dimensional anatomic animation of linear-array endoscopic ultrasound images. Endoscopy 36:726–730. doi:10.1055/s-2004-825669
China MoHo (2011) China health statistics yearbook. China Union Medical College Publishing, China
Ge W, Li Y, Li ZS, Zhang SH, Sun YJ, Hu PZ, Wang XM, Huang Y, Si SY, Zhang XM, Sui YF (2009) The antitumor immune responses induced by nanoemulsion-encapsulated MAGE1-HSP70/SEA complex protein vaccine following peroral administration route. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:201–208. doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0539-9
Hisley KC, Anderson LD, Smith SE, Kavic SM, Tracy JK (2008) Coupled physical and digital cadaver dissection followed by a visual test protocol provides insights into the nature of anatomical knowledge and its evaluation. Anat Sci Educ 1:27–40
Howard JM, Cathcart MC, Healy L, Beddy P, Muldoon C, Pidgeon GP, Reynolds JV (2014) Leptin and adiponectin receptor expression in oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg 101:643–652. doi:10.1002/bjs.9469
Keedy AW, Durack JC, Sandhu P, Chen EM, O’Sullivan PS, Breiman RS (2011) Comparison of traditional methods with 3D computer models in the instruction of hepatobiliary anatomy. Anat Sci Educ 4:84–91. doi:10.1002/ase.212
Lei S, Hu-jian L, Xun J (2009) Comparison of constitution indexes of Han male youth recruited from different areas. Chin J Public Health 2:017
Li Y, Li DH, Yao YQ, Min BH, Zhang CL, Hou XH, Huang L, Zhao HX (2005) Alteration and potential role of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase receptor 1 in preeclampsia. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 40:581–584
Linke R, Leichtle A, Sheikh F, Schmidt C, Frenzel H, Graefe H, Wollenberg B, Meyer JE (2013) Assessment of skills using a virtual reality temporal bone surgery simulator. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 33:273–281
Nash R, Sykes R, Majithia A, Arora A, Singh A, Khemani S (2012) Objective assessment of learning curves for the Voxel-Man TempoSurg temporal bone surgery computer simulator. J Laryngol Otol 126:663–669. doi:10.1017/S0022215112000734
Pflesser B, Petersik A, Pommert A, Riemer M, Schubert R, Tiede U, Hohne KH, Schumacher U, Richter E (2001) Exploring the visible human’s inner organs with the VOXEL-MAN 3D navigator. Stud Health Technol Inform 81:379–385
Reddy-Kolanu G, Alderson D (2011) Evaluating the effectiveness of the Voxel-Man TempoSurg virtual reality simulator in facilitating learning mastoid surgery. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 93:205–208. doi:10.1308/003588411X565987
Rosseau G, Bailes J, del Maestro R, Cabral A, Choudhury N, Comas O, Debergue P, De Luca G, Hovdebo J, Jiang D, Laroche D, Neubauer A, Pazos V, Thibault F, Diraddo R (2013) The development of a virtual simulator for training neurosurgeons to perform and perfect endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 73(Suppl 1):85–93. doi:10.1227/NEU.000000000000011200006123-201310001-00016
Sai XY, Yan YP, Xu DZ, Zhang ZY, Cai KP, Li YS, Zhou XN (2005) The use of unsupervised classification of Landsat-5 TM images in analysing the types of vegetation in the areas of “breaking dikes or opening sluice for water store”. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 26:88–91
Saltarelli AJ, Roseth CJ, Saltarelli WA (2014) Human cadavers vs. multimedia simulation: a study of student learning in anatomy. Anat Sci Educ 7:331–339. doi:10.1002/ase.1429
Schiemann T, Freudenberg J, Pflesser B, Pommert A, Priesmeyer K, Riemer M, Schubert R, Tiede U, Hohne KH (2000) Exploring the Visible Human using the VOXEL-MAN framework. Comput Med Imaging Graph 24:127–132. doi:10.1016/S0895-6111(00)00013-6
Schubert R, Schiemann T, Tiede U, Hohne KH (1997) Applications and perspectives in anatomical 3-dimensional modelling of the visible human with VOXEL-MAN. Acta Anat (Basel) 160:123–131
Shi JR, Zhang XH, Shi CH, Cao YX, Wu CG, Li Y, Fan XL, Qi HW (2005) The effects of rBCG expressing Der p2 in the form of lipoprotein on murine immune response. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 21:287–289
Sidloff DA, Gokani VJ, Stather PW, Choke E, Bown MJ, Sayers RD (2014) National Vascular Registry Report on surgical outcomes and implications for vascular centres. Br J Surg 101:637–642. doi:10.1002/bjs.9462
Teishima J, Hattori M, Matsubara A (2013) Psychological factor, metacognition, is associated with the advantage of suturing techniques acquired on a virtual reality simulator of robot-assisted surgery. Int J Urol. doi:10.1111/iju.12286
Wang HS, Shao SJ, Wang YY, Qin YL, Cheng Z, Yan ZG, Zhuang TG, Min YJ (2006) Three-D visualization study on the acupoint of Jianliao (TE 14) based on the operational platform of Voxel-man. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 26:789–792
Wang HS, Yan ZG, Cheng Z, Shao SJ, Zhuang TG (2009) Study on force feedback of acupuncture manipulation at Jianliao (TE 14) based on VOXEL-MAN. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 29:745–748
Wu Y, Luo N, Tan L, Fang B, Li Y, Xie B, Liu K, Chu C, Li M, Zhang S (2013) Three-dimensional reconstruction of thoracic structures: based on Chinese Visible Human. Comput Math Methods Med 2013:795650
Wu Y, Luo N, Tan LW, Fang BJ, Li Y, Xie B, Xu HT, Hu N, Yang WP, Wu W, Lamers WH, Zhang SX (2012) Comparative study of thin sectional anatomical images from Chinese visible human data set and computed tomography images of superior mediastinum. Clin Anat 25:1051–1061. doi:10.1002/ca.22048
Wu Y, Tan LW, Li Y, Fang BJ, Xie B, Wu TN, Li QY, Qiu MG, Liu GJ, Li K, Xu HT, Luo N, Zhang SX (2012) Creation of a female and male segmentation dataset based on Chinese Visible Human (CVH). Comput Med Imaging Graph 36:336–342. doi:10.1016/j.compmedimag.2012.01.003
Wu Y, Zhang SX, Luo N, Qiu MG, Tan LW, Li QY, Liu GJ, Li K (2010) Creation of the digital three-dimensional model of the prostate and its adjacent structures based on Chinese visible human. Surg Radiol Anat 32:629–635. doi:10.1007/s00276-010-0625-5
Xu P, Dou KF, Chen ZN, Xing JL, Li Y, Kong LE (2005) High expression of hepatoma associated antigen HAb18G in prokaryotic cells and study on its function in vitro. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 21:734–737
Yang X-G, Li Y-P, Ma G-S, Hu X-Q, Wang J-Z, Cui Z-H, Wang Z-H, Yu W-T, Yang Z-X, Zhai F-Y (2005) Study on weight and height of the Chinese people and the differences between 1992 and 2002. Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi = Zhonghua liuxingbingxue zazhi 26:489–493
Zhang SX, Heng PA, Liu ZJ (2006) Chinese visible human project. Clin Anat 19:204–215. doi:10.1002/ca.20273
Acknowledgments
We thank the donors of the cadavers for contributing the body to our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81100480 and 61190122) (http://www.nsfc.gov.cn).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
B. Fang and Y. Wu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (AVI 5984 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, B., Wu, Y., Chu, C. et al. Creation of a Virtual Anatomy System based on Chinese Visible Human data sets. Surg Radiol Anat 39, 441–449 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1741-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1741-7