Abstract
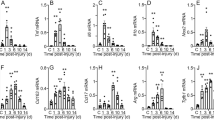
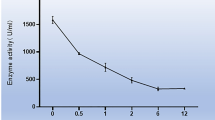
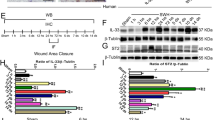
We investigated mRNA expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) and inflammatory cell dynamics for wound age estimation of bruises in mice. Neutrophils were detected from 1 h post-injury. Up to 8 h, they accumulated in subcutaneous tissue and the lower part of the dermis, and thereafter they extended to all the layers. Macrophages became detectable 3 h post-injury, and moderate infiltration of lymphocytes was seen from 144 h. In addition, epidermal thickening was also seen from 72 h. tPA mRNA expression peaked at 1 h, and increased slightly at 72 h post-injury. tPA mRNA was detected in epidermal cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells before and after injury, from 3 h in neutrophils and from 72 h in macrophages, respectively. This study presents the time-dependent expression of tPA mRNA in bruises in relation to temporal histologic characteristics during wound healing, which was considered to be useful for wound age estimation. Furthermore, it is suggested that tPA plays an important role in the first step of tissue remodeling.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anggard E, Johnson CE (1972) Prostaglandins form faster after a burn. Hosp Trib 6:18
Arumugam S, Jang YC, Chen-Jensen C, Gibran NS, Isik FF (1999) Temporal activity of plasminogen activators and matrix metalloproteinases during cutaneous wound repair. Surgery 125:587–593
Berg S, Ebel R (1969) Altersbestimmung subcutaner Blutungen. Munch Med Wochenschr 111:1185–1190
Betz P, Tubel J, Eisenmenger W (1995) Immunohistochemical analysis of markers for different macrophage phenotypes and their use for a forensic wound estimation. Int J Legal Med 107:197–200
Bonelli A, Bacci S, Norelli GA (2003) Affinity cytochemistry analysis of mast cells in skin lesions: a possible tool to assess the timing of lesions after death. Int J Legal Med 117:331–334
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Bichem 162:156–159
Dano K, Andreasen PA, Grondahl-Hansen J, Kristensen P, Nielsen LS, Skriver L (1985) Plasminogen activators, tissue degeneration and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 44:139–266
Dore-Duffy P, Guha A, Rothman BL, Rothman BL, Zurier RB (1988) Synthesis of prostaglandin E by peritoneal macrophages from NZB/W mice. Life Sci 42:2669–2676
Grondahl-Hansen J, Lund LR, Ralkkiaer E, Ottevanger V, Dano K (1988) Urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in keratinocytes during wound reepithelialization in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 90:790–795
Grulich-Henn J, Muller-Berghaus G (1989) The role of vascular endothelial cells in the regulation of fibrinolysis. Z Kardiol 78 [Suppl 6]:25–29
Hart PH, Vitti GF, Burgess DK, Singleton DK, Hamilton JA (1989) Human monocytes can produce tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Exp Med 169:1509–1514
Heiple JM, Ossowski L (1986) Human neutrophil plasminogen activator is localized in specific granules and is translocated to the cell by exocytosis. J Exp Med 164:826–840
Ichinose A, Kiesel W, Fujikawa K (1984) Proteolytic activation of tissue plasminogen activator by plasma and tissue enzymes. FEBS Lett 175:412–418
Jansen W (ed) (1984) Age determination of lesions and hemorrhages. In: Forensic histopathology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 88–97
Myers B, Rightor M (1978) Augmentation of wound tensile strength in rats by induction of inflammation with autogenous blood. Surgery 83:78–82
Ortiz-Rey JA, Suarez-Penaranda JM, Munoz-Barus JI, Alvarez C, San Miguel P, Rodriguez-Calvo MS, Concheiro-Carro L (2003) Expression of fibronectin and tenascin as a demonstration of vital reaction in rat skin and muscle. Int J Legal Med 117:356–360
Postlethwaite AE, Kang AH (1976) Collagen- and collagen peptide-induced chemotaxis of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med 143:1299–1307
Stecher VJ, Sorkin E (1972) The chemotactic activity of fibrin lysis products. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 43:879–886
Vanezis P (2001) Interpreting bruises at necropsy. J Clin Pathol 54:348–355
Vassalli JD, Hamilton J, Reich E (1976) Macrophage plasminogen activator: modulation of enzyme production by anti-inflammatory steroids, mitotic inhibitors, and cyclic nucleotides. Cell 8:271–281
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants-in-aid for General Scientific Research (Y.A and M.T; 14570395) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takamiya, M., Saigusa, K., Kumagai, R. et al. Studies on mRNA expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator in bruises for wound age estimation. Int J Legal Med 119, 16–21 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-004-0453-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-004-0453-4