Abstract
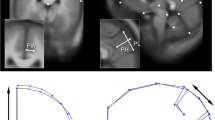
In a large sample of 428 healthy adults balanced for gender and manual preference (MP), we investigated planum temporale (PT) surface area variability in relation with Heschl’s gyrus (HG) duplication pattern, MP, and familial sinistrality (FS), considering different PT definitions. In a sub-sample of 362 participants, we also investigated whether variability of PT asymmetry was associated with differences in verbal abilities. On each participant brain hemisphere MRI, we delineated a posterior PT area (PTpost), excluding the second Heschl gyrus in case of either complete posterior duplication (CPD) or common stem partial duplication (CSD). We then defined a total PT area (PTtot) as the union of PTpost and of the second HG when present, and a HGPT area as the union of PTtot and of the first HG. The HG duplication pattern of one hemisphere was found to significantly affect the PTpost surface area of the same hemisphere, a larger reduction being present in case of CPD than in case of CSD, leading to a strong impact of both left and right HG duplication patterns on PTpost asymmetry. The HG duplication pattern had no effect on PTtot surface areas, while a significant effect of the left HG duplication was present on PTtot asymmetry that was larger in case of a CSD as compared to a single HG. By contrast, the type of HG duplication did not affect HGPT and neither left nor right HG duplication pattern had an effect on HGPT asymmetry. Meanwhile, MP had no effect on PTpost, PTtot, HGPT, or their asymmetries. The absence of a left PTpost was associated with existence of FS (FS+) (7FS+ among nine without PTpost). Removing the nine individuals lacking PTpost, a lower left PTpost surface area was observed in FS+ participants with left CPD. In the sub-sample of 362 participants, we observed a significant interaction between PTpost asymmetry and cognitive abilities due to poorer lexical performances in individuals having a symmetric PTpost as compared to individuals having either a leftward or a rightward asymmetric PTpost. By contrast, there was no significant effect of PTtot or HGPT asymmetry on cognitive abilities. This study shows that HG duplication pattern mainly affects the surface area of the most posterior part of PT and its asymmetry, this PTpost area being specifically associated with variability in verbal performances. This study also shows, for the first time, an association between decreased performances and lack of PTpost anatomical asymmetry, being rightward asymmetrical having no deleterious effect on verbal abilities, thereby supporting the idea that anatomical lateralization is necessary for optimal verbal performances.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Kareem IA, Sluming V (2008) Heschl gyrus and its included primary auditory cortex: structural MRI studies in healthy and diseased subjects. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:287–299
Altarelli I, Leroy F, Monzalvo K, Fluss J, Billard C, Dehaene-Lambertz G, Galaburda AM, Ramus F (2014) Planum temporale asymmetry in developmental dyslexia: revisiting an old question. Hum Brain Mapp 35:5717–5735
Baddeley A, Cocchini G, DellaSala S, Logie RH, Spinnler H (1999) Working memory and vigilance: evidence from normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Cogn 41:87–108
Barrick TR, Mackay CE, Prima S, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Crow TJ, Roberts N (2005) Automatic analysis of cerebral asymmetry: an exploratory study of the relationship between brain torque and planum temporale asymmetry. Neuroimage 24:678–691
Bhojraj TS, Francis AN, Rajarethinam R, Eack S, Kulkarni S, Prasad KM, Montrose DM, Dworakowski D, Diwadkar V, Keshavan MS (2009) Verbal fluency deficits and altered lateralization of language brain areas in individuals genetically predisposed to schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 115:202–208
Binois DR, Pichot DP (1956) Test de vocabulaire: manuel d’application. Editions du Centre de psychologie appliquée
Bishop DVM (2013) Cerebral asymmetry and language development: cause, correlate, or consequence? Science 340:1230531
Bishop DV, Holt G, Whitehouse AJ, Groen M (2014) No population bias to left-hemisphere language in 4-year-olds with language impairment. PeerJ 2:e507
Bloom JS, Garcia-Barrera MA, Miller CJ, Miller SR, Hynd GW (2013) Planum temporale morphology in children with developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 51:1684–1692
Da Costa S, van der Zwaag W, Marques JP, Frackowiak RS, Clarke S, Saenz M (2011a) Human primary auditory cortex follows the shape of Heschl’s Gyrus. J Neurosci 31:14067–14075
Da Costa S, van der Zwaag W, Marques JP, Frackowiak RS, Clarke S, Saenz M (2011b) Human primary auditory cortex follows the shape of Heschl’s Gyrus. J Neurosci 31:14067–14075
Dalby MA, Elbro C, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H (1998) Temporal lobe asymmetry and dyslexia: Anin Vivostudy using MRI. Brain Lang 62:51–69
Daneman M, Carpenter PA (1980) individual differences in working memory and reading. J Verb Learn Verb Behav 19:450–466
Desmette D, Hupet M, Schelstraete MA, Van der Linden M (1995) Adaptation en langue française du “Reading Span Test” de Daneman et Carpenter (1980). L’année Psychol 95:459–482
Diallo B, Dolidon F, Travere J-, Mazoyer B (1998) VoxeLine: a software for 3D real-time visualization of biomedical images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 22:275–289
Galaburda A, Sanides F (1980) Cytoarchitectonic organization of the human auditory cortex. J Comp Neurol 190:597–610
Galaburda AM, Sanides F, Geschwind N (1978) Human brain. Cytoarchitectonic left-right asymmetries in the temporal speech region. Arch Neurol 35:812–817
Galaburda AM, Corsiglia J, Rosen GD, Sherman GF (1987) Planum temporale asymmetry, reappraisal since Geshwind and Levitsky. Neuropsychologia 25:853–868
Geschwind N, Levitsky W (1968) Human brain left-right asymmetries in temporal speech region. Science 161:186–187
Golestani N, Pallier C (2007) Anatomical correlates of foreign speech sound production. Cereb Cortex 17:929–934
Golestani N, Molko N, Dehaene S, LeBihan D, Pallier C (2007) Brain structure predicts the learning of foreign speech sounds. Cereb Cortex 17:575–582
Golestani N, Price CJ, Scott SK (2011) Born with an ear for dialects? Structural plasticity in the expert phonetician brain. J Neurosci 31:4213–4220
Guadalupe T, Willems RM, Zwiers MP, Arias Vasquez A, Hoogman M, Hagoort P, Fernandez G, Buitelaar J, Franke B, Fisher SE, Francks C (2014a) Differences in cerebral cortical anatomy of left- and right-handers. Front Psychol 5
Guadalupe T, Zwiers MP, Wittfeld K, Teumer A, Vasquez AA, Hoogman M, Hagoort P, Fernandez G, Buitelaar J, van Bokhoven H, Hegenscheid K, Völzke H, Franke B, Fisher SE, Grabe HJ, Francks C (2014b) Asymmetry within and around the human planum temporale is sexually dimorphic and influenced by genes involved in steroid hormone receptor activity. Cortex
Habas PA, Scott JA, Roosta A, Rajagopalan V, Kim K, Rousseau F, Barkovich AJ, Glenn OA, Studholme C (2012) Early folding patterns and asymmetries of the normal human brain detected from in utero MRI. Cereb Cortex 22:13–25
Heiervang E, Hugdahl K, Steinmetz H, Inge SA, Stevenson J, Lund A, Ersland L, Lundervold A (2000) Planum temporale, planum parietale and dichotic listening in dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 38:1704–1713
Hill J, Dierker D, Neil J, Inder T, Knutsen A, Harwell J, Coalson T, Van Essen D (2010) A surface-based analysis of hemispheric asymmetries and folding of cerebral cortex in term-born human infants. J Neurosci 30:2268–2276
Isenberg AL, Vaden KI, Saberi K, Muftuler LT, Hickok G (2012) Functionally distinct regions for spatial processing and sensory motor integration in the planum temporale. Hum Brain Mapp 33:2453–2463
Jäncke L, Steinmetz H (1993) Auditory lateralization and planum temporale asymmetry. Neuroreport 5:169–172
Jäncke L, Schlaug G, Huang Y, Steinmetz H (1994) Asymmetry of the planum parietale. Neuroreport 5:1161–1163
Kibby MY, Kroese JM, Morgan AE, Hiemenz JR, Cohen MJ, Hynd GW (2004) The relationship between perisylvian morphology and verbal short-term memory functioning in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Brain Lang 89:122–135
Kulynych JJ, Vladar K, Jones DW, Weinberger DR (1993) Three-dimentional surface rendering in MRI morphometry: a study of the planum temporale. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17:529–535
Kushch A, Gross-Glenn K, Jallad B, Lubs H, Rabin M, Feldman E, Duara R (1993) Temporal lobe surface area measurements on MRI in normal and dyslexic readers. Neuropsychologia 31:811–821
Leask SJ, Crow TJ (1997) How far does the brain lateralize?: an unbiased method for determining the optimum degree of hemispheric specialization. Neuropsychologia 35:1381–1387
Leff AP, Schofield TM, Crinion JT, Seghier ML, Grogan A, Green DW, Price CJ (2009) The left superior temporal gyrus is a shared substrate for auditory short-term memory and speech comprehension: evidence from 210 patients with stroke. Brain 132:3401–3410
Leonard CM, Eckert MA (2008) Asymmetry and dyslexia. Dev Neuropsychol 33:663–681
Leonard CM, Puranik C, Kuldau JM, Lombardino LJ (1998) Normal variation in the frequency and location of human auditory cortex landmarks. Heschl’s gyrus: where is it? Cereb Cortex 8:397–406
Leonard CM, Eckert MA, Lombardino LJ, Oakland T, Kranzler J, Mohr CM, King WM, Freeman A (2001) Anatomical risk factors for phonological dyslexia. Cereb Cortex 11:148–157
Leonard CM, Lombardino LJ, Walsh K, Eckert MA, Mockler JL, Rowe LA, Williams S, DeBose CB (2002) Anatomical risk factors that distinguish dyslexia from SLI predict reading skill in normal children. J Commun Disord 35:501–531
Ma Y, Koyama MS, Milham MP, Castellanos FX, Quinn BT, Pardoe H, Wang X, Kuzniecky R, Devinsky O, Thesen T, Blackmon K (2015) Cortical thickness abnormalities associated with dyslexia, independent of remediation status. Neuroimage Clin 7:177–186
Marie D, Jobard G, Crivello F, Perchey G, Petit L, Mellet E, Joliot M, Zago L, Mazoyer B, Tzourio-Mazoyer N (2015) Descriptive anatomy of Heschl’s gyri in 430 healthy volunteers, including 198 left-handers. Brain Struct Funct 220:729–743
Mazoyer BM, Tzourio-Mazoyer NG (2004) Planum temporale asymmetry and models of dominance for language: a reappraisal. Neuroreport 15:1057–1059
Mazoyer B, Mellet E, Perchey G, Zago L, Crivello F, Jobard G, Delcroix N, Vigneau M, Leroux G, Petit L, Joliot M, Tzourio-Mazoyer N (2015) BIL&GIN: A neuroimaging, cognitive, behavioral, and genetic database for the study of human brain lateralization. Neuroimage 124:1225–1231
McGettigan C, Warren JE, Eisner F, Marshall CR, Shanmugalingam P, Scott SK (2011) Neural correlates of sublexical processing in phonological working memory. J Cogn Neurosci 23:961–977
Mellet E, Jobard G, Zago L, Crivello F, Petit L, Joliot M, Mazoyer B, Tzourio-Mazoyer N (2013) Relationships between hand laterality and verbal and spatial skills in 436 healthy adults balanced for handedness. Laterality 19:1–22
Mellet E, Zago L, Jobard G, Crivello F, Petit L, Joliot M, Mazoyer B, Tzourio-Mazoyer N (2014) Weak language lateralization affects both verbal and spatial skills: an fMRI study in 297 subjects. Neuropsychologia 65:56–62
Moffat SD, Hampson E, Lee DH (1998) Morphology of the planum temporale and corpus callosum in left handers with evidence of left and right hemisphere speech representation. Brain 121:2369–2379
Morgan AE, Hynd GW (1998) Dyslexia, neurolinguistic ability, and anatomical variation of the planum temporale. Neuropsychol Rev 8:79–93
Penhune VB, Zatorre RJ, MacDonald JD, Evans AC (1996) Interhemispheric anatomical differences in human primary auditory cortex: probabilistic mapping and volume measurement from magnetic resonance scans. Cereb Cortex 6:661–672
Pillay SB, Stengel BC, Humphries C, Book DS, Binder JR (2014) Cerebral localization of impaired phonological retrieval during rhyme judgment. Ann Neurol 76:738–746
Rademacher J, Caviness VS, Steinmetz H, Galaburda AM (1993) Topographical variation of the human primary cortices: implications for neuroimaging, brain mapping, and neurobiology. Cereb Cortex 3:313–329
Raven JC (1960) Guide to the standard progressive matrices: sets A, B, C, D and E. HK Lewis, London
Rey A (1958) L’examen clinique en psychologie. Presses Universitaires De France
Rosen GD, Sherman GF, Galaburda AM (1992) Biological substrates of anatomic asymmetry. Prog Neurobiol 39:507–515
Schneider P, Scherg M, Dosch HG, Specht HJ, Gutschalk A, Rupp A (2002) Morphology of Heschl’s gyrus reflects enhanced activation in the auditory cortex of musicians. Nat Neurosci 5:688–694
Schneider P, Sluming V, Roberts N, Scherg M, Goebel R, Specht HJ, Dosch HG, Bleeck S, Stippich C, Rupp A (2005) Structural and functional asymmetry of lateral Heschl’s gyrus reflects pitch perception preference. Nat Neurosci 8:1241–1247
Shapleske J, Rossell SL, Woodruff PW, David AS (1999a) The planum temporale: a systematic, quantitative review of its structural, functional and clinical significance. Brain Res Rev 29:26–49
Simmonds AJ, Leech R, Collins C, Redjep O, Wise RJ (2014) Sensory-motor integration during speech production localizes to both left and right plana temporale. J Neurosci 34:12963–12972
Steinmetz H, Rademacher J, Huang Y, Hefter H, Zilles K, Thron A, Freund H (1989) Cerebral asymmetry: MR planimetry of the human planum temporale. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13:996–1005
Steinmetz H, Rademacher J, Jäncke L, Huang Y, Thron A, Zilles K (1990) Total surface of temporoparietal intrasylvian cortex: diverging left-right asymmetries. Brain Lang 39:357–372
Steinmetz H, Volkmann J, Jäncke L, Freund H (1991) Anatomical left-right asymmetry of language-related temporal cortex is different in left- and right-handers. Ann Neurol 29:315–319
Teszner D, Tzavaras A, Gruner J, Hecaen H (1972) L’asymetrie droite-gauche du planum temporale; a propos de l’etude anatomique de 100 cerveaux. Rev Neurol (Paris) 126:444–449
Tremblay P, Deschamps I, Gracco VL (2011) Regional heterogeneity in the processing and the production of speech in the human planum temporale. Cortex
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Simon G, Crivello F, Jobard G, Zago L, Perchey G, Hervé PY, Joliot M, Petit L, Mellet E, Mazoyer B (2010) Effect of familial sinistrality on planum temporale surface and brain tissue asymmetries. Cereb Cortex 20:1476–1485
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Perrone-Bertolotti M, Jobard G, Mazoyer B, Baciu M (2016) Multi-factorial modulation of hemispheric specialization and plasticity for language in healthy and pathological conditions: a review. Cortex
Vandenberg S, Kuse A (1978) Mental rotations, a group test of three-dimensional spatial visualization. Percept Mot Skills 47:599–604
Warrier C, Wong P, Penhune V, Zatorre R, Parrish T, Abrams D, Kraus N (2009) Relating structure to function: Heschl’s gyrus and acoustic processing. J Neurosci 29:61–69
Xia Z, Hoeft F, Zhang L, Shu H (2016) Neuroanatomical anomalies of dyslexia: disambiguating the effects of disorder, performance, and maturation. Neuropsychologia 81:68–78
Zatorre RJ (2013) Predispositions and plasticity in music and speech learning: neural correlates and implications. Science 342:585–589
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Fabrice Crivello, Gael Jobard, Marc Joliot, Emmanuel Mellet, Guy Perchey, Laurent Petit, Mathieu Vigneau, and Laure Zago for their contribution to the BIL&GIN conception, acquisition, and/or analysis, and Fabrice Crivello and Emmanuel Mellet for their in-depth reading of the manuscript and thoughtful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Mazoyer, B. Variations of planum temporale asymmetries with Heschl’s Gyri duplications and association with cognitive abilities: MRI investigation of 428 healthy volunteers. Brain Struct Funct 222, 2711–2726 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1367-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1367-5