Abstract
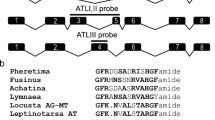
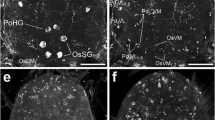
Mas-allatotropin (Mas-AT) and Lom-accessory gland-myotropin I (Lom-AG-MTI) are two members of a conserved family of insect neuropeptides, collectively termed allatotropins, which have diverse functions, ranging from stimulation of juvenile hormone secretion to myotropic effects on heart and hindgut. In addition, allatotropins appear to be abundant within the nervous system, suggesting neuroactive roles. To identify neurons in the insect brain suitable for a neurophysiological analysis of the roles of allatotropins, we used antisera against Mas-AT and Lom-AG-MTI to map allatotropin-immunoreactive neurons in the brain of a suitable insect, the locust Schistocerca gregaria. Both antisera revealed basically identical staining patterns throughout the locust brain with more than 12,500 immunostained interneurons per brain hemisphere. Neurosecretory cells were not labeled, and the retrocerebral complex was devoid of immunostaining. Prominent immunoreactive cell types include about 9,600 lamina monopolar neurons, medulla to lobula interneurons, local neurons of the antennal lobe, a giant interneuron of the mushroom body, projection neurons of the glomerular lobe to the mushroom body, and three systems of tangential neurons of the central complex. Several groups of neurons showed colocalization of Mas-AT- and γ-aminobutyric acid immunostaining. Mass spectrometric analysis identified a peptide with a molecular mass identical to Lom-AG-MTI in all major parts of the locust brain but not in the retrocerebral complex. This study strongly suggests that Lom-AG-MTI is highly abundant in the locust brain, and is likely to play a neuroactive role in many brain circuits including all stages of sensory processing, learning and memory, and higher levels of motor control.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie M (1946) Estimation of nuclear population from microtome sections. Anat Rec 94:239–247
Anton S, Hansson B (1996) Antennal lobe interneurons in the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria (Forskal): processing of aggregation pheromones in adult males and females. J Comp Neurol 370:85–96
Anton S, Homberg U (1999) Antennal lobe structure. In: Hansson BS (ed) Insect olfaction. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 97–124
Bernard F (1937) Recherches sur la morphogénèse des yeux composés d’arthropodes. Bull Biol Fr Belg Suppl 23:1–162
Blaney WM (1974) Electrophysiological responses of the terminal sensilla on the maxillary palps of Locusta migratoria (L.) to some electrolytes and non-electrolytes. J Exp Biol 60:275–293
Bogus MI, Scheller K (1994) Identification of allatotropin-secreting cells in the brain of an insect larva. Naturwissenschaften 81:87–89
Duve H, Thorpe A (2003) Neuropeptide co-localization in the lepidopteran frontal ganglion studied by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 311:79–89
Duve H, East PD, Thorpe A (1999) Regulation of lepidopteran foregut movement by allatostatins and allatotropin from the frontal ganglion. J Comp Neurol 413:405–416
Duve H, Audsley N, Weaver RJ, Thorpe A (2000) Triple co-localization of two types of allatostatin and an allatotropin in the frontal ganglion of the lepidopteran Lacanobia oleracea (Noctuidae): innervation and action on the foregut. Cell Tissue Res 300:153–163
Ehmer B, Gronenberg W (2002) Segregation of visual input to the mushroom bodies in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). J Comp Neurol 451:362–373
Elekonich MM, Horodyski FM (2003) Insect allatotropins belong to a family of structurally-related myoactive peptides present in several invertebrate phyla. Peptides 24:1623–1632
Elphick MR, Williams L, O’Shea M (1996) New features of the locust optic lobe: evidence of a role for nitric oxide in insect vision. J Exp Biol 199:2395–2407
Ernst KD, Boeckh J, Boeckh V (1977) A neuroanatomical study on the organization of the central antennal pathways in insects. Cell Tissue Res 176:285–308
Frambach I, Schürmann F-W (2004) Separate distribution of deutocerebral projection neurones in the mushroom bodies of the cricket brain. Acta Biol Hung 55:21–29
Gronenberg W (2001) Subdivisions of hymenopteran mushroom body calyces by their afferent supply. J Comp Neurol 463:474–489
Hanström B (1928) Vergleichende Anatomie des Nervensystems der wirbellosen Tiere unter Berücksichtigung seiner Funktion. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Helfrich-Förster C, Stengl M, Homberg U (1998) Organization of the circadian system in insects. Chronobiol Int 15:567–594
Hoffmann KH, Meyering-Vos M, Lorenz MW (1999). Allatostatins and allatotropins: is the regulation of corpora allata activity their primary function? Eur J Entomol 96:256–266
Homberg U (1994) Distribution of neurotransmitters in the insect brain. Progress in zoology, vol 40. Fischer, Stuttgart
Homberg U (2002) Neurotransmitters and neuropeptides in the brain of the locust. Microsc Res Tech 56:189–209
Homberg U, Paech A (2002) Ultrastructure and orientation of ommatidia in the dorsal rim area of the locust compound eye. Arthropod Struct Dev 30:271–280
Homberg U, Montague RA, Hildebrand JG (1988) Anatomy of antenno-cerebral pathways in the brain of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Cell Tissue Res 254:255–281
Homberg U, Kingan TG, Hildebrand JG (1990) Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the brain and suboesophageal ganglion of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta and colocalization with SCPB-, BPP-, and GABA-like immunoreactivity. Cell Tissue Res 259:401–419
Homberg U, Vitzthum H, Müller M, Binkle U (1999) Immunocytochemistry of GABA in the central complex of the locust Schistocerca gregaria: identification of immunoreactive neurons and colocalization with neuropeptides. J Comp Neurol 409:495–507
Homberg U, Reischig T, Stengl M (2003) Neural organization of the circadian system of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. Chronobiol Int 20:577–591
Horodyski FM, Bhatt SR, Lee K-Y (2001) Alternative splicing of transcripts expressed by the Manduca sexta allatotropin (Mas-AT) gene is regulated in a tissue-specific manner. Peptides 22:263–269
Ignell R (2001) Monoamines and neuropeptides in antennal lobe interneurons of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria: an immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 306:143–156
Ignell R, Anton S, Hansson BS (1998) Central nervous processing of behaviourally relevant odours in solitary and gregarious fifth instar locusts, Schistocerca gregaria. J Comp Physiol A 183:453–465
Ignell R, Anton S, Hansson BS (1999) Integration of behaviourally relevant odours at the central nervous level in solitary and gregarious third instar locusts, Schistocerca gregaria. J Insect Physiol 45:993–1000
Ignell R, Anton S, Hansson BS (2000) The maxillary palp sensory pathway of Orthoptera. Arthropod Struct Dev 29:295–305
Ignell R, Anton S, Hansson BS (2001) The antennal lobe of Orthoptera—anatomy and evolution. Brain Behav Evol 57:1–17
Jawłowski, H (1954) Über die Struktur des Gehirnes bei Saltatoria. Ann Univ Mariae Curie-Skłodowska C8:403–434
Kataoka H, Toschi A, Li JP, Carney RL, Schooley DA, Kramer SJ (1989) Identification of an allatotropin from adult Manduca sexta. Science 243:1481–1483
Koladich PM, Tobe SS, McNeil JN (2002a) Enhanced haemolymph circulation by insect ventral nerve cord: hormonal control by Pseudaletia unipuncta allatotropin and serotonin. J Exp Biol 205:3123–3131
Koladich PM, Cusson M, Bendena WG, Tobe SS, McNeil JN (2002b) Cardioacceleratory effects of Manduca sexta allatotropin in the true armyworm moth, Pseudaletia unipuncta. Peptides 23:645–651
Laurent G (2002) Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional signals. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:884–895
Laurent G, Wehr M, Davidowitz H (1996) Temporal representations of odors in an olfactory network. J Neurosci 16:3837–3847
Lee K-Y, Horodyski FM, Chamberlin ME (1998) Inhibition of midgut ion transport by allatotropin (Mas-AT) and Manduca FLRFamide peptides in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. J Exp Biol 201:3067–3074
Lee K-Y, Chamberlin ME, Horodyski FM (2002) Biological activity of Manduca sexta allatotropin-like peptides, predicted products of tissue-specific and developmentally regulated alternatively spliced mRNAs. Peptides 23:1933–1941
Leitch B, Laurent G (1996) GABAergic synapses in the antennal lobe and mushroom body of the locust olfactory system. J Comp Neurol 372:487–514
Li Y, Unnithan GC, Veenstra JA, Feyereisen R, Noriega FG (2003) Stimulation of JH biosynthesis by the corpora allata of adult female Aedes aegypti in vitro: effect of farnesoic acid and Aedes allatotropin. J Exp Biol 206:1825–1832
MacLeod K, Laurent G (1996) Distinct mechanisms of synchronization and temporal patterning of odor-encoding neural assemblies. Science 274:976–979
Meeusen T, Mertens I, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2003) G protein-coupled receptors in invertebrates: a state of the art. Int Rev Cytol 230:189–261
Mobbs PG (1982) The brain of the honeybee Apis mellifera. I. The connections and spatial organization of the mushroom bodies. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 298:309–354
Nässel DR (1987) Neuroactive substances in the insect CNS. In: Ali MA (ed) Nervous system in invertebrates. Plenum, New York, pp 171–212
Nässel DR (2000) Functional roles of neuropeptides in the insect central nervous system. Naturwissenschaften 87:439–449
Nowel MS, Shelton PMJ (1981) A Golgi-electron-microscopical study of the structure and development of the lamina ganglionaris of the locust optic lobe. Cell Tissue Res 216:377–401
Nusbaum MP, Blitz DM, Swensen AM, Wood D, Marder E (2001) The roles of co-transmission in neural network modulation. Trends Neurosci 24:146–154
Oeh U, Lorenz MW, Dyker H, Lösel P, Hoffmann KP (2000) Interaction between Manduca sexta allatotropin and Manduca sexta allatostatin in the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:719–727
Paemen L, Tips A, Schoofs L, Proost P, Van Damme J, De Loof A (1991) Lom-AG-myotropin: a novel myotropic peptide from the male accessory glands of Locusta migratoria. Peptides 12:7–10
Paemen L, Schoofs L, De Loof A (1992) Localization of Lom-AG-myotropin I-like substances in the male reproductive and nervous tissue of the locust, Locusta migratoria. Cell Tissue Res 268:91–97
Park C, Jeon SK, Kim M-Y, Han SS, Yu CH, Lee BH (2001) Postembryonic localization of allatotropin- and allatostatin-producing cells in central nervous system of the silk moth Bombyx mori. Zool Sci 18:367–379
Park C, Hwang JS, Kang SW, Lee BH (2002) Molecular characterization of a cDNA from the silk moth Bombyx mori encoding Manduca sexta allatotropin peptide. Zool Sci 19:287–292
Persson MGS, Nässel DR (1999) Neuropeptides in insect sensory neurons: tachykinin, FMRFamide- and allatotropin-related peptides in terminals of locust thoracic sensory afferents. Brain Res 816:131–141
Petri B, Stengl M, Würden S, Homberg U (1995) Immunocytochemical characterization of the accessory medulla in Leucophaea maderae. Cell Tissue Res 282:3–19
Petri B, Homberg U, Loesel R, Stengl M (2002) Evidence for a role of GABA and Mas-allatotropin in photic entrainment of the circadian clock of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. J Exp Biol 205:1459–1469
Rachinsky A, Feldlaufer MF (2000) Responsiveness of honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) corpora allata to allatoregulatory peptides from four insect species. J Insect Physiol 46:41–46
Rachinsky A, Srinivasan A, Ramaswamy SB (2003) Regulation of juvenile hormone biosynthesis in Heliothis virescens by Manduca sexta allatotropin. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 54:121–133
Riehle MA, Garczynski SF, Crim JW, Hill CA, Brown MR (2002) Neuropeptides and peptide hormones in Anopheles gambiae. Science 298:172–175
Rudwall AJ, Sliwowska J, Nässel DR (2000) Allatotropin-like neuropeptide in the cockroach abdominal nervous system: myotropic actions, sexually dimorphic distribution and colocalization with serotonin. J Comp Neurol 428:159–173
Satija RC (1958) A histological and experimental study of nervous pathways in the brain and thoracic nerve cord of Locusta migratoria migratoriodes (R & F). Res Bull Panjab Univ 9:13–32
Sattelle DB (1990) GABA receptors of insects. Adv Insect Physiol 22:1–113
Spittaels K, Vankeerberghen A, Schoofs L, Proost P, Van Damme J, De Loof A (1996) Isolation and characterization of Locusta migratoria accessory gland myotropin I (Lom-AG-MT-I) from the brain of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 31:149–155
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. Wiley, New York
Stopfer M, Bhagvan S, Smith BH, Laurent G (1997) Impaired odour discrimination of odour-encoding neural assemblies. Nature 390:70–74
Strausfeld NJ, Hansen L, Li Y, Gomez RS, Ito K (1998) Evolution, discovery, and interpretations of arthropod mushroom bodies. Learn Mem 5:11–37
Taylor PA III, Bhatt TR, Horodyski FM (1996) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of Manduca sexta allatotropin. Eur J Biochem 239:588–596
Truesdell PF, Koladich PM, Kataoka H, Kojima K, Suzuki A, McNeil J, Mizoguchi A, Tobe SS, Bendena WG (2000) Molecular characterization of a cDNA from the true armyworm Pseudaletia unipuncta encoding Manduca sexta allatotropin peptide. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:691–702
Tu MT, Kou R, Wang Z-S, Stoffolano JG Jr, Yin C-M (2001) Immunolocalization and possible effect of a moth allatotropin-like substance in a fly, Phormia regina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J Insect Physiol 47:233–244
Veelaert D, Schoofs L, De Loof A (1998) Peptidergic control of the corpus cardiacum-corpora allata complex of locusts. Int Rev Cytol 182:249–302
Veenstra JA, Costes L (1999) Isolation and identification of a peptide and its cDNA from the mosquito Aedes aegypti related to Manduca sexta allatotropin. Peptides 20:1145–1151
Veenstra JA, Hagedorn HH (1993) Sensitive enzyme immunoassay for Manduca allatotropin and the existence of an allatotropin-immunoreactive peptide in Periplaneta americana. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 23:99–109
Veenstra JA, Lehman HK, Davis NT (1994) Allatotropin is a cardioacceleratory peptide in Manduca sexta. J Exp Biol 188:347–354
Vitzthum H, Homberg U (1998) Immunocytochemical demonstration of locustatachykinin-related peptides in the central complex of the locust brain. J Comp Neurol 390:455–469
Vitzthum H, Müller M, Homberg U (2002) Neurons of the central complex of the locust Schistocerca gregaria are sensitive to polarized light. J Neurosci 22:1114–1125
Wilson RI, Turner GC, Laurent G (2004) Transformation of olfactory representations in the Drosophila antennal lobe. Science 303:366–370
Würden S, Homberg U (1995) Immunocytochemical mapping of serotonin and neuropeptides in the accessory medulla of the locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J Comp Neurol 362:305–319
Zars T (2000) Behavioral functions of the insect mushroom bodies. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:790–795
Žitňan D, Sehnal F, Bryant PJ (1993) Neurons producing specific neuropeptides in the central nervous system of normal and pupariation-delayed Drosophila. Dev Biol 156:117–135
Žitňan D, Kingan TG, Kramer SJ, Beckage NE (1995) Accumulation of neuropeptides in the cerebral neuroseretory system of Manduca sexta larvae parasitized by the braconid wasp Cotesia congregata. J Comp Neurol 356:83–100
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Timothy Kingan for the donation of anti-GABA antiserum. We thank Dr. Lez Williams for advice regarding nomenclature and are grateful to Ulrike Binkle and Jutta Seyfarth for expert technical assistance. E. Clynen is a post-doc of the FWO Flanders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by DFG grant HO 950/14 to U.H.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homberg, U., Brandl, C., Clynen, E. et al. Mas-allatotropin/Lom-AG-myotropin I immunostaining in the brain of the locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Cell Tissue Res 318, 439–457 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0913-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0913-7