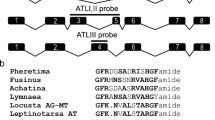
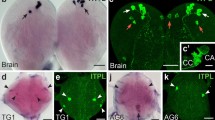
Abstract
Regulatory peptides were immunolocalized in the midgut of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Endocrine cells were found to produce six different peptides: allatostatins A, B and C, neuropeptide F, diuretic hormone 31, and the tachykinins. Small neuropeptide-F (sNPF) was found in neurons in the hypocerebral ganglion innervating the anterior midgut, whereas pigment-dispersing factor was found in nerves on the most posterior part of the posterior midgut. Neuropeptide-F (NPF)-producing endocrine cells were located in the anterior and middle midgut and in the very first part of the posterior midgut. All NPF endocrine cells also produced tachykinins. Endocrine cells containing diuretic hormone 31 were found in the caudal half of the posterior midgut; these cells also produced tachykinins. Other endocrine cells produced exclusively tachykinins in the anterior and posterior extemities of the midgut. Allatostatin-immunoreactive endocrine cells were present throughout the midgut. Those in the caudal half of the posterior midgut produced allatostatins A, whereas those in the anterior, middle, and first half of the posterior midgut produced allatostatin C. In the middle of the posterior midgut, some endocrine cells produced both allatostatins A and C. Allatostatin-C-immunoreactive endocrine cells were particularly prominent in the first half of the posterior midgut. Allatostatin B/MIP-immunoreactive cells were not consistently found and, when present, were only weakly immunoreactive, forming a subgroup of the allatostatin-C-immunoreactive cells in the posterior midgut. Previous work on Drosophila and other insect species suggested that (FM)RFamide-immunoreactive endocrine cells in the insect midgut could produce NPF, sNPF, myosuppressin, and/or sulfakinins. Using a combination of specific antisera to these peptides and transgenic fly models, we showed that the endocrine cells in the adult Drosophila midgut produced exclusively NPF. Although the Drosophila insulin gene Ilp3 was abundantly expressed in the midgut, Ilp3 was not expressed in endocrine cells, but in midgut muscle.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, et al (2000) The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287:2185–2195
Agricola H-J, Bräunig P (1995) Comparative aspects of peptidergic signalling pathways in the nervous system of arthropods. In: Breidbach O, Kutsch W (eds) The nervous system of invertebrates: an evolutionary and comparative approach. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 303–327
Agricola H-J, Bräunig P, Meissner R, Nauman W, Wollweber L, Davis N (1995) Colocalization of allostatin-like immunoreactivity with other neuromodulators in the CNS of Periplaneta americana. In: Elsner N, Menzel R (eds) Learning and memory. Thieme, Stuttgart, p 616
Andriès JC, Tramu G (1985) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study of endocrine cells in the midgut of the cockroach Blaberus craniifer (Insecta, Dictyoptera). Cell Tissue Res 240:323–332
Andriès JC, Belemtougri G, Tramu G (1991) Multiple peptide immunoreacivities in the nervous system of Aeschna cyanea (Insecta, Odonata). Histochemistry 96:139–148
Baggerman G, Cerstiaens A, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2002) Peptidomics of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system. J Biol Chem 277:40368–40374
Baggerman G, Boonen K, Verleyen P, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2005) Peptidomic analysis of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system by two-dimensional capillary liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 40:250–260
Birgül N, Weise C, Kreienkamp HJ, Richter D (1999) Reverse physiology in Drosophila: identification of a novel allatostatin-like neuropeptide and its cognate receptor structurally related to the mammalian somatostatin/galanin/opioid receptor family. EMBO J 18:5892–5900
Blackburn MB, Wagner RM, Kochansky JP, Harrison DJ, Thomas-Laemont P, Raina AK (1995) The identification of two myoinhibitory peptides, with sequence similarities to the galanins, isolated from the ventral nerve cord of Manduca sexta. Regul Pept 57:213–219
Blackburn MB, Jaffe H, Kochansky J, Raina AK (2001) Identification of four additional myoinhibitory peptides (MIPs) from the ventral nerve cord of Manduca sexta. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 48:121–128
Boer HH, Schot LPC, Veenstra JA, Reichelt D (1980) Immunocytochemical identification of neural elements in the central nervous systems of a snail, some insects, a fish, and a mammal with an antiserum to the molluscan cardio-excitatory tetrapeptide FMRF-amide. Cell Tissue Res 231:21–27
Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Ikeya T, Rintelen F, Fernandez R, Hafen E (2001) An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr Biol 11:213–221
Brown MR, Raikhel AS, Lea AO (1985) Ultrastructure of midgut endocrine cells in the adult mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Tissue Cell 17:709–721
Brown MR, Crim JW, Arata RC, Cai HN, Chun C, Shen P (1999) Identification of a Drosophila brain-gut peptide related to the neuropeptide Y family. Peptides 20:1035–1042
Cabrero P, Radford JC, Broderick KE, Costes L, Veenstra JA, Spana EP, Davies SA, Dow JAT (2002) The Dh gene of Drosophila melanogaster encodes a diuretic peptide that acts through cyclic AMP. J Exp Biol 205:3799–3807
Chen Y, Veenstra JA, Davis NT, Hagedorn HH (1994) A comparative study of leucokinin-immunoreactive neurons in insects. Cell Tissue Res 276:69–83
Chintapalli VR, Wang J, Dow JAT (2007) Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nature Genetics 39:715–720
Coast GM, Webster SG, Schegg KM, Tobe SS, Schooley DA (2001) The Drosophila melanogaster homologue of an insect calcitonin-like diuretic peptide stimulates V-ATPase activity in fruit fly Malpighian tubules. J Exp Biol 204:1795–1804
Dircksen H, Zahnow CA, Gaus G, Keller R, Rao KR, Riehm JP (1987) The ultrastructure of nerve endings containing pigment-dispersing hormone (PDH) in crustacean sinus glands: identification by antiserum against synthetic PDH. Cell Tissue Res 250:377–387
Dircksen H, Tesfai LK, Albus C, Nässel DR (2008) Ion transport peptide splice forms in central and peripheral neurons throughout postembryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 509:23–41
Dubreuil RR (2004) Copper cells and stomach acid secretion in the Drosophila midgut. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:745–752
Dubreuil RR, Frankel J, Wang P, Howrylak J, Kappil M, Grushko TA (1998) Mutations of a spectrin and labial block cuprophilic cell differentiation and acid secretion in the middle midgut of Drosophila larvae. Dev Biol 194:1–11
Duve H, Johnsen AH, Scott AG, Yu CG, Yagi K, Tobe SS, Thorpe A (1993) Callatostatins: neuropeptides from the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria with sequence homology to cockroach allatostatins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2456–2460
Fernlund P (1976) Structure of a light-adapting hormone from the shrimp, Pandalus borealis. Biochim Biophys Acta 439:17–25
Fuse M, Bendena WG, Donly BC, Tobe SS, Orchard I (1998) In situ hybridization analysis of leucomyosuppressin mRNA expression in the cockroach, Diploptera punctata. J Comp Neurol 395:328–341
Gonzalez R, Orchard I (2008) Physiological activity of neuropeptide F on the hindgut of the blood-feeding hemipteran, Rhodnius prolixus. J Insect Sci (in press)
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Graff D (1986) Isolation of pyroGlu-Gly-Arg-Phe-NH2 (Antho-RFamide), a neuropeptide from sea anemones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9817–9821
Harlow E, Lane D (1988) Antibodies. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Hauser F, Williamson M, Cazzamali G, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (2006) Identifying neuropeptide and protein hormone receptors in Drosophila melanogaster by exploiting genomic data. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 4:321–430
Hernández-Martínez S, Li Y, Lanz-Mendoza H, Rodríguez MH, Noriega FG (2005) Immunostaining for allatotropin and allatostatin-A and -C in the mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Anopheles albimanus. Cell Tissue Res 321:105–113
Herrero P, Magariños M, Torroja L, Canal I (2003) Neurosecretory identity conferred by the apterous gene: lateral horn leucokinin neurons in Drosophila. J Comp Neurol 457:123–132
Holman GM, Cook BJ, Nachman RJ (1986) Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of leucomyosuppressin, an insect neuropeptide that inhibits spontaneous contractions of the cockroach hindgut. Comp Biochem Physiol 85C:329–333
Hoppler S, Bienz M (1994) Specification of a single cell type by a Drosophila homeotic gene. Cell 76:689–702
Hoppler S, Bienz M (1995) Two different thresholds of wingless signalling with distinct developmental consequences in the Drosophila midgut. EMBO J 14:5016–5026
Horodyski FM, Ewer J, Riddiford LM, Truman JW (1993) Isolation, characterization and expression of the eclosion hormone gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Eur J Biochem 215:221–228
Hua Y-J, Tanaka Y, Nakamura K, Sakakibara M, Nagata S, Kataoka H (1999) Identification of a prothoracicostatic peptide in the larval brain of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem 274:31169–31173
Ikeya T, Galic M, Belawat P, Nairz K, Hafen E (2002) Nutrient-dependent expression of insulin-like peptides from neuroendocrine cells in the CNS contributes to growth regulation in Drosophila. Curr Biol 12:1293–1300
Isabel G, Martin JR, Chidami S, Veenstra JA, Rosay P (2005) AKH-producing neuroendocrine cell ablation decreases trehalose and induces behavioral changes in Drosophila. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R531–R538
Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Takeda N, Endo Y, Lederis K (1986) Urotensin-like immunoreactivity in the midgut endocrine cells of the insects Gryllus bimaculatus and Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 244:565–568
Johard HAD, Coast GM, Mordue W, Nässel DR (2003) Diuretic action of the peptide locustatachykinin. I. Cellular localisation and effects on fluid secretion in Malpighian tubules of locusts. Peptides 24:1571–1579
Johard HAD, Enell LE, Gustafsson E, Trifilieff P, Veenstra JA, Nässel DR (2008) Intrinsic neurons of Drosophila mushroom bodies express short neuropeptide F: relations to extrinsic neurons expressing different neurotransmitters. J Comp Neurol 507:1479–1496
Johnson EC, Bohn LM, Barak LS, Birse RT, Nässel DR, Caron MG, Taghert PH (2003) Identification of Drosophila neuropeptide receptors by G protein-coupled receptors-beta-arrestin2 interactions. J Biol Chem 278:52172–52178
Johnson EC, Bohn LM, Taghert PH (2004) Drosophila CG8422 encodes a functional diuretic hormone receptor. J Exp Biol 207:743–748
Johnson EC, Shafer OT, Trigg JS, Park J, Schooley DA, Dow JAT, Taghert PH (2005) A novel diuretic hormone receptor in Drosophila: evidence for conservation of CGRP signaling. J Exp Biol 208:1239–1246
Kean L, Cazenave W, Costes L, Broderick KE, Graham S, Pollock VP, Davies SA, Veenstra JA, Dow JAT (2002) Two nitridergic peptides are encoded by the gene capability in Drosophila melanogaster. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:1297R–1307R
Kingan TG, Zitnan D, Jaffe H, Beckage NE (1997) Identification of neuropeptides in the midgut of parasitized insects: FLRFamides as candidate paracrines. Mol Cell Endocrinol 133:19–32
Klapper R (2000) The longitudinal visceral musculature of Drosophila melanogaster persists through metamorphosis. Mech Dev 95:47–54
Klapper R, Heuser S, Strasser T, Janning W (2001) A new approach reveals syncytia within the visceral musculature of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 128:2517–2524
Kramer SJ, Toschi A, Miller CA, Kataoka H, Quistad GB, Li JP, Carney RL, Schooley DA (1991) Identification of an allatostatin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9458–9462
Kreienkamp HJ, Larusson HJ, Witte I, Roeder T, Birgül N, Honck HH, Harder S, Ellinghausen G, Buck F, Richter D (2002) Functional annotation of two orphan G-protein-coupled receptors, Drostar1 and -2, from Drosophila melanogaster and their ligands by reverse pharmacology. J Biol Chem 277:39937–39943
Kubiak TM, Laraen MJ, Buron KJ, Bannow CA, Martin RA, Zantello MR, Lowery DE (2002) Cloning and functional expression of the first Drosophila melanogaster sulfakinin receptor DSK-R1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:313–320
Larsen MJ, Burton KJ, Zantello MR, Smith VG, Lowery DL, Kubiak TM (2001) Type A allatostatins from Drosophila melanogaster and Diplotera puncata activate two Drosophila allatostatin receptors, DAR-1 and DAR-2, expressed in CHO cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:895–901
Lee E, Lange A, Orchard I, Fuse M, Tobe SS, Bendena WG, Donly BC (2002) Characterization and baculovirus-directed expression of a myosuppressin encoding cDNA from the true armyworm, Pseudaletia unipuncta. Peptides 23:747–756
Lee KS, You KH, Choo JK, Han YM, Yu K (2004) Drosophila short neuropeptide F regulates food intake and body size. J Biol Chem 279:50781–50789
Lenz C, Williamson M, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (2000) Molecular cloning and genomic organization of an allatostatin preprohormone from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273:1126–1131
Lenz C, Williamson M, Hansen GN, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (2001) Identification of four Drosophila allatostatins as the cognate ligands for the Drosophila orphan receptor DAR-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:895–901
Lorenz MW, Kellner R, Hoffmann KH (1995) A family of neuropeptides that inhibit juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus. J Biol Chem 270:21103–21108
Lu D, Lee K-Y, Horodyski FM, Witten JL (2002) Molecular characterization and cell-specific expression of a Manduca sexta FLRFamide gene. J Comp Neurol 446:377–396
Lundquist CT, Clottens FL, Holman GM, Riehm JP, Bonkale W, Nässel DR (1994) Locustatachykinin immunoreactivity in the blowfly central nervous system and intestine. J Comp Neurol 341:225–240
Luo C-W, Dewey EM, Sudo S, Ewer J, Hsu SY, Honegger H-W, Hsueh AJW (2005) Bursicon, the insect cuticle-hardening hormone, is a heterodimeric cystine knot protein that activates G protein-coupled receptor LGR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2820–2825
McBrayer Z, Ono H, Shimell M, Parvy J-P, Beckstead RB, Warren JT, Thummel CS, Dauphin-Vilmant C, Gilbert LI, O’Connor MB (2007) Prothoracicotropic hormone regulates developmental timing and body size in Drosophila. Dev Cell 13:857–871
McCormick J, Nichols R (1993) Spatial and temporal expression identify dromyosuppressin as a brain-gut peptide in Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 338:278–288
McNulty M, Puljung M, Jefford G, Dubreuil RR (2001) Evidence that a copper-metallothionein complex is responsible for fluorescence in acid-secreting cells of the Drosophila stomach. Cell Tissue Res 304:383–389
Mertens I, Meeusen T, Huybrechts R, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2002) Characterization of the short neuropeptide F receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 297:1140–1148
Meyering-Vos M, Müller A (2007) RNA interference suggests sulfakinins as satiety effectors in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. J Insect Physiol 53:840–848
Micchelli CA, Perrimon N (2006) Evidence that stem cells reside in the adult Drosophila midgut epithelium. Nature 439:475–479
Muren JE, Lundquist CT, Nässel DR (1995) Abundant distribution of locustatachykinin-like peptide in the nervous system and intestine of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Biol 348:423–444
Nachman RJ, Holman GM, Haddon WF, Ling N (1986) Leucosulfakinin, a sulfated insect neuropeptide with homology to gastrin and cholecystokinin. Science 234:71–73
Nässel DR, Shiga S, Mohrherr CJ, Rao KR (1993) Pigment-dispersing hormone-like peptide in the nervous system of the flies Phormia and Drosophila: immunocytochemistry and partial characterization. J Comp Neurol 331:183–198
Nichols R, Lim IA (1996) Spatial and temporal immunocytochemical analysis of drosulfakinin (Dsk) gene products in the Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res 283:107–116
Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J, Endo Y (1981) Gut endocrine cells in insects: the ultrastructure of the endocrine cells in the cockroach midgut. Biomed Res 2:30–44
O’Brien MA, Schneider LE, Taghert PH (1991) In situ hybridization analysis of the FMRFamide neuropeptide gene in Drosophila. II. Constancy in the cellular pattern of expression during metamorphosis. J Comp Neurol 304:623–638
Ohlstein B, Spradling A (2006) The adult Drosophila posterior midgut is maintained by pluripotent stem cells. Nature 439:470–474
Ohlstein B, Spradling A (2007) Multipotent Drosophila intestinal stem cells specify daughter cell fates by differential notch signaling. Science 5814:988–992
Pabla N, Lange AB (1999) The distribution and myotropic activity of locustatachykinin-like peptides in locust midgut. Peptides 20:1159–1167
Park D, Veenstra JA, Park JH, Taghert PH (2008) Mapping peptidergic cells in Drosophila: where DIMM fits in. PLoS ONE 3:e1896 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001896)
Price MD, Merte J, Nichols R, Koladich PM, Tobe SS, Bendena WG (2002) Drosophila melanogaster flatline encodes a myotropin orthologue to Manduca sexta allatostatin. Peptides 23:787–794
Reichwald K, Unnithan GC, Davis NT, Agricola H, Feyereisen R (1994) Expression of the allatostatin gene in endocrine cells of the cockroach midgut. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:11894–11898
Renn SCP, Park JH, Rosbash M, Hall JC, Taghert PH (1999) A PDF neuropeptide gene mutation and ablation of PDF neurons each cause severe abnormalities of behavioral circadian rhythms in Drosophila. Cell 99:791–802
Riehle MA, Fan Y, Cao C, Brown MR (2006) Molecular characterization of insulin-like peptides in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti: expression, cellular localization, and phylogeny. Peptides 27:2547–2560
Sakai T, Satake H, Minakata H, Takeda M (2004) Characterization of crustacean cardioactive peptide as a novel insect midgut factor: isolation, localization, and stimulation of α-amylase activity and gut contraction. Endocrinology 145:5671–5678
Sakai T, Satake H, Takeda M (2006) Nutrient-induced α-amylase and protease activity is regulated by crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) in the cockroach midgut. Peptides 27:2157–2164
Satake S, Masumura M, Ishizaki H, Nagata K, Kataoka H, Suzuki M, Mizoguchi A (1997) Bombyxin, an insulin-related peptide of insects, reduces the major storage carbohydrates in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Comp Biochem Physiol 118B:349–357
Schneider LE, O’Brien MA, Taghert PH (1991) In situ hybridization analysis of the FMRFamide neuropeptide gene in Drosophila. I. Restricted expression in embryonic and larval stages. J Comp Neurol 304:608–622
Schoofs L, Holman GM, Hayes TK, Nachman RJ, De Loof A (1990a) Locustatachykinin I and II, two novel insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. FEBS Lett 261:397–401
Schoofs L, Holman GM, Hayes TK, Kochansky JP, Nachman RJ, De Loof A (1990b) Locustatachykinin III and IV: two additional insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. Regul Pept 31:199–212
Schoofs L, Holman GM, Hayes TK, Nachman RJ, De Loof A (1991) Isolation, identification and synthesis of locustamyoinhibiting peptide (LOM-MIP), a novel biologically active neuropeptide from Locusta migratoria. Regul Pept 35:111–119
Schoofs L, Holman GM, Paemen L, Veelaert D, Amelinckx M, De Loof A (1993) Isolation, identification, and synthesis of PDVDHFLRFamide (SchistoFLRFamide) in Locusta migratoria and its association with the male accessory glands, the salivary glands, the heart, and the oviduct. Peptides 14:409–421
Schooneveld H, Tesser GI, Veenstra JA, Romberg-Privee HM (1983) Adipokinetic hormone and AKH-like peptide demonstrated in the corpora cardiaca and nervous system of Locusta migratoria by immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 230:68–76
Schooneveld H, Romberg-Privee HM, Veenstra JA (1986) Immunocytochemical differentiation between adipokinetic hormone (AKH)-like peptides in neurons and glandular cells in the corpus cardiacum of Locusta migratoria and Periplaneta americana with C-terminal and N-terminal specific antisera to AKH. Cell Tissue Res 243:9–14
Seecof RL, Dewhurst S (1974) Insulin is a Drosophila hormone and acts to enhance the differentiation of embryonic Drosophila cells. Cell Differ 3:63–70
Siviter RJ, Coast GM, Winther AM, Nachman RJ, Taylor CA, Shirras AD, Coates D, Isaac RE, Nässel DR (2000) Expression and functional characterization of a Drosophila neuropeptide precursor with homology to mammalian preprotachykinin A. J Biol Chem 275:23273–23280
Skaer H (1993) The alimentary canal. In: Bate M, Martínez Arias A (eds) The development of Drosophila melanogaster, vol II. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, pp 941–1012
Stanek DM, Pohl J, Crim JW, Brown MR (2002) Neuropeptide F and its expression in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Peptides 23:1367–1378
Stracker TH, Thompson G, Grossman Gl, Riehle MA, Brown MR (2002) Characterization of the AeaHP gene and its expression in the mosquito Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 39:331–342
Strasburger M (1932) Bau, Funktion und Variabilität des Darmtractus von Drosophila melanogaster. Z Wiss Zool 140:539–649
Sudo S, Kuwabara Y, Park J-I, Hsu SY, Hsueh AJW (2005) Heterodimeric fly glycoprotein hormone-α2 (GPA2) and glycoprotein hormone-β5 (GPB5) activate fly leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor-1 (DLGR1) and stimulation of human thyrotropin receptors by chimeric fly GPA2 and human GPB5. Endocrinology 146:3596–3604
Tager HS (1976) Coupling of peptides to albumin with difluorodinitrobenzene. Anal Biochem 71:367–275
Taghert PH (1999) FMRFamide neuropeptides and neuropeptide-associated enzymes in Drosophila. Microsc Res Tech 45:80–95
Taghert PH, Veenstra JA (2003) Drosophila neuropeptide signaling. Adv Genet 49:1–65
Teller JK, Pilc L (1985) Insulin in insects: analysis of immunoreactivity in tissue extracts. Comp Biochem Physiol 74:493–497
Terhzaz S, O’Connell FC, Pollock VP, Kean L, Davies SA, Veenstra JA, Dow JAT (1999) Isolation and characterization of a leucokinin-like peptide of Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol 202:3667–3676
Terhzaz S, Rosay P, Goodwin SF, Veenstra JA (2007) The neuropeptide SIFamide modulates sexual behavior in Drosophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:305–310
Triepel J, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (1984) Mapping of neurons in the central nervous system of the guinea pig by use of antisera specific to the molluscan neuropeptide FMRFamide. Cell Tissue Res 237:575–586
Vanden Broeck J (2001) Neuropeptides and their precursors in the fruitfly, Drosophila melanogaster. Peptides 22:241–254
Veenstra JA (1988) Immunocytochemical demonstration of vertebrate peptides in invertebrates: the homology concept. Neuropeptides 12:49–54
Veenstra JA (1989a) Do insects really have a homeostatic hypotrehalosaemic hormone? Biol Rev 64:305–316
Veenstra JA (1989b) Isolation and structure of two gastrin/CCK-like neuropeptides from the American cockroach homologous to the leucosulfakinins. Neuropeptides 14:145–149
Veenstra JA (2009) Allatostatin C and its paralog allatostatin double C. Insect Biochem Mol Biol (in press)
Veenstra JA, Davis NT (1993) Localization of corazonin in the nervous system of the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 274:57–64
Veenstra JA, Hagedorn HH (1993) A sensitive enzyme immuno assay for Manduca allatotropin and the existence of an allatotropin-immunoreactive peptide in Periplaneta americana. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 23:99–109
Veenstra JA, Lambrou G (1995) Isolation of a novel RFamide peptide from the midgut of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 213:519–524
Veenstra JA, Schooneveld H (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of neurons in the nervous system of the Colorado potato beetle with antisera against FMRFamide and bovine pancreatic polypeptide. Cell Tissue Res 235:303–308
Veenstra JA, Lau GW, Agricola HJ, Petzel DH (1995) Immunohistological localization of regulatory peptides in the midgut of the female mosquito Aedes aegypti. Histochem Cell Biol 104:337–347
Veenstra JA, Noriega FG, Graf R, Feyereisen R (1997) Identification of three allatostatins and their cDNA from the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Peptides 18:937–942
Wang J, Meyering-Vos M, Hoffmann KH (2004) Cloning and tissue-specific localization of cricket-type allatostatins from Gryllus bimaculatus. Mol Cell Endrinol 227:41–51
Wei Z, Baggerman G, Nachman JR, Goldsworthy G, Verhaert P, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2000) Sulfakinins reduce food intake in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J Insect Physiol 46:1259–1265
Weiß T (1997) Untersuchungen zur Lokalisation und Funktion von Neuropeptiden im Darmsystem der Schabe Periplaneta ameriocana (L.). Dissertation Friedrich-Schiller-Universität, Jena
Weiß T, Agricola H-J (1995) Neuropeptides in the cockroach midgut: occurence, distribution and colocalization—an immunocytochemical approach. In: Elsner N, Menzel R (eds) Learning and memory. Thieme, Stuttgart, p 615
Williams JC, Hagedorn HH, Beyenbach KW (1983) Dynamic changes in flow-rate and composition of urine during the post-bloodmeal diuresis in Aedes aegypti (L). J Comp Physiol 153:257–265
Williamson M, Lenz C, Winther AM, Nässel DR, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (2001a) Molecular cloning, genomic organization, and expression of a B-type (cricket-type) allatostatin preprohormone from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:544–550
Williamson M, Lenz C, Winther AM, Nässel DR, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (2001b) Molecular cloning, genomic organization, and expression of a C-type (Manduca sexta-type) allatostatin preprohormone from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282:124–130
Witek G, Verhaert P, Lorenz MW, Hoffmann KH (1999) Immunolocalization of two types of allatostatins in the central nervous system of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus (Ensifera: Gryllidae). Eur J Entomol 96:279–285
Woodhead AP, Stay B, Seidel SL, Khan MA, Tobe SS (1989) Primary structure of four allatostatins: neuropeptide inhibitors of juvenile hormone synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:5997–6001
Wu Q, Brown MR (2006) Signaling and function of insulin-like peptides in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 51:1–24
Wu Q, Wen T, Lee G, Park JH, Cai HN, Shen P (2003) Developmental control of foraging and social behavior by the Drosophila neurpeptide Y-like system. Neuron 39:147–161
Yalow RS, Eng J (1981) Peptide hormones in strange places—are they there? Peptides 6 (Suppl 2):17–23
Yamashita O, Yaginuma T, Hasegawa H (1981) Hormonal and metabolic control of egg diapause of the silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera Bombycidae). Entomol Gen 78:195–211
Yoon JG, Stay B (1995) Immunocytochemical localization of Diploptera punctata allatostatin-like peptide in Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 363:475–488
Zitnan D, Sauman I, Sehnal F (1993) Peptidergic innervation and endocrine cells of insect midgut. Archiv Insect Biochem Physiol 22:113–132
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Paul Taghert and Ping Shen for generously sending flies, to Gérard Tramu, Cor Grimmelikhuijzen, Liliane Schoofs, Klaus Hoffman, René Feyereisen, and Heinrich Dircksen for sharing valuable antisera, and to two anonymous reviewers for constructive criticism of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veenstra, J.A., Agricola, HJ. & Sellami, A. Regulatory peptides in fruit fly midgut. Cell Tissue Res 334, 499–516 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0708-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0708-3