Abstract
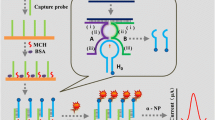
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a transcription factor that plays a central role in the signaling pathway and network of gene regulation. The dysregulation of NF-κB signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases. We report on a dual amplification strategy for the highly sensitive electrochemical sensing of NF-κB by means of a nicking endonuclease-assisted amplification reaction (NEAR). The quantity of the DNA obtained is subsequently determined by applying a gold nanoparticle-assisted electrochemical amplification step. This represents the first example of a combination of NEAR and a dual amplification strategy for the detection of a transcription factor. Experimental results show that the electrochemical signal generated by the redox probe (the ruthenium(III) hexammine complex) can be related to the concentration of NF-κB. The response of the electrode is linearly related to the concentration of NF-κB in the 100 pM to 10 nM range, with a detection limit as low as 80 pM.

An electrochemical biosensor for NF-κB with dual signal amplification is achieved. It was based on nicking endonuclease-assisted amplification reaction (NEAR) and gold nanoparticle-assisted electrochemical amplification (AuNP-EA). The method can be extended for the detection of universal DNA-binding proteins.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell 132(3):344–362. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.020
Li QT, Verma IM (2002) NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2(10):725–734. doi:10.1038/nri910
Eldor R, Yeffet A, Baum K, Doviner V, Amar D, Ben-Neriah Y, Christofori G, Peled A, Carel JC, Boitard C, Klein T, Serup P, Eizirik DL, Melloul D (2006) Conditional and specific NF-κB blockade protects pancreatic beta cells from diabetogenic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(13):5072–5077. doi:10.1073/pnas.0508166103
Collister KA, Albensi BC (2005) Potential therapeutic targets in the NF-κB pathway for Alzheimer’s disease. Drug News Perspect 18(10):623–629. doi:10.1358/dnp.2005.18.10.959576
Khoshnan A, Ko J, Watkin EE, Paige LA, Reinhart PH, Patterson PH (2004) Activation of the Iκ B kinase complex and nuclear factor-κB contributes to mutant huntingtin neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 24(37):7999–8008. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2675-04.2004
Karin M (2006) Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441(7092):431–436. doi:10.1038/nature04870
Naugler WE, Karin M (2008) NF-κB and cancer — identifying targets and mechanisms. Curr Opin Genet Dev 18(1):19–26. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2008.01.020
Pepper C, Hewamana S, Brennan P, Fegan C (2009) NF-κB as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Future Oncol 5(7):1027–1037. doi:10.2217/fon.09.72
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140(6):883–899. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
Tas SW, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP (2009) Gene therapy targeting nuclear factor-κB: towards clinical application in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Curr Gene Ther 9(3):160–170. doi:10.2174/156652309788488569
Schmid RM, Liptay S, Betts JC, Nabel GJ (1994) Structural and functional analysis of NF-κB. Determinants of DNA binding specificity and protein interaction. J Biol Chem 269(51):32162–32167
Bowen B, Steinberg J, Laemmli UK, Weintraub H (1980) The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res 8(1):1–20. doi:10.1093/nar/8.1.1
Renard P, Ernest I, Houbion A, Art M, Le Calvez H, Raes M, Remacle J (2001) Development of a sensitive multi-well colorimetric assay for active NF-κB. Nucleic Acids Res 29(4):e21. doi:10.1093/nar/29.4.e21
Wang JK, Li TX, Guo XY, Lu ZH (2005) Exonuclease III protection assay with FRET probe for detecting DNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 33(2):e23. doi:10.1093/nar/gni021
Wang Z, Gidwani V, Zhang DD, Wong PK (2008) Separation-free detection of nuclear factor kappa B with double-stranded molecular probes. Analyst 133(8):998–1000. doi:10.1039/b809113g
Zhang B, Yao J, Yan H, Fu W (2010) Specific binding DNA-based piezoelectric quartz crystal microbalance biosensor array for the study of NF-κB. Sens Actuators, B 149(1):259–263. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2010.05.013
Menotta M, Crinelli R, Carloni E, Bianchi M, Giacomini E, Valbusa U, Magnani M (2010) Label-free quantification of activated NF-κB in biological samples by atomic force microscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 25(11):2490–2496. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.04.022
Mullis KB, Faloona FA (1987) Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol 155:335–350
Ji HX, Yan F, Lei JP, Ju HX (2012) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of nucleic acids by template enhanced hybridization followed with rolling circle amplification. Anal Chem 84(16):7166–7171. doi:10.1021/Ac3015356
Huang J, Wu Y, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Yang X, Yang CJ, Wang K, Tan W (2011) Pyrene-excimer probes based on the hybridization chain reaction for the detection of nucleic acids in complex biological fluids. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(2):401–404. doi:10.1002/anie.201005375
An LX, Tang W, Ranalli TA, Kim HJ, Wytiaz J, Kong HM (2005) Characterization of a thermostable UvrD helicase and its participation in helicase-dependent amplification. J Biol Chem 280(32):28952–28958. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503096200
Lin ZY, Yang WQ, Zhang GY, Liu QD, Qiu B, Cai ZW, Chen GN (2011) An ultrasensitive colorimeter assay strategy for p53 mutation assisted by nicking endonuclease signal amplification. Chem Commun 47(32):9069–9071. doi:10.1039/c1cc13146j
Zhu XL, Zhao J, Wu Y, Shen ZM, Li GX (2011) Fabrication of a highly sensitive aptasensor for potassium with a nicking endonuclease-assisted signal amplification strategy. Anal Chem 83(11):4085–4089. doi:10.1021/ac200058r
Xu Y, Lunnen KD, Kong H (2001) Engineering a nicking endonuclease N.AlwI by domain swapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(23):12990–12995. doi:10.1073/pnas.241215698
Liu J, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1(1):246–252. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.38
Lao R, Song S, Wu H, Wang L, Zhang Z, He L, Fan C (2005) Electrochemical interrogation of DNA monolayers on gold surfaces. Anal Chem 77(19):6475–6480. doi:10.1021/ac050911x
Cao Y, Wang J, Xu YY, Li GX (2010) Combination of enzyme catalysis and electrocatalysis for biosensor fabrication: application to assay the activity of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygensae. Biosens Bioelectron 26(1):87–91. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.05.019
Miao P, Ning L, Li G (2013) Gold nanoparticles and cleavage-based dual signal amplification for ultrasensitive detection of silver ions. Anal Chem 85(16):7966–7970. doi:10.1021/ac401762e
Zayats M, Huang Y, Gill R, Ma C, Willner I (2006) Label-free and reagentless aptamer-based sensors for small molecules. J Am Chem Soc 128(42):13666–13667. doi:10.1021/ja0651456
Zhang J, Song SP, Wang LH, Pan D, Fan CH (2007) A gold nanoparticle-based chronocoulometric DNA sensor for amplified detection of DNA. Nat Protoc 2(11):2888–2895. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.419
Miao P, Ning L, Li X, Li P, Li G (2011) Electrochemical strategy for sensing protein phosphorylation. Bioconjugate Chem 23(1):141–145. doi:10.1021/bc200523p
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31200742, 81272601, 30973477), the “Chen Guang” project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation (No. 10CG42), the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 12YZ004) and the Leading Academic Discipline Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (J50108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Z., Zhang, B., Yang, Y. et al. Electrochemical biosensor for the nuclear factor kappa B using a gold nanoparticle-assisted dual signal amplification method. Microchim Acta 181, 139–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1080-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1080-x