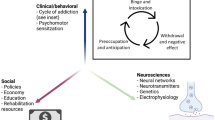
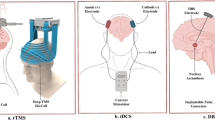
Abstract
Long has the standard of care for substance use disorder (SUD) been pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, or rehabilitation with varying success. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) may have a beneficial reduction in the addiction-reward pathway. Recent studies have found reduced relapse and improvements in quality of life following DBS stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. We aim to identify positive outcomes and adverse effects to assess the viability of DBS as a treatment of addiction. A PubMed search following PRISMA guidelines was conducted to identify the entirety of reports reporting DBS as a treatment for SUD. Outcomes were extracted from the literature to be summarized, and a review of the quality of publications was also performed. From 2305 publications, 14 studies were found to fit the inclusion criteria published between 2007 and 2019. All studies targeted the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and remission rates at 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, and more than 6 years were 61% (20/33), 53% (17/32), 43% (14/30), and 50% (3/6), respectively. Not all studies detailed the stimulation settings or coordinates. The most common adverse effect across studies was a weight change of at least 2 kg. DBS shows potential as a long-term treatment of SUD in refractory patients. Further studies with controlled double-blind paradigms are needed for evaluation of the efficacy and safety of this treatment. Future studies should also investigate other brain regions for stimulation and optimal device stimulation parameters.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bersani FS, Minichino A, Enticott PG, Mazzarini L, Khan N, Antonacci G, Raccah RN, Salviati M, Delle Chiaie R, Bersani G, Fitzgerald PB, Biondi M (2013) Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation as a treatment for psychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review. Eur Psychiatry 28:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2012.02.006
Camprodon JA, Martinez-Raga J, Alonso-Alonso M, Shih M-C, Pascual-Leone A (2007) One session of high frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) to the right prefrontal cortex transiently reduces cocaine craving. Drug Alcohol Depend 86:91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.06.002
Carroll KM, Weiss RD (2017) The role of behavioral interventions in buprenorphine maintenance treatment: a review. Am J Psychiatry 174:738–747. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.16070792
Cartwright WS (2000) Cost-benefit analysis of drug treatment services: review of the literature. J Ment Health Policy Econ 3:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-176x(200003)3:1<11::aid-mhp66>3.0.co;2-0
Chail A, Saini RK, Bhat PS, Srivastava K, Chauhan V (2018) Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a review of its evolution and current applications. Ind Psychiatry J 27:172–180. https://doi.org/10.4103/ipj.ipj
Chen L, Li N, Ge S, Lozano AM, Lee DJ, Yang C, Li L, Bai Q, Lu H, Wang J, Wang X, Li J, Jing J, Su M, Wei L, Wang X, Gao G (2019) Long-term results after deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens and the anterior limb of the internal capsule for preventing heroin relapse: an open-label pilot study. Brain Stimul 12:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2018.09.006
Chiken S, Nambu A (2016) Mechanism of deep brain stimulation: inhibition, excitation, or disruption? Neuroscientist 22:313–322. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858415581986
Deniau J-M, Degos B, Bosch C, Maurice N (2010) Deep brain stimulation mechanisms: beyond the concept of local functional inhibition. Eur J Neurosci 32:1080–1091. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07413.x
Dennis ML, Foss MA, Scott CK (2007) An eight-year perspective on the relationship between the duration of abstinence and other aspects of recovery. Eval Rev 31:585–612. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193841X07307771
Ekpu VU, Brown AK (2015) The economic impact of smoking and of reducing smoking prevalence: review of evidence. Tob Use Insights 8:TUI.S15628. https://doi.org/10.4137/tui.s15628
Fitzgerald PB, Fountain S, Daskalakis ZJ (2006) A comprehensive review of the effects of rTMS on motor cortical excitability and inhibition. Clin Neurophysiol 117:2584–2596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.06.712
French MT, Popovici I, Tapsell L (2008) The economic costs of substance abuse treatment: updated estimates and cost bands for program assessment and reimbursement. J Subst Abus Treat 35:462–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2007.12.008
Garbutt JC (2010) Efficacy and tolerability of naltrexone in the management of alcohol dependence. Curr Pharm Des 16:2091–2097. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161210791516459
Ge S, Chen Y, Li N, Qu L, Li Y, Jing J, Wang X, Wang J, Wang X (2019) Deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens for methamphetamine addiction: two case reports. World Neurosurg 122:512–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.11.056
Ge S, Geng X, Wang X, Li N, Chen L, Zhang X, Huang Y, Li Y, Chen Y, Wang S, Gao G (2018) Oscillatory local field potentials of the nucleus accumbens and the anterior limb of the internal capsule in heroin addicts. Clin Neurophysiol 129:1242–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2018.03.008
Gonçalves-Ferreira A, Do Couto FS, Rainha Campos A, Lucas Neto LP, Gonçalves-Ferreira D, Teixeira J (2016) Deep brain stimulation for refractory cocaine dependence. Biol Psychiatry 79:e87–e89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.06.023
Hariz MI, Hariz GM (2013) Therapeutic stimulation versus ablation, 1st edn. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam
Heilig M, Egli M (2006) Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 111:855–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.02.001
Herzog J, Fietzek U, Hamel W, Morsnowski A, Steigerwald F, Schrader B, Weinert D, Pfister G, Muller D, Mehdorn HM, Deuschl G, Volkmann J (2004) Most effective stimulation site in subthalamic deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 19:1050–1054. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20056
Hitti FL, Vaughan KA, Ramayya AG, McShane BJ, Baltuch GH (2019) Reduced long-term cost and increased patient satisfaction with rechargeable implantable pulse generators for deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg 131:799–806. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.4.JNS172995
Hser Y-I (2007) Predicting long-term stable recovery from heroin addiction: findings from a 33-year follow-up study. J Addict Dis 26:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1300/J069v26n01_07
Jonas DE, Amick HR, Feltner C, Bobashev G, Thomas K, Wines R, Kim MM, Shanahan E, Gass CE, Rowe CJ, Garbutt JC (2014) Pharmacotherapy for adults with alcohol use disorders in outpatient settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 311:1889–1900. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.3628
Kalakoti P, Ahmed O, Bollam P, Missios S, Wilden J, Nanda A (2015) Predictors of unfavorable outcomes following deep brain stimulation for movement disorders and the effect of hospital case volume on outcomes: an analysis of 33,642 patients across 234 US hospitals using the national (Nationwide) inpatient sample from 200. Neurosurg Focus 38:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.3.FOCUS1547
Kaskutas LA, Borkman TJ, Laudet A, Ritter LA, Witbrodt J, Subbaraman MS, Stunz A, Bond J (2014) Elements that define recovery: the experiential perspective. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 75:999–1010. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2014.75.999
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2008) Addiction and the brain antireward system. Annu Rev Psychol 59:29–53. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093548
Kuhn J, Bauer R, Pohl S, Lenartz D, Huff W, Kim EH, Klosterkoetter J, Sturm V (2009) Observations on unaided smoking cessation after deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Eur Addict Res 15:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1159/000228930
Kuhn J, Lenartz D, Huff W, Lee S, Koulousakis A, Klosterkoetter J, Sturm V (2007) Remission of alcohol dependency following deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: valuable therapeutic implications? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1152–1153. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.113092
Kuhn J, Möller M, Treppmann JF, Bartsch C, Lenartz D, Gruendler TOJ, Maarouf M, Brosig A, Barnikol UB, Klosterkötter J, Sturm V (2014) Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and its usefulness in severe opioid addiction. Mol Psychiatry 19:145–146. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.196
De La Fuente-Fernández R (2004) Uncovering the hidden placebo effect in deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 10:125–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2003.10.003
Li N, Wang J, Wang X, Chang C, Ge S, Gao L, Wu H, Zhao H, Geng N, Gao G (2013) Nucleus accumbens surgery for addiction. World Neurosurg 80:S28.e9–S28.19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.10.007
Lidstone SC, Schulzer M, Dinelle K (2011) Effects of expectation on placebo-induced dopamine release in Parkinson’s disease. Focus Park Dis 22:22–24
Luigjes J, Van Den Brink W, Feenstra M, Van Den Munckhof P, Schuurman PR, Schippers R, Mazaheri A, De Vries TJ, Denys D (2012) Deep brain stimulation in addiction: a review of potential brain targets. Mol Psychiatry 17:572–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.114
Luigjes J, Segrave R, de Joode N, Figee M, Denys D (2019) Efficacy of invasive and non-invasive brain modulation interventions for addiction. Neuropsychol Rev 29:116–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-018-9393-5
Lutz GK, Butzlaff ME, Atlas SJ, Keller RB, Singer DE, Deyo RA (1999) The relation between expectations and outcomes in surgery for sciatica. J Gen Intern Med 14:740–744. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1497.1999.10417.x
Mantione M, Van De Brink W, Schuurman PR, Denys D (2010) Smoking cessation and weight loss after chronic deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: therapeutic and research implications: case report. Neurosurgery 66:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000360570.40339.64
McGinty EE, Goldman HH, Pescosolido B, Barry CL (2015) Portraying mental illness and drug addiction as treatable health conditions: effects of a randomized experiment on stigma and discrimination. Soc Sci Med 126:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.12.010
McPherson ML, Costantino RC, McPherson AL (2018) Methadone: maximizing safety and efficacy for pain control in patients with cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 32:405–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2018.01.004
Mestre TA, Lang AE, Okun MS (2016) Factors influencing the outcome of deep brain stimulation: placebo, nocebo, lessebo, and lesion effects. Mov Disord 31:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26500
Müller S, Riedmüller R, van Oosterhout A (2015) Rivaling paradigms in psychiatric neurosurgery: adjustability versus quick fix versus minimal-invasiveness. Front Integr Neurosci 9:1–5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2015.00027
Müller UJ, Sturm V, Voges J, Heinze HJ, Galazky I, Büntjen L, Heldmann M, Frodl T, Steiner J, Bogerts B (2016) Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for alcohol addiction - safety and clinical long-term results of a pilot trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 49:170–173. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-104507
Müller UJ, Sturm V, Voges J, Heinze HJ, Galazky I, Heldmann M, Scheich H, Bogerts B (2009) Successful treatment of chronic resistant alcoholism by deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens: first experience with three cases. Pharmacopsychiatry 42:288–291. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1233489
Müller UJ, Voges J, Steiner J, Galazky I, Heinze H-J, Möller M, Pisapia J, Halpern C, Caplan A, Bogerts B, Kuhn J (2013) Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens for the treatment of addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1282:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06834.x
Okun MS (2012) Deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 367:1529–1538. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMct1208070
Perlmutter JS, Mink JW (2006) Deep brain stimulation. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:229–257. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.112824
Pettersen H, Landheim A, Skeie I, Biong S, Brodahl M, Benson V, Davidson L (2018) Why do those with long-term substance use disorders stop abusing substances? A qualitative study. Subst Abuse 12:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178221817752678
Phillips LA, Shaw A (2013) Substance use more stigmatized than smoking and obesity. J Subst Use 18:247–253. https://doi.org/10.3109/14659891.2012.661516
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:215–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.04.016
Raylu N, Kaur I (2012) Relationships between treatment expectations and treatment outcomes among outpatients with substance use problems. Int J Ment Heal Addict 10:607–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-011-9358-x
Rehm J, Barbosa C (2018) The cost-effectiveness of therapies to treat alcohol use disorders. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 18:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737167.2018.1392241
Richard JM, Castro DC, Difeliceantonio AG, Robinson MJF, Berridge KC (2013) Mapping brain circuits of reward and motivation: in the footsteps of Ann Kelley. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1919–1931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.12.008
Roehler DR (2019) Annual surveillance drug-related risks and outcomes: United States, 2019. 2019 Annu Surveill Rep Drug-Related Risks Outcomes - United States
Schruers K, Baldi S, van den Heuvel T, Goossens L, Luyten L, Leentjens AFG, Ackermans L, Temel Y, Viechtbauer W (2019) The effects of deep-brain non-stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Transl Psychiatry 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0522-6
Schumacher JE, Mennemeyer ST, Milby JB, Wallace D, Nolan K (2002) Costs and effectiveness of substance abuse treatments for homeless persons. J Ment Health Policy Econ 5:33–42
Serafini K, Decker S, Kiluk BD, Añez L, Paris M, Frankforter T, Carroll KM (2015) Outcome expectations and associated treatment outcomes in motivational enhancement therapy delivered in English and Spanish. Am J Addict 24:732–739. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12301.Outcome
Serafini K, Kiluk BD, Babuscio T, Carroll KM (2016) Patient pre-treatment expectations do not predict cocaine use outcomes: data from four clinical trials. Subst Use Misuse 51:1484–1492. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2016.1188945
Simpson KN, Welch MJ, Kozel FA, Demitrack MA, Nahas Z (2009) Cost-effectiveness of transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of major depression: a health economics analysis. Adv Ther 26:346–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0053-2
Singh S, Loke YK, Spangler JG, Furberg CD (2011) Risk of serious adverse cardiovascular events associated with varenicline: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ 183:1359–1366. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.110804
Skinner MD, Lahmek P, Pham H, Aubin HJ (2014) Disulfiram efficacy in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 9:e87366. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087366
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (Minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73:712–716. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
Soyka M, Kranzler HR, Van Den Brink W, Krystal J, Möller HJ, Kasper S (2011) The world federation of societies of biological psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the biological treatment of substance use and related disorders. Part 2: opioid dependence. World J Biol Psychiatry 12:160–187. https://doi.org/10.3109/15622975.2011.561872
Soyka M, Mutschler J (2016) Treatment-refractory substance use disorder: focus on alcohol, opioids, and cocaine. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 70:148–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.11.003
Spanagel R, Kiefer F (2008) Drugs for relapse prevention of alcoholism: ten years of progress. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2007.12.005
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration (2019) Results from the 2010 National Survey on drug use and health: detailed tables. Rockville, MD
Umemura A, Jaggi JL, Hurtig HI, Siderowf AD, Colcher A, Stern MB, Baltuch GH (2003) Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders: morbidity and mortality in 109 patients. J Neurosurg 98:779–784. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.98.4.0779
Valencia-Alfonso CE, Luigjes J, Smolders R, Cohen MX, Levar N, Mazaheri A, Van Den Munckhof P, Schuurman PR, Van Den Brink W, Denys D (2012) Effective deep brain stimulation in heroin addiction: a case report with complementary intracranial electroencephalogram. Biol Psychiatry 71:e35–e37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.12.013
Vitek JL (2008) Deep brain stimulation: how does it work? Cleve Clin J Med 75(Suppl 2):S59–S65. https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.75.suppl_2.s59
Voges J, Müller U, Bogerts B, Münte T, Heinze HJ (2013) Deep brain stimulation surgery for alcohol addiction. World Neurosurg 80:S28.e21–S28.e31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.07.011
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Hitzemann R, Logan J, Schlyer DJ, Dewey SL, Wolf AP (1993) Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse 14:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.890140210
Wang TR, Moosa S, Dallapiazza RF, Elias WJ, Lynch WJ (2018) Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of drug addiction. Neurosurg Focus 45:E11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.5.FOCUS18163
Williams D, Mcbride AJ (1998) The drug treatment of alcohol withdrawal symptoms: a systematic review. Alcohol Alcohol 33:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.alcalc.a008365
Wise RA (1996) Addictive drugs and brain stimulation reward. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:319–340. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ne.19.030196.001535
Wise RA, Rompre PP (1989) Brain dopamine and reward. Annu Rev Psychol 40:191–225. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ps.40.020189.001203
Zhang C, Li J, Li D, Sun B (2019) Deep brain stimulation removal after successful treatment for heroin addiction. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 00:0–1. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004867419890671
Zhou H, Xu J, Jiang J (2011) Deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens on heroin-seeking behaviors: a case report. Biol Psychiatry 69:69–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.02.012
(2016) Facing Addiction in America: the surgeon general’s report on alcohol, drugs, and health. Washington, DC
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Cheryl Vanier and Dr. Michael Olek for their advice and guidance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors, and written informed consent was not required.
Informed consent
The review was based on systematic literature and did not include personal data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, O., Phan, S., Wiecks, N. et al. Outcomes of deep brain stimulation surgery for substance use disorder: a systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 44, 1967–1976 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01415-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01415-y