Abstract
Object
To investigate the potential of a clinical 3 T scanner to perform MRI of small rodents.
Materials and methods
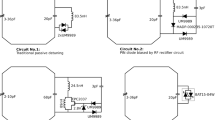
Different dedicated small animal coils and several imaging sequences were evaluated to optimize image quality with respect to SNR, contrast and spatial resolution. As an application, optimal grey-white-matter contrast and resolution were investigated for rats. Furthermore, manganese-enhanced MRI was applied in mice with unilateral crush injury of the optic nerve to investigate coil performance on topographic mapping of the visual projection.
Results
Differences in SNR and CNR up to factor 3 and more were observed between the investigated coils. The best grey-white matter contrast was achieved with a high resolution 3D T 2-weighted TSE (SPACE) sequence. Delineation of the retino-tectal projection and detection of defined visual pathway damage on the level of the optic nerve could be achieved by using a T 1-weighted, 3D gradient echo sequence with isotropic resolution of (0.2 mm)3.
Conclusions
Experimental studies in small rodents requiring high spatial resolution can be performed by using a clinical 3 T scanner with appropriate dedicated coils.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Original paper states an SNR of 16, but the SNR calculation from magnitude images does not include the correction factor of Eq. 1.
References
Boretius S, Kasper L, Tammer R, Michaelis T, Frahm J (2009) MRI of cellular layers in mouse brain in vivo. Neuroimage 47:1252–1260
Pinkernelle JG, Stelter L, Hamm B, Teichgraber U (2008) Small animal MRI: clinical MRI as an interface to basic biomedical research. Rofo 180:505–513
Chronik B, Alejski A, Rutt BK (2000) Design and fabrication of a three-axis multilayer gradient coil for magnetic resonance microscopy of mice. Magn Reson Mater Phys 10:131–146
Linn J, Schwarz F, Schichor C, Wiesmann M (2007) Cranial MRI of small rodents using a clinical MR scanner. Methods 43:2–11
Gareis D, Behr VC, Breuer F, Griswold M, Jakob P (2006) Multipurpose 4+4 channel array setup for parallel imaging in 3D. In Proceedings 14th scientific meeting, international society for magnetic resonance in medicine, p 499
Doty FD, Entzminger G, Kulkarni J, Pamarthy K, Staab JP (2007) Radio frequency coil technology for small-animal MRI. NMR Biomed 20:304–325
Herrmann KH, Wagner E, Deistung A, Hilger I, Reichenbach JR (2008) A robust optical respiratory trigger for small rodents in clinical whole-body MR systems. Biomed Tech (Berl) 53:138–144
Schubert MI, Porkess MV, Dashdorj N, Fone KC, Auer DP (2009) Effects of social isolation rearing on the limbic brain: a combined behavioral and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry study in rats. Neuroscience 159:21–30
Gaser C, Nenadic I, Buchsbaum BR, Hazlett EA, Buchsbaum MS (2001) Deformation-based morphometry and its relation to conventional volumetry of brain lateral ventricles in MRI. Neuroimage 13:1140–1145
Natt O, Watanabe T, Boretius S, Radulovic J, Frahm J, Michaelis T (2002) High-resolution 3D MRI of mouse brain reveals small cerebral structures in vivo. J Neurosci Methods 120:203–209
Hennig J, Nauerth A, Friedburg H (1986) RARE imaging: a fast imaging method for clinical MR. Magn Reson Med 3:823–833
Hennig J, Scheffler K (2001) Hyperechoes. Magn Reson Med 46:6–12
Weigel M, Hennig J (2008) Development and optimization of T2 weighted methods with reduced RF power deposition (Hyperecho-TSE) for magnetic resonance imaging. Z Med Phys 18:151–161
Horger W, Kiefer B, Menzel M, Mugler III J P (2006) Efficient phase-encoding for 3D turbo-spin-echo imaging with very long echo trains. In Proceedings 14th scientific meeting, international society for magnetic resonance in medicine, p 2429
Mugler III JP (2007) Signal and contrast properties of very-long spin-echo trains for 3D T2-weighted turbo-spin-echo imaging. In Proceedings 15th scientific meeting, international society for magnetic resonance in medicine, p 794
Hennig J, Weigel M, Scheffler K (2004) Calculation of flip angles for echo trains with predefined amplitudes with the extended phase graph (EPG)-algorithm: principles and applications to hyperecho and TRAPS sequences. Magn Reson Med 51:68–80
Park J, Mugler JP, Hughes T (2009) Reduction of B1 sensitivity in selective single-slab 3D turbo spin echo imaging with very long echo trains. Magn Reson Med 62:1060–1066
Lichy M P, Wietek B, Mugler III JP et al (2005) Whole-body applications of isotropic high-resolution T2-weighted MRI with a single-slab 3D-TSE-based sequence optimized for high sampling efficiency, called SPACE—initial clinical experiences. In Proceedings 13th scientific meeting, international society for magnetic resonance in medicine, p 794
Busse RF, Brau AC, Vu A, Michelich CR, Bayram E, Kijowski R, Reeder SB, Rowley HA (2008) Effects of refocusing flip angle modulation and view ordering in 3D fast spin echo. Magn Reson Med 60:640–649
Carr HY (1958) Steady-state free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys Rev 112:1693–1708
Sobol WT, Gauntt DM (1996) On the stationary states in gradient echo imaging. J Magn Reson Imag 6:384–398
Casselman J W, Kuhweide R, Deimling M, Ampe W, Dehaene I, Meeus L (1993) Constructive interference in steady state-3DFT MR imaging of the inner ear and cerebellopontine angle. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:47–57
Gaser C, Volz HP, Kiebel S, Riehemann S, Sauer H (1999) Detecting structural changes in whole brain based on nonlinear deformations-application to schizophrenia research. Neuroimage 10:107–113
Lau JC, Lerch JP, Sled JG, Henkelman RM, Evans AC, Bedell BJ (2008) Longitudinal neuroanatomical changes determined by deformation-based morphometry in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 42:19–27
Schmidt S, Bruehl C, Hagemann G, Witte OW, Redecker C (2006) Impairment of functional inhibition in the contralateral cortex following perinatally acquired malformations in rats. Exp Neurol 201:270–274
Bearer EL, Falzone TL, Zhang X, Biris O, Rasin A, Jacobs RE (2007) Role of neuronal activity and kinesin on tract tracing by manganese-enhanced MRI (MEMRI). Neuroimage 37(suppl 1):37–46
Chan KC, Fu QL, So KF, Wu EX (2007) Evaluation of the visual system in a rat model of chronic glaucoma using manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2007:67–70
Thuen M, Berry M, Pedersen TB, Goa PE, Summerfield M, Haraldseth O, Sandvig A, Brekken C (2008) Manganese-enhanced MRI of the rat visual pathway: acute neural toxicity, contrast enhancement, axon resolution, axonal transport, and clearance of Mn(2+). J Magn Reson Imag 28:855–865
Haenold R, Herrmann KH, Schmidt S et al (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging of the mouse visual pathway for in vivo studies of degeneration and regeneration in the CNS. Neuroimage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.069
Thuen M, Singstad TE, Pedersen TB, Haraldseth O, Berry M, Sandvig A, Brekken C (2005) Manganese-enhanced MRI of the optic visual pathway and optic nerve injury in adult rats. J Magn Reson Imag 22:492–500
Thuen M, Olsen O, Berry M, Pedersen TB, Kristoffersen A, Haraldseth O, Sandvig A, Brekken C (2009) Combination of Mn(2+)-enhanced and diffusion tensor MR imaging gives complementary information about injury and regeneration in the adult rat optic nerve. J Magn Reson Imag 29:39–51
Henkelman RM (1985) Measurement of signal intensities in the presence of noise in mr images. Med Phys 12:232–233
Kaufman L, Kramer DM, Crooks LE, Ortendahl DA (1989) Measuring signal-to-noise ratios in MR imaging. Radiology 173:265–267
Portnoy S, Kale SC, Feintuch A, Tardif C, Pike GB, Henkelman RM (2009) Information content of SNR/resolution trade-offs in three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Med Phys 36:1442–1451
Kale SC, Lerch JP, Henkelman RM, Chen XJ (2008) Optimization of the SNR-resolution tradeoff for registration of magnetic resonance images. Hum Brain Mapp 29:1147–1158
Weigel M, Schwenk S, Kiselev VG, Scheffler K, Hennig J (2010) Extended phase graphs with anisotropic diffusion. J Magn Reson 205:276–285
Elliott AM, Bernstein MA, Ward HA, Lane J, Witte RJ (2007) Nonlinear averaging reconstruction method for phase-cycle SSFP. Magn Reson Imag 25:359–364
Baltes C, Radzwill N, Bosshard S, Marek D, Rudin M (2009) Micro MRI of the mouse brain using a novel 400 MHz cryogenic quadrature RF probe. NMR Biomed 22:834–842
Acknowledgments
We thank Noras MRI products GmbH and Siemens Medical for their support and the mechanical workshop of the Friedrich-Schiller University Jena for their help in creating the various head holders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrmann, KH., Schmidt, S., Kretz, A. et al. Possibilities and limitations for high resolution small animal MRI on a clinical whole-body 3T scanner. Magn Reson Mater Phy 25, 233–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0284-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0284-5