Abstract
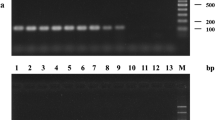
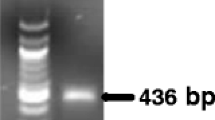
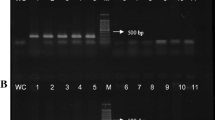
Xylella fastidiosa is an important pathogen of many commercial crops. Detection of X. fastidiosa is difficult due to low concentrations of the bacteria in insects and asymptomatic plant tissue, and non-uniform distribution in infected plants. A dual purpose conventional PCR and quantitative PCR (TaqMan™) system was developed for the generic detection of X. fastidiosa strains. Primers HL5 and HL6, designed to amplify a unique region common to the sequenced genomes of four Xylella strains, amplified a 221 bp fragment from strains associated with Pierce’s disease of grapes, almond leaf scorch, and oleander leaf scorch disease and from DNA from an Xf strain associated with citrus variegated chlorosis. Standard curves were obtained using concentrations of Xylella ranging from 5 to 105 cells per reaction in water and grape extracts and 10–105 cells in insect DNA. Regression curves were similar, with correlation coefficients of r 2 > 0.97. In quantitative PCR, Ct values ranged between 20 and 36 cycles for 5–105 bacterial cells per reaction. No amplicons were obtained with several non-Xf bacterial strains tested including related plant pathogenic, grape endophytic bacteria and endosymbiotic bacteria isolated from glassy-winged sharpshooters. The method was evaluated for clinical diagnosis of Xf in grapes, almonds and insect vectors. The procedure described is reliable for detection of the pathogen with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALSD:
-
almond leaf scorch disease
- CTAB:
-
hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
- GWSS:
-
glassy-winged sharpshooter
- ITS:
-
internal transcribed spacer
- OLSD:
-
oleander leaf scorch disease
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PD:
-
Pierce’s disease
- Q-PCR:
-
quantitative PCR
- Xf:
-
Xylella fastidiosa.
References
Almeida RPP, Purcell HA (2003) Homoladisca coagulata (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa to almond Plant Disease 87:1255–1259
Bextine BR, Miller TA (2004) Comparison of whole tissue and xylem fluid collection techniques to detect Xylella fastidiosa in grapevines and oleander Plant Disease 88: 600–604
Bextine B, Tuan SJ, Shaikh H, Blua M, Miller TA (2004) Evaluation of methods for extracting Xylella fastidiosa DNA from the glassy-winged sharpshooter Journal of Economic Entomology 97: 757–763
Bextine B, Blua M, Harshman D, Miller TA (2005) A SYBR green-based real-time polymerase chain reaction protocol and novel DNA extraction technique to detect Xylella fastidiosa in Homalodisca coagulate Journal of Economic Entomology 98: 667–672
Bhattacharyya A, Stilwagen S, Ivanova N, D’Souza M, Bernal A, Lykidis A, Kapatral V, Anderson I, Larsen N, Los T, Reznik G, Selkov E Jr., Walunas TL, Feil H, Feil WS, Purcell A, Lassez JL, Hawkins TL, Haselkorn R, Overbeek R, Predki PF, Kyrpides NC (2002) Whole-genome comparative analysis of three phytopathogenic Xylella fastidiosa strains Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99: 12403–12408
Ciapina LP, Carareto Alves LM, Lemos EGM (2004) A nested-PCR assay for detection of Xylella fastidiosa in citrus plants and sharpshooter leafhoppers Journal of Applied Microbiology 96: 546–551
Chen JC, Banks D, Jarret RL, Chang CJ, Smith BJ (2000) Use of 16S rDNA sequence as signature characters to identify Xylella fastidiosa Current Microbiology 40: 29–33
Da Silva AC, Ferro JA, Reinach FC, Farah CS, Furlan LR, Quaggio RB, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Van Sluys MA, Almeida NF, Alves LM, do Amaral AM, Bertolini MC, Camargo LE, Camarotte G, Cannavan F, Cardozo J, Chambergo F, Ciapina LP, Cicarelli RM, Coutinho LL, Cursino-Santos JR, El-Dorry H, Faria JB, Ferreira AJ, Ferreira RC, Ferro MI, Formighieri EF, Franco MC, Greggio CC, Gruber A, Katsuyama AM, Kishi LT, Leite RP, Lemos EG, Lemos MV, Locali EC, Machado MA, Madeira AM, Martinez-Rossi NM, Martins EC, Meidanis J, Menck CF, Miyaki CY, Moon DH, Moreira LM, Novo MT, Okura VK, Oliveira MC, Oliveira VR, Pereira HA, Rossi A, Sena JA, Silva C, de Souza RF, Spinola LA, Takita MA, Tamura RE, Teixeira EC, Tezza RI, Trindade dos Santos M, Truffi D, Tsai SM, White FF, Setubal JC, Kitajima JP (2002) Comparison of the genomes of two Xanthomonas pathogens with differing host specificities Nature 417: 459–463
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2001) An overview of Real-Time quantitative PCR: Applications to quantify cytokine gene expression Methods 25: 386–401
Hill BL, Purcell AH (1995) Acquisition and retention of Xylella fastidiosa by an efficient vector, Graphocephala atropunctata Phytopathology 85:209–212
Hopkins DL, Purcell AH (2002) Xylella fastidiosa: Cause of Pierce’s disease of grapevine and other emergent diseases Plant Disease 86: 1056–1066
Lin H, Walker MA (1997). Extracting DNA from cambium tissue for analysis of grape rootstocks HortScience 32: 1264–1266
Minsavage GV, Thompson CM, Hopkins DL, Leite RMVB, Stall RE (1994) Development of polymerase chain reaction protocol for the detection of Xylella fastidiosa in plant tissue Phytopathology 84: 456–461
Oliveira AC, Vallim MA, Semighini CP, Araujo WL, Goldman GH, Machado MA (2000) Quantification of Xylella fastidiosa from citrus trees by real-time polymerase chain reaction assay Phytopathology 92: 1040–1054
Pooler MR, Hartung JS (1995) Specific PCR detection and identification of Xylella fastidiosa strains causing citrus variegated chlorosis Current Microbiology 31: 377–81
Pooler MR, Myung IS, Bentz J, Sherald J, Hartung JS (1997) Detection of Xylella fastidiosa in potential insect vectors by immunomagnetic separation and nested polymerase chain reaction Letters in Applied Microbiology 25: 123–126
Purcell AH, Hopkins DL (1996) Fastidious xylem-limited bacterial plant pathogens Annual Review of Phytopathology 34: 131–151
Rodrigues LM, Silva-Stenico ME, Gomes JE, Lopes JR, Tsai SM (2003) Detection and diversity assessment of Xylella fastidiosa in field-collected plant and insect samples by using 16S rRNA and gyrB sequences Applied Environmental Microbiology 69: 4249–4255
Schaad NW, Opgenorth D, Gaush P (2002) Real-time polymerase chain reaction for one-hour on-site diagnosis of Pierce’s disease of grape in early season asymptomatic vines Phytopathology 92: 721–728
Simpson AJ, Reinach FC, Arruda P, Abreu FA, Acencio M, Alvarenga R, Alves LM, Araya JE, Baia GS, Baptista CS, Barros MH, Bonaccorsi ED, Bordin S, Bove JM, Briones MR, Bueno MR, Camargo AA, Camargo LE, Carraro DM, Carrer H, Colauto NB, Colombo C, Costa FF, Costa MC, Costa-Neto CM, Coutinho LL, Cristofani M, Dias-Neto E, Docena C, El-Dorry H, Facincani AP, Ferreira AJ, Ferreira VC, Ferro JA, Fraga JS, Franca SC, Franco MC, Frohme M, Furlan LR, Garnier M, Goldman GH, Goldman MH, Gomes SL, Gruber A, Ho PL, Hoheisel JD, Junqueira ML, Kemper EL, Kitajima JP, Krieger JE, Kuramae EE, Laigret F, Lambais MR, Leite LC, Lemos EG, Lemos MV, Lopes SA, Lopes CR, Machado JA, Machado MA, Madeira AM, Madeira HM, Marino CL, Marques MV, Martins EA, Martins EM, Matsukuma AY, Menck CF, Miracca EC, Miyaki CY, Monteriro-Vitorello CB, Moon DH, Nagai MA, Nascimento AL, Netto LE, Nhani A Jr., Nobrega FG, Nunes LR, Oliveira MA, de Oliveira MC, de Oliveira RC, Palmieri DA, Paris A, Peixoto BR, Pereira GA, Pereira HA Jr., Pesquero JB, Quaggio RB, Roberto PG, Rodrigues V, de M Rosa AJ, de Rosa VE Jr., de Sa RG, Santelli RV, Sawasaki HE, da Silva AC, da Silva AM, da Silva FR, da Silva WA Jr., da Silveira JF, Silvestri ML, Siqueira WJ, de Souza AA, de Souza AP, Terenzi MF, Truffi D, Tsai SM, Tsuhako MH, Vallada H, Van Sluys MA, Verjovski-Almeida S, Vettore AL, Zago MA, Zatz M, Meidanis J, Setubal JC (2000) The genome sequence of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa Nature 406: 151–157
Van Sluys MA, de Oliveira MC, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Miyaki CY, Furlan LR, Camargo LE, da Silva AC, Moon DH, Takita MA, Lemos EG, Machado MA, Ferro MI, da Silva FR, Goldman MH, Goldman GH, Lemos MV, El-Dorry H, Tsai SM, Carrer H, Carraro DM, de Oliveira RC, Nunes LR, Siqueira WJ, Coutinho LL, Kimura ET, Ferro ES, Harakava R, Kuramae EE, Marino CL, Giglioti E, Abreu IL, Alves LM, do Amaral AM, Baia GS, Blanco SR, Brito MS, Cannavan FS, Celestino AV, da Cunha AF, Fenille RC, Ferro JA, Formighieri EF, Kishi LT, Leoni SG, Oliveira AR, Rosa VE Jr., Sassaki FT, Sena JA, de Souza AA, Truffi D, Tsukumo F, Yanai GM, Zaros LG, Civerolo EL, Simpson AJ, Almeida NF Jr., Setubal JC (2003) Comparative analyses of the complete genome sequences of Pierce’s disease and Citrus Variegated Chlorosis strains of Xylella fastidiosa Journal of Bacteriology 185: 1018–1026
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Kirkpatrick, D. Darjean, L. Bolkan and P. Ronald (University of California, Davis), A.H. Purcell (University of California, Berkeley), for providing bacterial strains; E. Lemos (Universidade Stadual Paulista, Jaboticabal, SP, Brazil) for providing DNA from Xylella fastidiosa strains␣associated with citrus variegated chlorosis;␣K. Tubajika (USDA-APHIS) for supplying samples from grapevines naturally-affected with Pierce’s disease; R. Groves (USDA-ARS) for providing field-collected glassy-winged sharpshooters (GWSS); D. Morgan (California Department of Food and Agriculture, Arvin, CA) for providing the GWSS insect for transmission assays; C. Gispert (University of California Extension, Davis, CA) for X. fastidiosa-free GWSS; and D. Wade and P. Sahota for their technical assistance. We also acknowledge advice provided by G.E. Bruening (UC-Davis).
This work was supported by a Specific Cooperative Agreement between USDA-ARS and the University of California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, M., Lin, H., Rosa, J.CL. et al. Genome-based PCR Primers for Specific and Sensitive Detection and Quantification of Xylella fastidiosa . Eur J Plant Pathol 115, 203–213 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-006-9009-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-006-9009-4