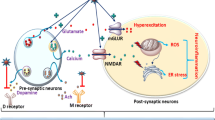
Abstract
Lead (Pb), a ubiquitous and potent neurotoxicant, induces several neurophysiological and behavioural changes, while Pb alters the function of multiple organs and systems, it primarily affects the central nervous system. In human adults, encephalopathy resulting from Pb intoxication is often characterized by sleeplessness, poor attention span, vomiting, convulsions and coma; in children, Pb-induced encephalopathy is associated with mental dullness, vomiting, irritability and anorexia; diminished cognitive function resulting in a mental deficit has been also observed during Prolonged exposure to Pb. Pb can produce oxidative stress, disrupt the blood–brain barrier and alter several Ca2+-dependent processes, including physiological processes that involve nitric oxide synthesis on central nervous system in development and adult animals. This review summarizes recent evidence showing that Pb can interfere with the production of nitric oxide and can disrupt the function of nitric oxide synthase. Lead interferes with nitric oxide-related physiological mechanisms, and Pb neurotoxicity may affect processes involved in learning and memory.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adonaylo VN, Oteiza PI (1999) Lead intoxication: antioxidant defences and oxidative damage in rat brain. Toxicology 135:77–85
Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2007) Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Department of Health and Humans Services, Public Health Service, Centres for Diseases Control, Atlanta, GA
Akar CA, Feinstein DL (2009) Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by sumoylation. J Neuroinflammation 6:12–21
Alderton WK, Cooper CE, Knowles RG (2001) Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition. Biochem J 357:593–615
Al-Saleh I, Nester M, DeVol E et al (2001) Relationship between blood lead concentrations, intelligence, and academia achievement of Arabian schoolgirls. Int J Hyg Environ Health 204:165–174
Altmann L, Weinsber F, Sveinsson K et al (1993) Impairment of long-term potentiation and learning following chronic lead exposure. Toxicol Lett 66:105–112
Antonio MT, Corredor L, Leret ML (2003) Study of the activity of several brain enzymes like markers of the neurotoxicity induced by perinatal exposure to lead and/or cadmium. Toxicol Lett 143:331–340
Aschner M (1996) The functional significance of brain metallothioneins. FASEB J 10:1129–1136
Audesirk G (1993) Electrophysiology of lead intoxication: effects on voltage-sensitive ion channels. Neurotoxicology 14:137–148
Bellinger CD, Bellinger MA (2006) Childhood lead poisoning: the torturous path from science to policy. J Clin Invest 116:853–957
Bellinger DC, Needleman HL (2003) Intelectual impairment and blood lead levels. N Engl J Med 349:500–502
Bellinger DC, Stiles KM, Needelman HL (1992) Low-level lead exposure, intelligence and academic achievement: a long-term follow-up study. Pediatrics 90:855–861
Bennet C, Rajanna B, Sharada R et al (2007) Region specific increase in the antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation products in the brain of rats exposed to lead. Free Radic Res 41:267–273
Boissel JP, Schwarz PM (1998) Neuronal-type NO synthase: transcript diversity and expressional regulation. Nitric Oxide 2:337–349
Bressler JP, Goldstein GW (1991) Mechanisms of lead neurotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol 41:479–484
Bressler J, Kim KA, Chakraborti T et al (1999) Molecular mechanisms of lead neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 24:595–600
Bridges CC, Zalups RK (2005) Molecular and ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:274–308
Bruckdorfer R (2005) The basics about nitric oxide. Mol Aspects Med 26:3–31
Burns RS, Chiueh CC, Markey SP et al (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra by N-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4546–4550
Canfield RL, Kreher DA, Cornwell C et al (2003) Low level lead exposure executive functioning, and learning in early childhood. Child Neuropsychol 9:35–53
Carpenter DO, Matthews MR, Parsons PJ et al (1994) Long-term potentiation in the piriform cortex is blocked by lead. Cell Mol Neurobiol 14:723–733
Chatterjee A, Catravas JD (2008) Endothelial nitric oxide (NO) and its pathophysiologic regulation. Vasc Pharmacol 49:134–140
Chen MS, Huber AB, Vander Daar ME et al (2000) Nogo A is a myelin-associated neurite outgrowth inhibitor and an antigen for monoclonal antibody IN-1. Nature 403:434–439
Chetty CS, Reddy GR, Murthy KS et al (2000) Perinatal lead exposure alters the expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in rat brain. Int J Toxicol 20:113–120
Chrousos GP (1995) The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N Engl J Med 332:1351–1362
Chung YE, Kim YS, Lee WB (2004) Distribution of neuronal nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive neurons in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus during postnatal development. J Mol Histol 35:765–770
Costa LG, Aschner M, Vitalone A et al (2004) Developmental neuropathology of environmental agents. Annu Rev Pharmacol 44:87–110
Daniel S, Limson JL, Dairam A (2004) Through metal binding, curcumin protects against lead-and cadmium-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenates and against lead-induced tissue damage in rat brain. J Inorg Biochem 98:266–275
Dawson VL, Dawson TM (1996) Nitric oxide actions in neurochemistry. Neurochem Int 29:97–110
Dawson TM, Sasaki M, Gonzalez-Zuluta M et al (1998) Regulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and identification of novel nitric oxide signaling pathways. Prog Brain Res 118:3–11
Devi CB, Reddy GH, Prasanthi RP et al (2005) Developmental lead exposure alters mitochondrial monoamine oxidase and synaptosomal chatecolamine levels in rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 23:375–381
Dinerman JL, Dawson TM, Schell J, Snowman A, Syner SH (1994) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase localized to hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for synaptic plasticity. PNAS 91:4214–4218
Doyle CA, Slater P (1997) Localization of neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase isoforms in human hippocampus. Neuroscience 76:387–395
Emory E, Ansari Z, Patillo R et al (2003) Maternal blood lead effects on infant intelligence at age 7 months. Am J Obstet Gynecol 188:S26–S32
Environmental Protection Agency (2006) U.S., Air quality criteria for lead Volume I and II of II, Research Triangle Park NC: National Center for Environmental Assessment-RTO Office
Estrada C, Murillo-Carretero M (2005) Nitric oxide and neurogenesis in health and disease. Neuroscientist 11:294–307
García A, Baltrons MA (2004) The nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway in CNS glial cells. Adv Mol Cell Biol 31:575–593
García-Arenas G, Claudio L, Pérez-Severiano F et al (1999) Lead acetate exposure inhibits nitric oxide synthase activity in capillary and synaptosomal fractions of mouse brain. Tox Sci 50:244–248
García-Arenas G, Ramírez-Amaya V, Balderas I et al (2004) Cognitive deficits in adult rats by lead intoxiation are related with regional specific inhibition of cNOS. Behav Brain Res 149:49–59
Garthwaite J (2008a) Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell signaling in nervous system. Trends Neurosci 14:60–67
Garthwaite J (2008b) Concepts of neural nitric oxide-mediated transmission. Eur J Neurosci 27:2783–2802
Gilbert ME, Mack CM (1990) The NMDA antagonist, MK-801, suppresses long-term potentiation, kindling, and kindling-induced potentiation in the perforant path of the unanesthetized rat. Brain Res 519:89–96
Gilbert ME, Mack CM, Lasley SM (1996) Chronic developmental lead (Pb2+) exposure increases threshold for long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus in vivo. Brain Res 736:125–134
Gomaa A, Howard H, Bellinger D (2002) Maternal bone lead as an independent risk factor for fetal neurotoxicity: a perspective study. Pediatrics 110:110–118
Goyer RA (1993) Lead toxicity: current concerns. Environ Health Perspect 100:177–187
Goyer RA (1997) Toxic and essential metals interactions. Annu Rev Nutr 17:37–50
Goyer RA, Clarkson TW (2001) Toxic effects of metals. In: Klaassen CD (ed) Casarett and Doull’s, toxicology: the basic science of poisons, 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 811–867
Gu Y, Wang L, Xiao C et al (2005) Effects of lead on voltaje-gated sodium channels in rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. Neuroscience 133:679–690
Gurer H, Ercal N (2000) Can antioxidants be beneficial in the treatment of lead poisoning? Free Radic Biol Med 29:927–945
Gurer H, Ozgunes H, Neal R et al (1988) Antioxidant effects of N-acetylcysteine and succiner in red blood cells from lead-exposed. Toxicology 128:181–189
Gwalteney-Brant SM (2002) Heavy metals. In: Haschek WM, Rosseaux CG, Wallig AM (eds) Handbook of toxicologic pathology, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 701–732
Harry JG, Schmitt JT, Gong Z et al (1996) Lead-induced alterations of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the developing rat brain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 139:84–93
Hawkins RD, Son H, Arancio O (1998) Nitric oxide as a retrograde messenger during long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Prog Brain Res 72:155–172
Hirano A, Iwata M (1989) Neuropathology of lead intoxication. In: Vinken PJ, Beuyn GW (eds) Intoxication of the nervous system. North-Holland Publishing Company, New York, pp 35–64
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:67–182
Jett DA, Kuhlmann AC, Farmer SJ et al (1997) Age-dependent effects of developmental lead exposure on performance in the Morris water maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:271–279
Klein GL, Snodgrass WR (2003) Heavy metal toxicology. In: Caballero B, Trugo L, Finglas P (eds) Encyclopedia of food sciences and nutrition, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 3050–3057
Knott AB, Bossy WE (2009) Nitric oxide in health and disease of the nervous system. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:541–553
Kröncke DK, Fehsel K, Kolb BV (1997) Nitric oxide: cytotoxicity versus cytoprotection-how, why, when and where. Nitric Oxide 1:107–120
Kuhlmann AC, McGlothan JL, Guilarte TR (1997) Developmental lead exposure causes spatial learning deficits in adult rats. Neurosci Lett 233:101–104
Kühn K, Wellen J, Link N et al (2003) The mouse MPTP model: gene expression changes in dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 17:1–12
Leret ML, García-Uceda F, Antonio MT (2002) Effects of maternal lead administration on momoaminergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic systems. Brain Res Bull 58:469–473
Li H, Wallareth T, Münzel T et al (2002) Regulation of endothelial-type NO synthase expression in pathophysiology and in response to drugs. Nitric Oxide 7:149–164
Links JM, Schwartz BS, Simon D et al (2001) Characterization of toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics with linear systems theory: application to lead-associated cognitive decline. Environ Health Perspect 9:361–368
Lonze BE, Ginty DD (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35:605–623
Lüth HJ, Holzer M, Gärtner U et al (2001) Expression of endothelial and inducible NOS-isoforms is increased in Alzheimer’s disease, in APP23 transgenic mice and after experimental brain lesion in rat: evidence for an induction by amyloid pathology. Brain Res 913:57–67
Mac-Micking J, Xie QW, Nathan C (1997) Nitric oxide and macrophages function. Annu Rev Immunol 15:323–350
Marsden PA, Heng HHQ, Scherer SW et al (1993) Structure and chromosomal localization of the human constitutive endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene. J Biol Chem 268:17478–17488
Mendola P, Selevan SG, Gutter S et al (2002) Environmental factors associated with the spectrum of neurodevelopmental deficits. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 8:188–197
Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA (1989) Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from l-arginine: a pathway for regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol 38:1709–1715
Moreira GE, Rosa GJM, Barros SBM et al (2001a) Antioxidant defense in rat brain regions after developmental lead exposure. Toxicology 169:145–151
Moreira GE, Vassilief I, Vassillief VS (2001b) Developmental lead exposure: behavioural alterations in the short and long term. Neurotoxicol Teratol 23:489–495
Nava-Ruíz C, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Méndez-Armenta M et al (2010) Nitric oxide synthase immunolocalization and expression in the rat hippocampus after sub-acute lead acetate exposure in rats. Exp Tox Pathol 62:311–316
Nehru B, Kanwar SS (2004) N-acetylcysteine exposure on lead-induced lipid peroxidative damage and oxidative defense system in brain regions of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 101:257–264
O’Callaghan JP, Jensen KF (1992) Enhanced expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein and the cupric silver degeneration reaction can be used as sensitive and early indicators of neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 13:113–122
O’Dell TJ, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER et al (1991) Test of the roles of two diffusable substances in long-term potentiation: evidence for nitric oxide as a possible early retrograde messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:11285–11289
Oteiza PI, Verstraeten SV, Adonaylo VN (1995) Oxidative damage induced by metals without redox capacity in biological systems. Ci Cult 47:330–335
Papanikolaou CN, Hatzidaki GE, Belivanis S et al (2005) Lead toxicity update. A brief review. Med Sci Monit 11:329–336
Pautz A, Art J, Hahn S et al (2010) Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide 23:75–93
Riccio A, Alvania RS, Lonze BE et al (2006) A nitric oxide signaling pathway controls CREB-mediated gene expression in neurons. Mol Cell 21:283–294
Rice DC (1993) Lead induced changes in learning: evidence for behavioral mechanisms from experimental animals studies. Neurotoxicology 14:167–178
Rice DC (1996) Behavioral effects of lead: commonalities between experimental and epidemiologic data. Environ Health Perspect 104:337–351
Robinson GB, Reed GD (1992) Effect of MK-801 on the induction and subsequent decay of long-term potentiation in the unanesthetized rabbit hippocampal dentate gyrus. Brain Res 569:78–85
Santizo K, Baughman VL, Pelligrino DA (2000) Relative contributions from neuronal and endotelial nitric oxide synthases to regional cerebral blood flow changes during forebrain ischemia in rats. NeuroReport 11:1549–1553
Sasaki M, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Huang H et al (2000) Dynamic regulation of neuronal NO synthase transcription by calcium influx through a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. PNAS 97:8617–8622
Selvin-Testa A, Capani F, Loidl CF et al (1997) The nitric oxide synthase expression of rat cortical and hippocampal neurons changes after early lead exposure. Neurosci Lett 236:75–78
Sharifi AM, Baniasadi S, Jorjani M, Rahimi F, Bakhshayesh M (2002) Investigation of acute lead poisoning on apoptosis in rat hippocampus in vivo. Neurosci Lett 329:45–48
Simonian NA, Coyle JT (1996) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:83–106
Skoczynska A, Smolik R, Jelen M (1993) Lipid abnormalities in rats given small doses of lead. Arch Toxicol 97:200–204
Soltaninejad K, Kebriaeezadeh A, Minaiee B et al (2003) Biochemical and ultrastructural evidences for toxicity of lead through free radicals in rat brain. Hum Exp Toxicol 22:417–423
Song XJ, Wang ZB, Gan Q et al (2006) cAMP and cGMP contribute to sensory neuron hiperexcitability and hiperalgesia in rats with dorsal root ganglia compression. J Neurophysiol 95:479–492
Squire LR, Knowlton BJ (1995) Memory, hippocampus and brain systems. In: Gazzaniga KS (ed) The cognitive neurosciences, xx edn. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 825–837
Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Pünder I, Peters B et al (1996) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and RNA expression in adult rat hippocampus following low-level lead exposure during development. Histochem Cell Biol 105:431–442
Strużyñska L, Bubko I, Walski M et al (2001) Astroglial reaction during the early phase of acute lead toxicity in the adult rat brain. Toxicology 165:121–131
Sun L, Zhan ZY, Hu J et al (2005) Potential association of lead exposure during early development of mice with alteration of hippocampus nitric oxide levels and learning memory. Biomed Environ Sci 18:375–378
Talarek S, Fidecka S (2003) Role of nitric oxide in anticonvulsant effects of benzodiazepines in mice. Pol J Pharmacol 55:181–191
Talavera CE, Condes LM, Martínez LG (2003) Aspectos sobre las funciones del óxido nítrico como mensajero celular en el sistema nervioso central. Salud Ment 26:42–50
Thorns V, Hansen L, Masliah E (1998) nNOS expressing neurons in the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus are affected in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 150:14–20
Tiffany-Castiglioni E (1993) Cell culture models for lead toxicity in neuronal and glial cells. Neurotoxicology 14:513–536
Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Qian Y (2001) Astroglia as metal depots: molecular mechanisms for metal accumulation, storage and release. Neurotoxicology 22:577–592
Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Sanabria E, Wu E et al (1990) Lead uptake by cultured astroglia. In vitro Cell Develop Bio 26:66A
Toda N, Okamura T (2003) The pharmacology of nitric oxide in the peripheral nervous system of blood vessels. Pharmacol Rev 57:315–338
Toscano CD, Guilarte RT (2005) Lead neurotoxicity: from exposure to molecular effects. Brain Res Rev 49:529–554
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J et al (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1–40
Van Den Berg KJ, Lammers JHCM, Hoogendijk EMG et al (1996) Changes in regional brain GFAP levels and behavioral functioning following subchronic lead acetate exposure in adult rats. Neurotoxicology 17:725–734
Villeda-Hernández J, Barroso-Moguel R, Méndez-Armenta M et al (2001) Enhanced brain regional lipid peroxidation in developing rats exposed to low level lead acetate. Brain Res Bull 55:247–251
Villeda-Hernández J, Méndez-Armenta M, Barroso-Moguel R et al (2006) Morphometric analysis of brain lesions in rat fetuses prenatally exposed to low-level lead acetate: correlation with lipid peroxidation. Histol Histopathol 21:609–617
Wang Y, Newton DC, Marsden PA (1999) Neuronal NOS: gene structure mRNA diversity, and functional relevance. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:21–43
Wang J, Wu J, Zhang Z (2006) Oxidative stress in mouse brain exposed to lead. Ann Occup Hyg 50:405–409
Weiss SW, Albers DS, Iadarola MJ et al (1998) NMDA R1 glutamate receptor subunit isoforms in neostriatal, neocortical, and hippocampal nitric oxide synthase neurons. J Neurosci 18:1725–1734
White LD, Cory-Slechta DA, Gilbert ME et al (2007) New and evolving concepts in the neurotoxicology of lead. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 225:1–27
Wiencken AE, Casagrande VA (1999) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in astrocytes another source of nitric oxide in neocortex. Glia 26:280–290
Xu YZ, Ruan DY, Wu Y et al (1998) Nitric oxide affects LTP in area CA1 and CA3 of the hippocampus in low-level lead-exposed rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 20:69–73
Yang Y, Ma Y, Ni L et al (2003) Lead exposure through gestation-only caused long-term learning/memory deficits in young adult offspring. Exp Neurol 184:489–495
Zengh W, Aschner M, Ghersi-Egea JF (2003) Brain barrier system: a new frontier in metal neurotoxicological research. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 192:1–11
Zhang S, Chen J, Huang S (1998) Spatial learning and memory induce up-regulation of nitric oxide-producing neurons in rat brain. Brain Res 801:101–106
Zhao Y, Brandish PE, Ballou PD et al (1999) A molecular basis for nitric oxide sensing by soluble guaylate cyclise. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:14753–14758
Zhou I, Zhu DY (2009) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase: structure, subcellular localization, regulation, and clinical implications. Nitric Oxide 20:223–230
Zhu ZW, Yang RL, Dong GJ et al (2005) Study on the neurotoxic effects of low-level lead exposure in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 6:686–692
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nava-Ruiz, C., Méndez-Armenta, M. & Ríos, C. Lead neurotoxicity: effects on brain nitric oxide synthase. J Mol Hist 43, 553–563 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9414-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9414-2