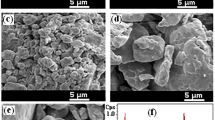
Abstract
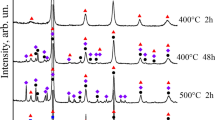
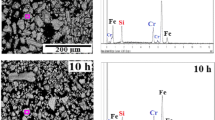
Nanostructured (Fe0.5Ni0.5)92Zr5B3 alloy was prepared by milling a blend of pre-alloyed Fe50Ni50 precursor and high purity chemical elemental powders of Zr and B in a high-energy ball mill setup. Rietveld refinement of the X-ray diffraction pattern of the final sample (30 h of milling) revealed presence of two Fe–Ni rich phases [disordered fcc γ–(Fe,Ni) alloy with Zr and B and the atomically ordered FeNi] with grain sizes in nanometer scale. Fe and Ni atoms were locally probed using extended X-ray absorption fine structure EXAFS and 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy. Whilst EXAFS analysis of milled samples suggested structural properties similar to the pre-alloyed precursor, Mössbauer data have shown the Fe2B phase formation after 3 h of milling, suggesting that the final material consists of nanograins of ordered FeNi (8%) and Fe2B (6%) phases dispersed in solid solution of γ–(Fe,Ni) alloy rich in nickel (86%) with Zr and B atoms impregnated in grain boundary defects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available from the authors on request.
References
Benjamin, J.S.: Dispersion strengthened super-alloys by mechanical alloying. Metall. Trans. 1, 2943–2951 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03037835
Koch, C.C.: Materials Synthesis by Mechanical Alloying. Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 19, 121–143 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ms.19.080189.001005
Zoz, H.: Attritor Technology-Latest Developments. Mater. Sci. Forum 179–181, 419–424 (1995). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.179-181.419
Basset, D., Matteazzi, P., Mani, F.: Designing a high energy ball-mill for synthesis of nanophase materials in large quantities. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 168, 149–152 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(93)90718-T
Miglierini, M., Lančok, A., Kohout, J.: Hyperfine fields in nanocrystalline Fe–Zr–B probed by 57Fe nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 211902 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3431612
Stankov, S., Sepiol, B., Kaňuch, T., Scherjau, D., Würschum, R., Miglierini, M.: High temperature Mössbauer effect study of Fe90Zr7B3 nanocrystalline alloy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17, 3183–3196 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/21/013
Suzuki, K., Makino, A., Inoue, A., Masumoto, T.: Soft magnetic properties of nanocrystalline bcc Fe-Zr-B and Fe-M-B-Cu (M=transition metal) alloys with high saturation magnetization (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 70, 6232–6237 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.350006
Świerczek, J.: Medium range ordering and some magnetic properties of amorphous Fe90Zr7B3 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2696–2702 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.04.010
Świerczek, J., Mydlarz, T.: Magnetic entropy changes at early stages of nanocrystallization in amorphous Fe90Zr7B3 ribbons. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 9340–9345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.07.033
Gao, Y., Shindo, D., Bitoh, T., Makino, A.: Domain structures of nanocrystalline Fe90Zr7B3 alloy studied by Lorentz microscopy. Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater. 4, 353–359 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stam.2003.09.001
Hua, Z., Sun, Y.M., Yu, W.Q., Wei, M.B., Liu, L.H.: Preparation and properties of FeZrB amorphous-nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mat. Sci. Edit. 24, 747–749 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-009-5747-4
Hua, Z., Sun, Y.M., Yu, W.Q., Wei, M.B., Liu, L.H.: Structure and magnetic properties of Fe88−xZrxB12 (x = 5, 10, 20) alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 477, 529–531 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.10.075
Saravanan, T.T., Kumaran, S., Srinivasa Rao, T.: Structural evolution and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed metastable Fe–Ni–Zr–B system. Mater. Lett. 63, 780–782 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.01.003
Suñol, J.J., González, A., Bonastre, J., Clavaguera-Mora, M.T., Arcondo, B.: Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline FeNiZrB developed by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 434–435, 415–419 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.08.319
Suzuki, K., Kataoka, N., Inoue, A., Makino, A., Masumoto, T.: High Saturation Magnetization and Soft Magnetic Properties of bcc Fe–Zr–B Alloys with Ultrafine Grain Structure. Mater. Trans. JIM 31(8), 743–746 (1990). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.31.743
Yoshizawa, Y., Oguma, S., Yamauchi, K.: New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 64, 6044–6046 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.342149
Pereira, R.D., Passamani, E.C., Larica, C., Freitas, J.C.C., Takeuchi, A.Y.: Nanostructured FeZrCuB alloys prepared by mechanosynthesis. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 033515 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2768009
Peña Rodríguez, V.A., Quispe Marcatoma, J., Rojas Ayala, Ch., Baggio-Saitovitch, E.M., Passamani, E.C.: Local environments of Fe and Co in (Fe0.5Co0.5)75Si15B10 mechanically alloyed. J. Alloy. Compd. 475, 29–34 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.104
Guérault, H., Bureau, B., Silly, G., Buzaré, J.Y., Grenèche, J.M.: Local structural orders in nanostructured fluoride powders. J. Non Cryst. Solids 287(1–3), 65–69 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(01)00541-5
Herr, U., Jing, J., Birringer, R., Gonser, U., Gleiter, H.: Investigation of nanocrystalline iron materials by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 50, 472–474 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.98177
Grafouté, M., Labaye, Y., Calvayrac, F., Grenèche, J.M.: Structure of grain boundaries in nanostructured powders: a Monte-Carlo/EAM numerical investigation. Eur. Phys. J. B 45, 419–424 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00199-x
Herzer, G.: Nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. In: Handbook of Magnetic Materials, Vol. 10, Chapter 3, 415–462. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (1997)
Pillaca Quispe, M., Landauro, C.V., Pinto Vergara, M.Z., Quispe-Marcatoma, J., Rojas-Ayala, C., Peña-Rodríguez, V.A., Baggio-Saitovitch, E.M.: Influence of high energy milling on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the Al–Cu–Fe phases: the case of the i-Al64Cu23Fe13quasicrystalline and the ω-Al70Cu20Fe10 crystalline phases. RSC Adv. 6, 5367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA21093C
Peña Rodríguez, V.A., Rojas-Ayala, C., Medina Medina, J., Paucar Cabrera, P., Quispe-Marcatoma, J., Landauro, C.V., Rojas Tapia, J., Baggio-Saitovitch, E.M., Passamani, E.C.: Fe50Ni50 synthesized by high energy ball milling: A systematic study using X-ray diffraction, EXAFS and Mössbauer methods. Mater. Charact. 149, 249–254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.01.036
Lee, S., Edalati, K., Iwaoka, H., Horita, Z., Ohtsuki, T., Ohkochi, T., Kotsugi, M., Kojima, T., Mizuguchi, M.: and Koki Takanashi: Formation of FeNi with L10-ordered structure using high-pressure torsion. Philos. Mag. 94(10), 639–646 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500839.2014.955546
BrukerAXS. DIFFRACPlus TOPAS: TOPAS 4.2 User Manual, Bruker-AXS GmbH,.Karlsruhe, Germany (2008)
Newville, M.: IFEFFIT: interactive XAFS analysis and FEFF fitting. J. Synchrotron Rad. 8, 322–324 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049500016964
Ravel, B., Newville, M.: ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 12(4), 537–541 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049505012719
Peña Rodríguez, V.A., Quispe Marcatoma, J., Rojas Ayala, Ch., Baggio-Saitovitch, E.M., Passamani, E.C.: Local environments of Fe and Co in (Fe0.5Co0.5)75Si15B10 mechanically alloyed. J. Alloys and Compd. 45, 29–34 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.104
Zabinsky, S.I., Rehr, J.J., Ankudinov, A., Albers, R.C., Eller, M.J.: Multiple-scattering calculations of x-ray-absorption spectra. Phys. Rev. B 52, 2995–3009 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.52.2995
Ankudinov, A.L., Ravel, B., Rehr, J.J., Conradson, S.D.: Real-space multiple-scattering calculation and interpretation of x-ray-absorption near-edge structure. Phys. Rev. B 58, 7565–7576 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.58.7565
Müller, J.E., Jepsen, O., Wilkins, J.W.: X-ray absorption spectra: K-edge of 3d transition metals, L-edges of 3d and 4d metals and M-edges of palladium. Solid State Commun. 42(5), 365–368 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(82)90154-5
Benitez Rodríguez, E.D., Rodríguez, H.B., Oyola Lozano, D., Rojas Martínez, Y.A., Pérez Alcázar, G.A.: Mössbauer study of alloy Fe67.5Ni32.5, prepared by mechanical alloying. Hyperfine Interact. 232, 87–95 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-015-1138-8
Suryanarayana, C., Sharma, S.: Lattice contraction during amorphization by mechanical alloying. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 103503 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3020531
Hong, L.B., Fultz, B.: Two-phase coexistence in Fe–Ni alloys synthesized by ball milling. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 3946–3955 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.361821
Lima, E., Drago, V.: Influence of chemical disorder on the magnetic behaviour and phase diagram of the FexNi1−x system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 280, 251–256 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.03.020
Zhang, F.X., Jin, K., Zhao, S., Mu, S., Bei, H., Liu, J.C., Xue, H.Z., Popov, D., Park, C., Stocks, G.M., Weber, W.J., Zhang, Y.: X-ray absorption investigation of local structural disorder in Ni1-x Fex (x=0.10, 0.20, 0.35, and 0.50) alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 121, 165105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4982705
Clarke, R.S., Jr., Scott, E.R.D.: Tetrataenite-ordered FeNi, a new mineral in meteorite. Am. Mineral. 65(7–8), 624–630 (1980)
Abdu, Y.A., Ericsson, T., Annersten, H., Dubrovinskaia, N.A., Dubrovinsky, L.S., Gimselseed, A.M.: Mössbauer studies on the metallic phases of Al Kidirate and New Haifa meteorites. Hyperfine Interact. (C) 5, 375–378 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0281-3_93
Scorzelli, R.B., Danon, J.: Mössbauer Spectroscopy andX-Ray Diffraction Studies of Fe-Ni Order-Disorder Processes in a 35% Ni Meteorite (Santa Catharina). Phys. Scr. 32(2), 143–148 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/32/2/010
Lima, E., Jr., Drago, V.: A New Process to Produce Ordered Fe50Ni50 Tetrataenite. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 187(1), 119–124 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-396X(200109)187:1%3c119::AID-PSSA119%3e3.0.CO;2-L
Albertsen, J.F., Roy-Poulsen, N.O., Vistisen, L.: Ordered FeNi, Tetrataenite, and the Cooling Rate of Iron Meteorites Below 320 °C. Meteoritics 15, 258 (1980)
González, J.M., Pérez Alcazar, G.A., Zamora, L.E., Tabares, J.A., Bohórquez, A., Gancedo, J.R.: Development of magnetic softness in high-energy ball milling alloyed Fe50B50. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 261, 337–346 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)01321-5
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS) under proposal XAFS1 – 1304. The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Fund for Scientific and Technological Development, FONDECYT [contract 011-2014-FONDECYT], FAPERJ-Brazil (Emeritus fellowship, EBS, E26/210.715/2014, E-26/010.002990/2014 grants), FINEP, FAPES, CNPq, and Latin American Center of Physics. The authors would also like to acknowledge the San Marcos National University for providing research facilities and financial support [CSI-projects: 061301011-0801301011-091301031].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.A. Peña Rodríguez: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing-Original draft preparation, Project administration, Funding acquisition. J. Medina Medina: Investigation, Validation, Data curation, Software, Resources. C. Rojas-Ayala: Software, Formal analysis, Investigation. P. Paucar Cabrera: Investigation. C.V. Landauro: Writing, reviewing and editing, Funding acquisition, Visualization. J. Quispe-Marcatoma: Investigation, Formal analysis, Resources. J. Rojas Tapia: Software, Visualization. E.M. Baggio-Saitovitch: Writing, reviewing and editing, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. E.C. Passamani: Writing, reviewing and editing, Formal analysis, Visualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no significant competing financial, professional, or personal interests in this manuscript submission.
Author agreement
The authors declare that this manuscript contains original scientific work and has not been published before elsewhere. All the authors listed have approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the International Conference on the Applications of the Mössbauer Effect (ICAME 2021), 5-10 September 2021, Brasov, Romania
Edited by Victor Kuncser
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peña Rodríguez, V.A., Medina Medina, J., Rojas-Ayala, C. et al. Nanostructured FeNiZrB powders synthesized by high-energy ball milling: structural and hyperfine characterizations. Hyperfine Interact 242, 27 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-021-01758-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-021-01758-y