Abstract
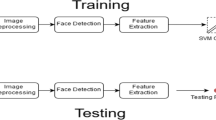
This paper discusses the development of an efficient and automated system for the recognition of facial expressions, which is essentially an application augmented with many multimedia computing systems. The proposed scheme works in three stages. In the first stage, ripplet transform type II (ripplet-II) is employed to extract the features from facial images because of its efficiency in representing edges and textures. In the next stage, a principal component analysis (PCA)+linear discriminant analysis (LDA) approach is utilized to obtain a more compact and discriminative feature set. In the final stage, classification is performed using a least squares variant of support vector machine (LS-SVM) with radial basis function (RBF) kernel. The proposed system is validated on two benchmark datasets namely the Extended Cohn-Kanade (CK + ) and Japanese female facial expression (JAFFE). The experimental results demonstrate that the propose system yields superior performance as compared to other state-of-the-art schemes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FER:
-
Face expression recognition
- Ripplet-II:
-
Ripplet transform type II
- CK+:
-
Extended Cohn-Kanade
- JAFFE:
-
Japanese female facial expression
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- LDA:
-
Linear discriminant analysis
- HOG:
-
Histograms of Oriented Gradient
- DWT:
-
Discrete wavelet transform
- SWT:
-
Statyionary wavelet transform
- RBF:
-
Radial basis function
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- LS-SVM:
-
Least square support vector machine
References
Bartlett M S, Littlewort G, Frank M, Lainscsek C, Fasel I, Movellan J (2006) Fully automatic facial action recognition in spontaneous behavior. In: 7th international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition. IEEE, pp 223–230. https://doi.org/10.1109/FGR.2006.55
Ben-Hur A, Horn D, Siegelmann HT, Vapnik V (2002) Support vector clustering. J Mach Learn Res 2:125–137
Bettadapura V (2012) Face expression recognition and analysis: the state of the art. arXiv:1203.6722
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning. Springer
Chen J, Chen D, Gong Y, Yu M, Zhang K, Wang L (2012) Facial expression recognition using geometric and appearance features. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on internet multimedia computing and service. ACM, pp 29–33. https://doi.org/10.1145/2382336.2382345
Chen J, Chen Z, Chi Z, Fu H (2014) Facial expression recognition based on facial components detection and HOG features. In: International workshops on electrical and computer engineering subfields
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994018
Dahmane M, Meunier J (2011) Emotion recognition using dynamic grid-based HoG features. In: International conference on automatic face & gesture recognition and workshops (FG 2011). IEEE, pp 884–888. https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2011.5771368
Deshmukh S, Patwardhan M, Mahajan A (2016) Survey on real-time facial expression recognition techniques. IET Biom 5(3):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-bmt.2014.0104
Dongcheng S, Jieqing J (2010) The method of facial expression recognition based on DWT-PCA/LDA. In: International congress on image and signal processing (CISP), vol 4. IEEE, pp 1970–1974. https://doi.org/10.1109/CISP.2010.5648166
Ekman P, Friesen W V (1971) Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J Pers Soc Psychol 17(2):124. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0030377
Elaiwat S, Bennamoun M, Boussaid F (2016) A spatio-temporal RBM-based model for facial expression recognition. Pattern Recogn 49:152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.07.006
Gandhi T, Trivedi MM (2008) Image based estimation of pedestrian orientation for improving path prediction. In: The proceedings of the IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium, pp 506–511. https://doi.org/10.1049/10.1109/IVS.2008.4621257
Gritti T, Shan C, Jeanne V, Braspenning R (2008) Local features based facial expression recognition with face registration errors. In: 8th IEEE international conference on automatic face & gesture recognition, FG’08. IEEE, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/AFGR.2008.4813379
Guo M, Hou X, Ma Y, Wu X (2016) Facial expression recognition using ELBP based on covariance matrix transform in KLT. Multimedia Tools and Applications 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3282-9
Happy SL, Routray A (2015) Automatic facial expression recognition using features of salient facial patches. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 6(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2386334
Hsieh C-C, Hsih M-H, Jiang M-K, Cheng Y-M, Liang E-H (2015) Effective semantic features for facial expressions recognition using SVM. Multimedia Tools and Applications 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2598-1
Jung H, Lee S, Park S, Lee I, Ahn C, Kim J (2015) Deep temporal appearance-geometry network for facial expression recognition. arXiv:1503.01532
Kar NB, Babu KS, Jena SK (2017) Face expression recognition using histograms of oriented gradients with reduced features. In: Proceedings of international conference on computer vision and image processing. Springer, pp 209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2107-7_19
Kazmi SB, Jaffar MA et al (2012) Wavelets-based facial expression recognition using a bank of support vector machines. Soft Comput 16(3):369–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-011-0721-4
Lucey P, Cohn JF, Kanade T, Saragih J, Ambadar Z, Matthews I (2010) The Extended Cohn-Kanade dataset (CK+): a complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In: IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, pp 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543262
Lyons M, Akamatsu S, Kamachi M, Gyoba J (1998) Coding facial expressions with Gabor wavelets. In: Third IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition. IEEE, pp 200–205. https://doi.org/10.1109/AFGR.1998.670949
Martínez AM, Kak AC (2001) PCA Versus LDA. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(2):228–233. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.908974
Michel P, El Kaliouby R (2003) Real time facial expression recognition in video using support vector machines. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on multimodal interfaces. ACM, pp 258–264. https://doi.org/10.1145/958432.958479
Mlakar U, Potočnik B (2015) Automated facial expression recognition based on histograms of oriented gradient feature vector differences. SIViP 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0810-4
Moraes D, Wainer J, Rocha A (2016) Low false positive learning with support vector machines. J Vis Commun Image Represent 38:340–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2016.03.007
Nayak DR, Dash R, Majhi B (2016) Brain mr image classification using two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform and adaboost with random forests. Neurocomputing 177:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.11.034
Nayak DR, Dash R, Majhi B (2017) Stationary wavelet transform and adaboost with svm based pathological brain detection in mri scanning. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 16(2):137–149. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527315666161024142036
Qayyum H, Majid M, Anwar S M, Khan B (2017) Facial expression recognition using stationary wavelet transform features. Math Probl Eng 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9854050
Saeed A, Al-Hamadi A, Niese R, Elzobi M (2014) Frame-based facial expression recognition using geometrical features. Advances in Human-Computer Interaction 2014:4
Shimizu H, Poggio T (2003) Direction estimation of pedestrian from images. In: AI Memo 2003-020, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, pp 1–11
Siddiqi MH, Lee S (2013) Human facial expression recognition using wavelet transform and hidden markov model. In: International workshop on ambient assisted living. Springer, pp 112–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03092-0
Siddiqi MH, Ali R, Khan AM, Park Y-T, Lee S (2015) Human facial expression recognition using stepwise linear discriminant analysis and hidden conditional random fields. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(4):1386–1398. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2405346
Sun Y, Kamel MS, Wong AKC, Wang Y (2007) Cost-sensitive boosting for classification of imbalanced data. Pattern Recogn 40(12):3358–3378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2007.04.009
Suwa M, Sugie N, Fujimora K (1978) A preliminary note on pattern recognition of human emotional expression. In: International joint conference on pattern recognition, pp 408–410
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018628609742
Theodoridis S, Koutroumbas K (1999) Pattern recognition. Academic Press, New York
Tsai H-H, Lai Y-S, Zhang Y-C (2010) Using SVM to design facial expression recognition for shape and texture features. In: International conference on machine learning and cybernetics, vol 5. IEEE, pp 2697–2704. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLC.2010.5580938
Uçar A, Demir Y, Güzeliş C (2016) A new facial expression recognition based on curvelet transform and online sequential extreme learning machine initialized with spherical clustering. Neural Comput & Applic 27(1):131–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1569-1
Uddin MZ (2016) A depth video-based facial expression recognition system utilizing generalized local directional deviation-based binary pattern feature discriminant analysis. Multimedia Tools and Applications 75(12):6871–6886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2614-5
Uddin MZ (2016) Facial expression recognition using depth information and spatiotemporal features. In: 18th international conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT), 2016. IEEE, pp 726–731. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACT.2016.7423536
Uddin MZ, Hassan MM, Almogren A, Alamri A, Alrubaian M, Fortino G (2017) Facial expression recognition utilizing local direction-based robust features and deep belief network. IEEE Access 5:4525–4536. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2676238
Valstar MF, Pantic M (2012) Fully automatic recognition of the temporal phases of facial actions. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 42(1):28–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2163710
Viola P, Jones M (2001) Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, vol 1, pp I–511. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2001.990517
Wang S-H, Phillips P, Dong Z-C, Zhang Y-D (2017) Intelligent facial emotion recognition based on stationary wavelet entropy and jaya algorithm. Neurocomputing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.015
Wang X, Jin C, Liu W, Hu M, Xu L, Ren F (2013) Feature fusion of HOG and WLD for facial expression recognition. In: International symposium on system integration (SII). IEEE, pp 227–232. https://doi.org/10.1109/SII.2013.6776664
Wu SH, Lin KP, Chien HH, Chen CM, Chen MS (2013) On generalizable low false-positive learning using asymmetric support vector machines. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(5):1083–1096. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2012.46
Xu J, Wu D (2008) Ripplet transform for feature extraction. In: SPIE defense and security symposium, pages 69700x–69700x. International society for optics and photonics. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.777302
Xu J, Wu D (2012) Ripplet transform type II transform for feature extraction. IET Image Process 6(4):374–385. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-ipr.2010.0225
Yu H, Yang J (2001) A direct LDA algorithm for high-dimensional data—with application to face recognition. Pattern Recogn 34(10):2067–2070
Zhang L, Tjondronegoro D (2011) Facial expression recognition using facial movement features. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 2(4):219–229. https://doi.org/10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.13
Zhang Y-D, Yang Z-J, Lu H-M, Zhou X -X, Phillips P, Liu Q-M, Wang S-H (2016) Facial emotion recognition based on biorthogonal wavelet entropy, fuzzy support vector machine, and stratified cross validation. IEEE Access 4:8375–8385. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2628407
Acknowledgments
This research is partially supported by the following project: Grant No. ETI/359/2014 by Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure in Universities and Higher Educational Institutions (FIST) Program 2016, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, N.B., Babu, K.S., Sangaiah, A.K. et al. Face expression recognition system based on ripplet transform type II and least square SVM. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 4789–4812 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5485-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5485-0