Abstract
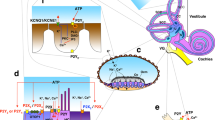
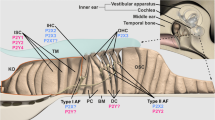
Purinergic signaling in the mammalian cochleovestibular hair cells and afferent neurons is reviewed. The scope includes P2 and P1 receptors in the inner hair cells (IHCs) of the cochlea, the type I spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) that convey auditory signals from IHCs, the vestibular hair cells (VHCs) in the vestibular end organs (macula in the otolith organs and crista in the semicircular canals), and the vestibular ganglion neurons (VGNs) that transmit postural and rotatory information from VHCs. Various subtypes of P2X ionotropic receptors are expressed in IHCs as well as P2Y metabotropic receptors that mobilize intracellular calcium. Their functional roles still remain speculative, but adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) could regulate the spontaneous activity of the hair cells during development and the receptor potentials of mature hair cells during sound stimulation. In SGNs, P2Y metabotropic receptors activate a nonspecific cation conductance that is permeable to large cations as NMDG+ and TEA+. Remarkably, this depolarizing nonspecific conductance in SGNs can also be activated by other metabotropic processes evoked by acetylcholine and tachykinin. The molecular nature and the role of this depolarizing channel are unknown, but its electrophysiological properties suggest that it could lie within the transient receptor potential channel family and could regulate the firing properties of the afferent neurons. Studies on the vestibular partition (VHC and VGN) are sparse but have also shown the expression of P2X and P2Y receptors. There is still little evidence of functional P1 (adenosine) receptors in the afferent system of the inner ear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fields RD, Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic signalling in neuron–glia interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:423–436
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Housley GD, Bringmann A, Reichenbach A (2009) Purinergic signaling in special senses. Trends Neurosci 32:128–141
Mockett BG, Housley GD, Thorne PR (1994) Fluorescence imaging of extracellular purinergic receptor sites and putative ecto-ATPase sites on isolated cochlear hair cells. J Neurosci 14:6992–7007
Housley GD, Raybould NP, Thorne PR (1998) Fluorescence imaging of Na+ influx via P2X receptors in cochlear hair cells. Hear Res 119:1–13
Housley GD, Luo L, Ryan AF (1998) Localization of mRNA encoding the P2X2 receptor subunit of the adenosine 5′-triphosphate-gated ion channel in the adult and developing rat inner ear by in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol 393:403–414
Jarlebark LE, Housley GD, Thorne PR (2000) Immunohistochemical localization of adenosine 5′-triphosphate-gated ion channel P2X(2) receptor subunits in adult and developing rat cochlea. J Comp Neurol 421:289–301
Jarlebark LE, Housley GD, Raybould NP, Vlajkovic S, Thorne PR (2002) ATP-gated ion channels assembled from P2X2 receptor subunits in the mouse cochlea. NeuroReport 13:1979–1984
Housley GD, Kanjhan R, Raybould NP, Greenwood D, Salih SG, Jarlebark L, Burton LD, Setz VC, Cannell MB, Soeller C, Christie DL, Usami S, Matsubara A, Yoshie H, Ryan AF, Thorne PR (1999) Expression of the P2X(2) receptor subunit of the ATP-gated ion channel in the cochlea: implications for sound transduction and auditory neurotransmission. J Neurosci 19:8377–8388
Huang LC, Greenwood D, Thorne PR, Housley GD (2005) Developmental regulation of neuron-specific P2X3 receptor expression in the rat cochlea. J Comp Neurol 484:133–143
Huang LC, Ryan AF, Cockayne DA, Housley GD (2006) Developmentally regulated expression of the P2X3 receptor in the mouse cochlea. Histochem Cell Biol 125:681–692
Nikolic P, Housley GD, Thorne PR (2003) Expression of the P2X7 receptor subunit of the adenosine 5′-triphosphate-gated ion channel in the developing and adult rat cochlea. Audiol Neurootol 8:28–37
Mockett BG, Bo X, Housley GD, Thorne PR, Burnstock G (1995) Autoradiographic labelling of P2 purinoceptors in the guinea-pig cochlea. Hear Res 84:177–193
Xiang Z, Bo X, Burnstock G (1999) P2X receptor immunoreactivity in the rat cochlea, vestibular ganglion and cochlear nucleus. Hear Res 128:190–196
Nikolic P, Housley GD, Luo L, Ryan AF, Thorne PR (2001) Transient expression of P2X(1) receptor subunits of ATP-gated ion channels in the developing rat cochlea. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 126:173–182
Salih SG, Housley GD, Raybould NP, Thorne PR (1999) ATP-gated ion channel expression in primary auditory neurones. NeuroReport 10:2579–2586
Salih SG, Housley GD, Burton LD, Greenwood D (1998) P2X2 receptor subunit expression in a subpopulation of cochlear type I spiral ganglion neurones. NeuroReport 9:279–282
Wang JC, Raybould NP, Luo L, Ryan AF, Cannell MB, Thorne PR, Housley GD (2003) Noise induces up-regulation of P2X2 receptor subunit of ATP-gated ion channels in the rat cochlea. NeuroReport 14:817–823
Vlajkovic SM, Thorne PR, Sevigny J, Robson SC, Housley GD (2002) NTPDase1 and NTPDase2 immunolocalization in mouse cochlea: implications for regulation of p2 receptor signaling. J Histochem Cytochem 50:1435–1442
Vlajkovic SM, Thorne PR, Sevigny J, Robson SC, Housley GD (2002) Distribution of ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases 1 and 2 in rat cochlea. Hear Res 170:127–138
Vlajkovic SM, Vinayagamoorthy A, Thorne PR, Robson SC, Wang CJ, Housley GD (2006) Noise-induced up-regulation of NTPDase3 expression in the rat cochlea: implications for auditory transmission and cochlear protection. Brain Res 1104:55–63
Bobbin RP, Thompson MH (1978) Effects of putative transmitters on afferent cochlear transmission. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 87:185–190
Kujawa SG, Erostegui C, Fallon M, Crist J, Bobbin RP (1994) Effects of adenosine 5′-triphosphate and related agonists on cochlear function. Hear Res 76:87–100
Kujawa SG, Fallon M, Bobbin RP (1994) ATP antagonists cibacron blue, basilen blue and suramin alter sound-evoked responses of the cochlea and auditory nerve. Hear Res 78:181–188
Munoz DJ, Thorne PR, Housley GD, Billett TE, Battersby JM (1995) Extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) in the endolymphatic compartment influences cochlear function. Hear Res 90:106–118
Sueta T, Paki B, Everett AW, Robertson D (2003) Purinergic receptors in auditory neurotransmission. Hear Res 183:97–108
Thorne PR, Munoz DJ, Housley GD (2004) Purinergic modulation of cochlear partition resistance and its effect on the endocochlear potential in the Guinea pig. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 5:58–65
Dulon D, Mollard P, Aran JM (1991) Extracellular ATP elevates cytosolic Ca2+ in cochlear inner hair cells. NeuroReport 2:69–72
Sugasawa M, Erostegui C, Blanchet C, Dulon D (1996) ATP activates non-selective cation channels and calcium release in inner hair cells of the guinea-pig cochlea. J Physiol 491(Pt 3):707–718
Raybould NP, Jagger DJ, Housley GD (2001) Positional analysis of guinea pig inner hair cell membrane conductances: implications for regulation of the membrane filter. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2:362–376
Cho H, Harada N, Yamashita T (1997) Extracellular ATP-induced Ca2+ mobilization of type I spiral ganglion cells from the guinea pig cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol 117:545–552
Salih SG, Jagger DJ, Housley GD (2002) ATP-gated currents in rat primary auditory neurones in situ arise from a heteromultimeric P2X receptor subunit assembly. Neuropharmacology 42:386–395
Ito K, Dulon D (2002) Nonselective cation conductance activated by muscarinic and purinergic receptors in rat spiral ganglion neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C1121–C1135
Ito K, Rome C, Bouleau Y, Dulon D (2002) Substance P mobilizes intracellular calcium and activates a nonselective cation conductance in rat spiral ganglion neurons. Eur J Neurosci 16:2095–2102
Shen J, Harada N, Yamashita T (2003) Nitric oxide inhibits adenosine 5′-triphosphate-induced Ca2+ response in inner hair cells of the guinea pig cochlea. Neurosci Lett 337:135–138
Shen J, Harada N, Nakazawa H, Yamashita T (2005) Involvement of the nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in ATP-induced Ca2+ signalling in cochlear inner hair cells. Eur J Neurosci 21:2912–2922
Yukawa H, Shen J, Harada N, Cho-Tamaoka H, Yamashita T (2005) Acute effects of glucocorticoids on ATP-induced Ca2+ mobilization and nitric oxide production in cochlear spiral ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 130:485–496
Rennie KJ, Ashmore JF (1993) Effects of extracellular ATP on hair cells isolated from the guinea-pig semicircular canals. Neurosci Lett 160:185–189
Nagata N, Harada N, Chen L, Cho H, Tomoda K, Yamashita T (2000) Extracellular adenosine 5′-ATP-induced calcium signaling in isolated vestibular ganglion cells of the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol 120:704–709
Ito K, Chihara Y, Iwasaki S, Komuta Y, Sugasawa M, Sahara Y (2010) Functional ligand-gated purinergic receptors (P2X) in rat vestibular ganglion neurons. Hear Res. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2010.03.081
Vlajkovic SM, Abi S, Wang CJ, Housley GD, Thorne PR (2007) Differential distribution of adenosine receptors in rat cochlea. Cell Tissue Res 328:461–471
Vlajkovic SM, Lee KH, Wong AC, Guo CX, Gupta R, Housley GD, Thorne PR (2010) Adenosine amine congener mitigates noise-induced cochlear injury. Purinergic Signal (this issue)
Wong AC, Guo CX, Gupta R, Housley GD, Thorne PR, Vlajkovic SM (2010) Post exposure administration of A(1) adenosine receptor agonists attenuates noise-induced hearing loss. Hear Res 260:81–88
Hu BH, Zheng XY, McFadden SL, Kopke RD, Henderson D (1997) R-phenylisopropyladenosine attenuates noise-induced hearing loss in the chinchilla. Hear Res 113:198–206
Hight NG, McFadden SL, Henderson D, Burkard RF, Nicotera T (2003) Noise-induced hearing loss in chinchillas pre-treated with glutathione monoethyl ester and R-PIA. Hear Res 179:21–32
Tritsch NX, Yi E, Gale JE, Glowatzki E, Bergles DE (2007) The origin of spontaneous activity in the developing auditory system. Nature 450:50–55
Greenwood D, Jagger DJ, Huang LC, Hoya N, Thorne PR, Wildman SS, King BF, Pak K, Ryan AF, Housley GD (2007) P2X receptor signaling inhibits BDNF-mediated spiral ganglion neuron development in the neonatal rat cochlea. Development 134:1407–1417
Munoz DJ, Thorne PR, Housley GD, Billett TE (1995) Adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) concentrations in the endolymph and perilymph of the guinea-pig cochlea. Hear Res 90:119–125
Munoz DJ, Kendrick IS, Rassam M, Thorne PR (2001) Vesicular storage of adenosine triphosphate in the guinea-pig cochlear lateral wall and concentrations of ATP in the endolymph during sound exposure and hypoxia. Acta Otolaryngol 121:10–15
Zhao HB, Yu N, Fleming CR (2005) Gap junctional hemichannel-mediated ATP release and hearing controls in the inner ear. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:18724–18729
Jagger DJ, Housley GD (2003) Membrane properties of type II spiral ganglion neurones identified in a neonatal rat cochlear slice. J Physiol 552:525–533
Weisz C, Glowatzki E, Fuchs P (2009) The postsynaptic function of type II cochlear afferents. Nature 461:1126–1129
Venkatachalam K, Montell C (2007) TRP channels. Annu Rev Biochem 76:387–417
Pedersen SF, Owsianik G, Nilius B (2005) TRP channels: an overview. Cell Calcium 38:233–252
Corey DP, Garcia-Anoveros J, Holt JR, Kwan KY, Lin SY, Vollrath MA, Amalfitano A, Cheung EL, Derfler BH, Duggan A, Geleoc GS, Gray PA, Hoffman MP, Rehm HL, Tamasauskas D, Zhang DS (2004) TRPA1 is a candidate for the mechanosensitive transduction channel of vertebrate hair cells. Nature 432:723–730
Nagata K, Duggan A, Kumar G, Garcia-Anoveros J (2005) Nociceptor and hair cell transducer properties of TRPA1, a channel for pain and hearing. J Neurosci 25:4052–4061
Balaban CD, Zhou J, Li HS (2003) Type 1 vanilloid receptor expression by mammalian inner ear ganglion cells. Hear Res 175:165–170
Ishibashi T, Takumida M, Akagi N, Hirakawa K, Anniko M (2008) Expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) 1, 2, 3, and 4 in mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 128:1286–1293
Takumida M, Ishibashi T, Hamamoto T, Hirakawa K, Anniko M (2009) Age-dependent changes in the expression of klotho protein, TRPV5 and TRPV6 in mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 129:1340–1350
Takumida M, Anniko M (2009) Expression of canonical transient receptor potential channel (TRPC) 1–7 in the mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 129:1351–1358
Tadros SF, Kim Y, Phan PA, Birnbaumer L, Housley GD (2010) TRPC3 ion channel subunit immunolocalization in the cochlea. Histochem Cell Biol 133:137–147
Takumida M, Ishibashi T, Hamamoto T, Hirakawa K, Anniko M (2008) Expression of transient receptor potential channel melastin (TRPM) 1–8 and TRPA1 (ankyrin) in mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 129:1050–1060
Takumida M, Anniko M (2010) Expression of transient receptor potential channel mucolipin (TRPML) and polycystine (TRPP) in the mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 130:196–203
Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ, Myers KS (2007) Acoustic injury and TRPV1 expression in the cochlear spiral ganglion. Int Tinnitus J 13:21–28
Kitahara T, Li HS, Balaban CD (2005) Changes in transient receptor potential cation channel superfamily V (TRPV) mRNA expression in the mouse inner ear ganglia after kanamycin challenge. Hear Res 201:132–144
Ishibashi T, Takumida M, Akagi N, Hirakawa K, Anniko M (2009) Changes in transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) 1, 2, 3 and 4 expression in mouse inner ear following gentamicin challenge. Acta Otolaryngol 129:116–126
Phan PA, Tadros SF, Kim Y, Birnbaumer L, Housley GD (2010) Developmental regulation of TRPC3 ion channel expression in the mouse cochlea. Histochem Cell Biol 133:437–448
Lee YM, Kim BJ, Kim HJ, Yang DK, Zhu MH, Lee KP, So I, Kim KW (2003) TRPC5 as a candidate for the nonselective cation channel activated by muscarinic stimulation in murine stomach. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G604–G616
Kim JY, Saffen D (2005) Activation of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors stimulates the formation of a multiprotein complex centered on TRPC6 channels. J Biol Chem 280:32035–32047
Alvarez J, Coulombe A, Cazorla O, Ugur M, Rauzier JM, Magyar J, Mathieu EL, Boulay G, Souto R, Bideaux P, Salazar G, Rassendren F, Lacampagne A, Fauconnier J, Vassort G (2008) ATP/UTP activate cation-permeable channels with TRPC3/7 properties in rat cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H21–H28
Oh EJ, Gover TD, Cordoba-Rodriguez R, Weinreich D (2003) Substance P evokes cation currents through TRP channels in HEK293 cells. J Neurophysiol 90:2069–2073
Beck B, Zholos A, Sydorenko V, Roudbaraki M, Lehen'kyi V, Bordat P, Prevarskaya N, Skryma R (2006) TRPC7 is a receptor-operated DAG-activated channel in human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 126:1982–1993
Milenkovic I, Rinke I, Witte M, Dietz B, Rubsamen R (2009) P2 receptor-mediated signaling in spherical bushy cells of the mammalian cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 102:1821–1833
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, K., Dulon, D. Purinergic signaling in cochleovestibular hair cells and afferent neurons. Purinergic Signalling 6, 201–209 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-010-9183-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-010-9183-x