Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to quantitatively analyze cellular uptake following local ultrasound (US)-mediated cell permeabilization.
Procedures
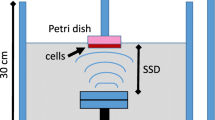
A 2 μM cell-impermeable dye Sytox Green was co-injected with 3 × 107 microbubbles in the presence of C6 rat glioblastoma cell monolayer in total volume of 10 ml. A 5.8-mm diameter mono-element US transducer was positioned at a distance of 8 mm to the Opticell® membrane. Acoustical pressure of pulsed US was varied from 0.62 MPa peak-to-peak (p-p) to 1.25 MPa p-p. Large field of view (FOV = 15 × 15 mm) 22 × 22 mosaic acquisitions were done under epifluorescence Leica DMR microscope and analyzed in Metamorph software to evaluate cell density as well as model drug uptake percentage.
Results
The size of acoustical field of the transducer closely matches the spatial pattern of the model drug internalized into the cells by US. Maximum of uptake percentage (42 ± 15 %) was found at 0.88 MPa p-p.
Conclusions
Spatial aspect of US-mediated model drug uptake has been quantitatively evaluated on adherent cells using robust 2D-mapping approach.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batrakova EV, Gendelman HE, Kabanov AV (2011) Cell-mediated drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 8(4):415–433. doi:10.1517/17425247.2011.559457
Zhao N, Qi J, Zeng Z et al (2012) Transfecting the hard-to-transfect lymphoma/leukemia cells using a simple cationic polymer nanocomplex. J Control Release 159(1):104–110. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.007
Connolly RJ, Lopez GA, Hoff AM, Jaroszeski MJ (2010) Characterization of plasma mediated molecular delivery to cells in vitro. Int J Pharm 389(1-2):53–57. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.01.016
Paganin-Gioanni A, Bellard E, Escoffre JM, Rols MP, Teissie J, Golzio M (2011) Direct visualization at the single-cell level of siRNA electrotransfer into cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(26):10443–10447. doi:10.1073/pnas.1103519108
Deckers R, Moonen CT (2010) Ultrasound triggered, image guided, local drug delivery. J Control Release 148(1):25–33. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.07.117
Quesson B, Laurent C, Maclair G et al (2011) Real-time volumetric MRI thermometry of focused ultrasound ablation in vivo: a feasibility study in pig liver and kidney. NMR Biomed 24(2):145–153. doi:10.1002/nbm.1563
Catane R, Beck A, Inbar Y et al (2007) MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MRgFUS) for the palliation of pain in patients with bone metastases—preliminary clinical experience. Ann Oncol 18(1):163–167. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl335
McDannold N, Tempany CM, Fennessy FM et al (2006) Uterine leiomyomas: MR imaging-based thermometry and thermal dosimetry during focused ultrasound thermal ablation. Radiology 240(1):263–272. doi:10.1148/radiol.2401050717
Huber PE, Jenne JW, Rastert R et al (2001) A new noninvasive approach in breast cancer therapy using magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound surgery. Cancer Res 61(23):8441–8447
Hynynen K, Pomeroy O, Smith DN et al (2001) MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound surgery of fibroadenomas in the breast: a feasibility study. Radiology 219(1):176–185
Voogt MJ, Trillaud H, Kim YS et al (2012) Volumetric feedback ablation of uterine fibroids using magnetic resonance-guided high intensity focused ultrasound therapy. Eur Radiol 22(2):411–417. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2262-8
Huber PE, Pfisterer P (2000) In vitro and in vivo transfection of plasmid DNA in the Dunning prostate tumor R3327-AT1 is enhanced by focused ultrasound. Gene Ther 7(17):1516–1525. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3301242
Rahim A, Taylor SL, Bush NL, ter Haar GR, Bamber JC, Porter CD (2006) Physical parameters affecting ultrasound/microbubble-mediated gene delivery efficiency in vitro. Ultrasound Med Biol 32(8):1269–1279. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.04.014
Sorace AG, Warram JM, Umphrey H, Hoyt K (2012) Microbubble-mediated ultrasonic techniques for improved chemotherapeutic delivery in cancer. J Drug Target 20(1):43–54. doi:10.3109/1061186X.2011.622397
Yudina A, Lepetit-Coiffé M, De Smet M, Langereis S, Grüll H, Moonen C (2012) In vivo temperature controlled ultrasound-mediated intracellular delivery of cell-impermeable compounds. J Control Release 161(1):90–97. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.04.018
Kinoshita M, Hynynen K (2005) A novel method for the intracellular delivery of siRNA using microbubble-enhanced focused ultrasound. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 335(2):393–399. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.101
Escoffre JM, Kaddur K, Rols MP, Bouakaz A (2010) In vitro gene transfer by electrosonoporation. Ultrasound Med Biol 36(10):1746–1755. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.06.019
Hallow DM, Mahajan AD, Prausnitz MR (2007) Ultrasonically targeted delivery into endothelial and smooth muscle cells in ex vivo arteries. J Control Release 118(3):285–293. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.12.029
Yudina A, Lepetit-Coiffe M, Moonen CT (2011) Evaluation of the temporal window for drug delivery following ultrasound-mediated membrane permeability enhancement. Mol Imaging Biol 13(2):239–249. doi:10.1007/s11307-010-0346-5
Taylor SL, Rahim AA, Bush NL, Bamber JC, Porter CD (2007) Targeted retroviral gene delivery using ultrasound. J Gene Med 9(2):77–87. doi:10.1002/jgm.1003
Greis C (2004) Technology overview: sonovue (Bracco, Milan). Eur Radiol 14(Suppl 8):P11–P15
Madelin G, Hosten B, Biateau C, Mougenot C, Franconi JM, Thiaudiere E (2005) Comparison of laser interferometry and radiation force method of measuring ultrasonic power. Ultrasonics 43(9):769–774. doi:10.1016/j.ultras.2005.04.001
Brenner JF, Dew BS, Horton JB, King T, Neurath PW, Selles WD (1976) An automated microscope for cytologic research a preliminary evaluation. J Histochem Cytochem 24(1):100–111
Santos A, Ortiz de Solorzano C, Vaquero JJ, Pena JM, Malpica N, del Pozo F (1997) Evaluation of autofocus functions in molecular cytogenetic analysis. J Microsc 188(Pt 3):264–272
Chow SK, Hakozaki H, Price DL et al (2006) Automated microscopy system for mosaic acquisition and processing. J Microsc 222(Pt 2):76–84. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2818.2006.01577.x
Flaberg E, Sabelstrom P, Strandh C, Szekely L (2008) Extended field laser confocal microscopy (EFLCM): combining automated Gigapixel image capture with in silico virtual microscopy. BMC Med Imaging 8:13. doi:10.1186/1471-2342-8-13
Jacobs MD, Donaldson PJ, Cannell MB, Soeller C (2003) Resolving morphology and antibody labeling over large distances in tissue sections. Microsc Res Tech 62(1):83–91. doi:10.1002/jemt.10360
Price DL, Chow SK, Maclean NA et al (2006) High-resolution large-scale mosaic imaging using multiphoton microscopy to characterize transgenic mouse models of human neurological disorders. Neuroinformatics 4(1):65–80. doi:10.1385/NI:4:1:65
Hsu WY, Poon WF, Sun YN (2008) Automatic seamless mosaicing of microscopic images: enhancing appearance with colour degradation compensation and wavelet-based blending. J Microsc 231(3):408–418. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2818.2008.02052.x
Muggia FM, Young CW, Carter SK (1982) Anthracycline antibiotics in cancer therapy. Nijhoff, The Hague, pp 1–567
Nitiss JL (2002) DNA topoisomerases in cancer chemotherapy: using enzymes to generate selective DNA damage. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3(10):1512–1516
Larkin JO, Casey GD, Tangney M et al (2008) Effective tumor treatment using optimized ultrasound-mediated delivery of bleomycin. Ultrasound Med Biol 34(3):406–413
Gerace L, Burke B (1988) Functional organization of the nuclear envelope. Annu Rev Cell Biol 4:335–374
Deckers R, Yudina A, Cardoit LC, Moonen CT (2011) A fluorescent chromophore TOTO-3 as a “smart probe” for the assessment of ultrasound-mediated local drug delivery in vivo. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 6(4):267–274. doi:10.1002/cmmi.426
Yudina A, de Smet M, Lepetit-Coiffe M et al (2011) Temperature-controlled US-mediated intracellular delivery of a fluorescent cell-impermeant model drug using temperature sensitive liposomes and cavitation. J Control Release 155(3):442–448
Lionetti V, Fittipaldi A, Agostini S et al (2009) Enhanced caveolae-mediated endocytosis by diagnostic ultrasound in vitro. Ultrasound Med Biol 35:136–143
Van Wamel A, Kooiman K, Harteveld M et al (2006) Vibrating microbubbles poking individual cells: drug transfer into cells via sonoporation. J Control Release 112:149–155
Schlicher RK, Radhakrishna H, Tolentino TP et al (2006) Mechanism of intracellular delivery by acoustic cavitation. Ultrasound Med Biol 32:915–924
Meijering BD, Juffermans LJ, van Wamel A et al (2009) Ultrasound and microbubbletargeted delivery of macromolecules is regulated by induction of endocytosis and pore formation. Circ Res 104:679–687
Rahim AA, Taylor SL, Bush NL, ter Haar GR, Bamber JC, Porter CD (2006) Spatial and acoustic pressure dependence of microbubble-mediated gene delivery targeted using focused ultrasound. J Gene Med 8(11):1347–1357. doi:10.1002/jgm.962
Graves EE, Ripoll J, Weissleder R, Ntziachristos V (2003) A submillimeter resolution fluorescence molecular imaging system for small animal imaging. Med Phys 30(5):901–911
Neil MA, Juskaitis R, Wilson T (1997) Method of obtaining optical sectioning by using structured light in a conventional microscope. Opt Lett 22(24):1905–1907
Breuninger T, Greger K, Stelzer EH (2007) Lateral modulation boosts image quality in single plane illumination fluorescence microscopy. Opt Lett 32(13):1938–1940
Mertz J, Kim J (2010) Scanning light-sheet microscopy in the whole mouse brain with HiLo background rejection. J Biomed Opt 15(1):016027. doi:10.1117/1.3324890
Vercauteren T, Perchant A, Malandain G, Pennec X, Ayache N (2006) Robust mosaicing with correction of motion distortions and tissue deformations for in vivo fibered microscopy. Med Image Anal 10(5):673–692. doi:10.1016/j.media.2006.06.006
O’Neill BE, Vo H, Angstadt M, Li KP, Quinn T, Frenkel V (2009) Pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound mediated nanoparticle delivery: mechanisms and efficacy in murine muscle. Ultrasound Med Biol 35(3):416–424. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.09.021
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by EC project SonoDrugs (FP7-ICT-2007-1-213706) and by the project ULTRAFITT (Foundation InNaBioSanté).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepetit-Coiffé, M., Yudina, A., Poujol, C. et al. Quantitative Evaluation of Ultrasound-Mediated Cellular Uptake of a Fluorescent Model Drug. Mol Imaging Biol 15, 523–533 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0615-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0615-1