Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the intensity of nocturnal hypoxemia associated with sleepiness in Peruvian men with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Methods
We carried out a secondary data analysis based on a study which includes patients with OSA who were seen in a private hospital in Lima, Peru from 2006 to 2012. We included male adults who had polysomnographic recordings and who answered the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESE). The intensity of nocturnal hypoxemia (oxygen saturation ≤90 %) was classified in four new categories: 0, <1, 1 to 10 and >10 % total sleep time with nocturnal hypoxemia (NH). When the ESE score was higher than 10, we used the definitions presence or absence of sleepiness. We used Poisson regression models with robust variance to estimate crude and adjusted prevalence ratios (PR) for association between sleepiness and NH.
Results
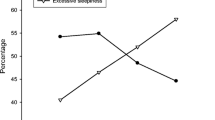
518 male patients with OSA were evaluated. Four hundred and fifty-two (87 %) patients had NH and 262 (51 %) had sleepiness. Of the 142 (27.4 %) patients who had >10 % total sleep time with NH, 98 (69.0 %) showed sleepiness and had a greater probability of sleepiness prevalence, with a crude PR of 1.82 (95 % CI 1.31–2.53). This association persisted in the multivariate models.
Conclusions
We found an association between NH and sleepiness. Only patients with the major intensity of NH (over 10 % of the total sleep time) had a greater probability of sleepiness. This suggests that sleepiness probably occurs after a chronic process and after overwhelming compensatory mechanisms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grupo Español de Sueño (2005) Definición y concepto, fisiopatología, clínica y exploración del SAHS. Arch Bronconeumol 41(Supl 4):12–29
Kapur VK (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea: diagnosis, epidemiology, and economics. Respir Care 55(9):1155–1167
Punjabi NM (2008) The epidemiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5(2):136–143
Hernandez Garcia C (2009) Sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome without excessive daytime sleepiness. Arch Bronconeumol 45(5):240–244
Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ (2002) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(9):1217–1239
Terán-Santos J, Jimenez-Gomez A, Cordero-Guevara J, Burgos–Santander CG (1999) The association between sleep apnea and the risk of traffic accidents. N Engl J Med 340:847–851
Jimenez-Correa U, Haro R, Gonzalez-Robles RO, Velazquez-Moctezuma J (2011) How is the Epworth Sleepiness Scale related with subjective sleep quality and polysomnographic features in patients with sleep-disordered breathing? Sleep Breath 15(3):513–518
Roure N, Gomez S, Mediano O, Duran J, Pena Mde L, Capote F, Teran J, Masa JF, Alonso ML, Corral J, Sanchez-Armengod A, Martinez C, Barcelo A, Gozal D, Marin JM, Barbe F (2008) Daytime sleepiness and polysomnography in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Med 9(7):727–731
Sun Y, Ning Y, Huang L, Lei F, Li Z, Zhou G, Tang X (2012) Polysomnographic characteristics of daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 16(2):375–381
Eiseman NA, Westover MB, Mietus JE, Thomas RJ, Bianchi MT (2012) Classification algorithms for predicting sleepiness and sleep apnea severity. J Sleep Res 21(1):101–112
Zhan G, Serrano F, Fenik P, Hsu R, Kong L, Pratico D, Klann E, Veasey SC (2005) NADPH oxidase mediates hypersomnolence and brain oxidative injury in a murine model of sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172(7):921–929
Heinonen IH, Kemppainen J, Kaskinoro K, Peltonen JE, Borra R, Lindroos M, Oikonen V, Nuutila P, Knuuti J, Boushel R, Kalliokoski KK (2010) Regulation of human skeletal muscle perfusion and its heterogeneity during exercise in moderate hypoxia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299(1):R72–R79. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00056.2010
Arnardottir ES, Mackiewicz M, Gislason T, Teff KL, Pack AI (2009) Molecular signatures of obstructive sleep apnea in adults: a review and perspective. Sleep 32(4):447–470
Colt HG, Haas H, Rich GB (1991) Hypoxemia vs sleep fragmentation as cause of excessive daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 100(6):1542–1548
Beebe DW, Gozal D (2002) Obstructive sleep apnea and the prefrontal cortex: towards a comprehensive model linking nocturnal upper airway obstruction to daytime cognitive and behavioral deficits. J Sleep Res 11(1):1–16
Yokoe T, Minoguchi K, Matsuo H, Oda N, Minoguchi H, Yoshino G, Hirano T, Adachi M (2003) Elevated levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome are decreased by nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Circulation 107(8):1129–1134
Lee SJ, Kang HW, Lee LH (2012) The relationship between the Epworth Sleepiness Scale and polysomnographic parameters in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(4):1143–1147
Saldias PF, Jorquera AJ, Diaz PO (2010) Predictive value of clinical features and nocturnal oximetry for the detection of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Rev Med Chil 138(8):941–950
Foster GE, Poulin MJ, Hanly PJ (2007) Intermittent hypoxia and vascular function: implications for obstructive sleep apnoea. Exp Physiol 92:51–65
Bausmer U, Gouveris H, Selivanova O, Goepel B, Mann W (2010) Correlation of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale with respiratory sleep parameters in patients with sleep-related breathing disorders and upper airway pathology. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267:1645–1648
Mediano O, Barcelo A, de la Pena M, Gozal D, Agusti A, Barbe F (2007) Daytime sleepiness and polysomnographic variables in sleep apnoea patients. Eur Respir J 30(1):110–113
Pértega Díaz S, Pita Fernández S (2006) Métodos no paramétricos para la comparación de dos muestras. Cad Aten Primaria 13:109–113
Rey de Castro J, Rosales-Mayor E (2011) Diferencias clínicas y polisomnográficas entre obesos y no obesos con síndrome de apneas-hipopneas del sueño. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publ 28(4):595–601
Rey de Castro J, Rosales-Mayor E (2013) Depressive symptoms in patients with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 17(2):615–620
Rey de Castro J, Rosales-Mayor E, Ferreyra-Pereyra J (2011) Using a generic measure of quality of life in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 15(4):729–735
Khawaja I, Olson E, van der Walt C, Bukartyk J, Somers V, Dierkhising R, Morgenthaler T (2010) Diagnostic accuracy of split-night polysomnograms. J Clin Sleep Med 6(4):357–362
Sanders M, Black J, Costantino J, Kern N, Studnicki K, Coates J (1991) Diagnosis of sleep-disordered breathing by half-night polysomnography. Am Rev Respir Dis 144(6):1256–1261
Rosales-Mayor E, Rey de Castro J, Huayanay L, Zagaceta K (2012) Validation and modification of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in Peruvian population. Sleep Breath 16(1):59–69
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14(6):540–545
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ (2003) Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 42(6):1206–1252
Lesack K, Naugler C (2011) An open-source software program for performing Bonferroni and related corrections for multiple comparisons. J Pathol Inf 2:52
Barros AJ, Hirakata VN (2003) Alternatives for logistic regression in cross-sectional studies: an empirical comparison of models that directly estimate the prevalence ratio. BMC Med Res Methodol 3:21
Kitagawa G, Konishi S (2010) Bias and variance reduction techniques for bootstrap information criteria. Ann Inst Stat Math 62:209–234
Almendros I, Farre R, Planas AM, Torres M, Bonsignore MR, Navajas D, Montserrat JM (2011) Tissue oxygenation in brain, muscle, and fat in a rat model of sleep apnea: differential effect of obstructive apneas and intermittent hypoxia. Sleep 34(8):1127–1133
Veasey SC, Davis CW, Fenik P, Zhan G, Hsu YJ, Pratico D, Gow A (2004) Long-term intermittent hypoxia in mice: protracted hypersomnolence with oxidative injury to sleep-wake brain regions. Sleep 27(2):194–201
Schwartz AR, Patil SP, Laffan AM, Polotsky V, Schneider H, Smith PL (2008) Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5(2):185–192
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Dr. Kim Hoffman for her recommendations on the final version of this manuscript. This study was developed as part of the activities of the Masters in Clinical Epidemiology offered jointly by the Cayetano Heredia University and the US Naval Medical Research Unit Six (NAMRU-6), Peru. This Master of Science (MSc) programme is sponsored by 2D43 TW007393 “Peru Epidemiology Research Training Consortium”, awarded to NAMRU-6 by the Fogarty International Center of the US National Institutes of Health. The first author (CHS) prepared this paper to meet the graduation requirements of this programme.
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate that there are no financial conflicts of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huamaní, C., Rey de Castro, J. & Mezones-Holguín, E. Sleepiness and nocturnal hypoxemia in Peruvian men with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 18, 467–473 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-013-0907-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-013-0907-3