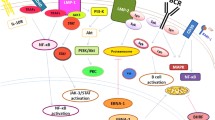
Abstract
While Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) was initially discovered and characterized as an oncogenic virus in B cell neoplasms, it also plays a complex and multifaceted role in T/NK cell lymphomas. In B cell lymphomas, EBV-encoded proteins have been shown to directly promote immortalization and proliferation through stimulation of the NF-κB pathway and increased expression of anti-apoptotic genes. In the context of mature T/NK lymphomas (MTNKL), with the possible exception on extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma (ENKTL), the virus likely plays a more diverse and nuanced role. EBV has been shown to shape the tumor microenvironment by promoting Th2-skewed T cell responses and by increasing the expression of the immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1. The type of cell infected, the amount of plasma EBV DNA, and the degree of viral lytic replication have all been proposed to have prognostic value in T/NK cell lymphomas. Latency patterns of EBV infection have been defined using EBV-infected B cell models and have not been definitively established in T/NK cell lymphomas. Identifying the expression profile of EBV lytic proteins could allow for individualized therapy with the use of antiviral medications. More work needs to be done to determine whether EBV-associated MTNKL have distinct biological and clinical features, which can be leveraged for risk stratification, disease monitoring, and therapeutic purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Connor OA, Bhagat G, Ganapathi K, Pedersen MB, D’Amore F, Radeski D, et al. Changing the paradigms of treatment in peripheral T-cell lymphoma: from biology to clinical practice. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(20):5240–54.
Dupuis J, Emile JF, Mounier N, Gisselbrecht C, Martin-Garcia N, Petrella T, et al. Prognostic significance of Epstein-Barr virus in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified: a Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte (GELA) study. Blood. 2006;108(13):4163–9.
Kanakry JA, Li H, Gellert LL, Lemas MV, Hsieh WS, Hong F, et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA predicts outcome in advanced Hodgkin lymphoma: correlative analysis from a large North American cooperative group trial. Blood. 2013;121(18):3547–53.
Park S, Lee J, Ko YH, Han A, Jun HJ, Lee SC, et al. The impact of Epstein-Barr virus status on clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2007;110(3):972–8.
Ito Y, Kimura H, Maeda Y, Hashimoto C, Ishida F, Izutsu K, et al. Pretreatment EBV-DNA copy number is predictive of response and toxicities to SMILE chemotherapy for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(15):4183–90.
Ferrajoli A, Ivan C, Ciccone M, Shimizu M, Kita Y, Ohtsuka M, et al. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs are expressed in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and correlate with overall survival. EBioMed. 2015;2(6):572–82.
Fox CP, Burns D, Parker AN, Peggs KS, Harvey CM, Natarajan S, et al. EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder following in vivo T-cell-depleted allogeneic transplantation: clinical features, viral load correlates and prognostic factors in the rituximab era. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(2):280–6.
Kimura H, Ito Y, Suzuki R, Nishiyama Y. Measuring Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) load: the significance and application for each EBV-associated disease. Rev Med Virol. 2008;18(5):305–19.
Bollard CM, Gottschalk S, Torrano V, Diouf O, Ku S, Hazrat Y, et al. Sustained complete responses in patients with lymphoma receiving autologous cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane proteins. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(8):798–808.
Alinari L, Mahasenan KV, Yan F, Karkhanis V, Chung JH, Smith EM, et al. Selective inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 blocks initiation and maintenance of B-cell transformation. Blood. 2015;125(16):2530–43.
Patton JT, Lustberg ME, Lozanski G, Garman SL, Towns WH, Drohan CM, et al. The translation inhibitor silvestrol exhibits direct anti-tumor activity while preserving innate and adaptive immunity against EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disease. Oncotarget. 2015;6(5):2693–708.
Nayar U, Lu P, Goldstein RL, Vider J, Ballon G, Rodina A, et al. Targeting the Hsp90-associated viral oncoproteome in gammaherpesvirus-associated malignancies. Blood. 2013;122(16):2837–47.
Fox CP, Shannon-Lowe C, Rowe M. Deciphering the role of Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of T and NK cell lymphoproliferations. Herpesviridae. 2011;2:8. doi:10.1186/2042-4280-2.
George LC, Rowe M, Fox CP. Epstein-barr virus and the pathogenesis of T and NK lymphoma: a mystery unsolved. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2012;7(4):276–84.
Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr VM. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet. 1964;1(7335):702–3.
Paul JR, Bunnell WW. The presence of heterophile antibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med Sci. 1932;183:90.
Henle G, Henle W, Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt’s tumor-associated herpes-type virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968;59(1):94–101.
Henle G, Henle W, Clifford P, et al. Antibodies to EB virus in Burkitt’s lymphoma and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969;43:1147–57.
Pattengale PK, Smith RW, Gerber P. Selective transformation of B lymphocytes by E.B. virus. Lancet. 1973;2(7820):93–4.
Steel CM, Morten JE, Foster E. The cytogenetics of human B lymphoid malignancy: studies in Burkitt’s lymphoma and Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines. IARC Sci Publ. 1985;60:265–92.
Nilsson K, Klein G, Henle W, Henle G. The establishment of lymphoblastoid lines from adult and fetal human lymphoid tissue and its dependence on EBV. Int J Cancer. 1971;8(3):443–50.
Rowe M, Young LS, Crocker J, Stokes H, Henderson S, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in the SCID mouse model: implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-positive lymphomas in man. J Exp Med. 1991;173(1):147–58.
Baiocchi RA, Ross ME, Tan JC, Chou CC, Sullivan L, Haldar S, et al. Lymphomagenesis in the SCID-hu mouse involves abundant production of human interleukin-10. Blood. 1995;85(4):1063–74.
Baiocchi RA, Caligiuri MA. Low-dose interleukin 2 prevents the development of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in scid/scid mice reconstituted i.p. with EBV-seropositive human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(12):5577–81.
Baiocchi RA, Ward JS, Carrodeguas L, Eisenbeis CF, Peng R, Roychowdhury S, et al. GM-CSF and IL-2 induce specific cellular immunity and provide protection against Epstein-Barr virus lymphoproliferative disorder. J Clin Invest. 2001;108(6):887–94.
Dierksheide JE, Baiocchi RA, Ferketich AK, Roychowdhury S, Pelletier RP, Eisenbeis CF, et al. IFN-gamma gene polymorphisms associate with development of EBV+ lymphoproliferative disease in hu PBL-SCID mice. Blood. 2005;105(4):1558–65.
Thomas RV, McAulay K, Higgins C, Wilkie G, Crawford DH. Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) polymorphism in posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease. Blood. 2005;106(4):1502–3. author reply 1503.
Baer R, Bankier AT, Biggin MD, et al. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein–Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984;310:207–11.
Miller G, Shope T, Lisco H, Stitt D, Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972;69(2):383–7.
Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Epstein Barr virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 2655–701.
Raab-Traub N, Dambaugh T, Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus VIII: B95-8, the previous prototype, is an unusual deletion derivative. Cell. 1980;22(1 Pt 1):257–67.
Dambaugh T, Hennessy K, Chamnankit L, Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81(23):7632–6.
Rowe M, Young LS, Cadwallader K, Petti L, Kieff E, Rickinson AB. Distinction between Epstein-Barr virus type A (EBNA 2A) and type B (EBNA 2B) isolates extends to the EBNA 3 family of nuclear proteins. J Virol. 1989;63(3):1031–9.
Palser AL, Grayson NE, White RE, Corton C, Correia S, Ba Abdullah MM, et al. Genome diversity of Epstein-Barr virus from multiple tumor types and normal infection. J Virol. 2015;89(10):5222–37.
Chang CM, Yu KJ, Mbulaiteye SM, Hildesheim A, Bhatia K. The extent of genetic diversity of Epstein-Barr virus and its geographic and disease patterns: a need for reappraisal. Virus Res. 2009;143(2):209–21.
Raab-Traub N, Flynn K. The structure of the termini of the Epstein-Barr virus as a marker of clonal cellular proliferation. Cell. 1986;47(6):883–9.
Dyson PJ, Farrell PJ. Chromatin structure of Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1985;66(Pt 9):1931–40.
Lieberman PM. Keeping it quiet: chromatin control of gammaherpesvirus latency. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11(12):863–75.
Woellmer A, Hammerschmidt W. Epstein-Barr virus and host cell methylation: regulation of latency, replication and virus reactivation. Curr Opin Virol. 2013;3(3):260–5.
Murata T, Tsurumi T. Switching of EBV cycles between latent and lytic states. Rev Med Virol. 2014;24(3):142–53.
Ghosh SK, Perrine SP, Williams RM, Faller DV. Histone deacetylase inhibitors are potent inducers of gene expression in latent EBV and sensitize lymphoma cells to nucleoside antiviral agents. Blood. 2012;119(4):1008–17.
Ritchie D, Piekarz RL, Blombery P, Karai LJ, Pittaluga S, Jaffe ES, et al. Reactivation of DNA viruses in association with histone deacetylase inhibitor therapy: a case series report. Haematologica. 2009;94(11):1618–22.
Roychowdhury S, Baiocchi RA, Vourganti S, Bhatt D, Blaser BW, Freud AG, et al. Selective efficacy of depsipeptide in a xenograft model of Epstein-Barr virus-positive lymphoproliferative disorder. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96(19):1447–57.
Chan AT, Tao Q, Robertson KD, Flinn IW, Mann RB, Klencke B, et al. Azacitidine induces demethylation of the Epstein-Barr virus genome in tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(8):1373–81.
Murata T, Kondo Y, Sugimoto A, et al. Epigenetic histone modifications of Epstein Barr Virus BZLF1 promoter during latency and reactivation in Raji cells. J Virol. 2012;86:4752–61.
Ramasubramanyan S, Osborn K, Flower K, Sinclair AJ. Dynamic chromatin environment of key lytic cycle regulatory regions of the Epstein Barr Virus genome. J Virol. 2012;86:1809–19.
Smeltzer JP, Viswanatha DS, Habermann TM, Patnaik MM. Secondary Epstein-Barr virus associated lymphoproliferative disorder developing in a patient with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma on vorinostat. Am J Hematol. 2012;87(9):927–8.
Erter J, Alinari L, Darabi K, Gurcan M, Garzon R, Marcucci G, et al. New targets of therapy in T-cell lymphomas. Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11(4):482–93.
Perrine SP, Hermine O, Small T, Suarez F, O’Reilly R, Boulad F, et al. A phase 1/2 trial of arginine butyrate and ganciclovir in patients with Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoid malignancies. Blood. 2007;109(6):2571–8.
Roychowdhury S, Peng R, Baiocchi RA, Bhatt D, Vourganti S, Grecula J, et al. Experimental treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63(5):965–71.
Bayraktar UD, Diaz LA, Ashlock B, Toomey N, Cabral L, Bayraktar S, et al. Zidovudine-based lytic-inducing chemotherapy for Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014;55(4):786–94.
Niller HH, Szenthe K, Minarovits J. Epstein-Barr virus-host cell interactions: an epigenetic dialog? Front Genet. 2014;5:367.
Arvey A, Tempera I, Tsai K, Chen HS, Tikhmyanova N, Klichinsky M, et al. An atlas of the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptome and epigenome reveals host-virus regulatory interactions. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12(2):233–45.
Zhou H, Schmidt SC, Jiang S, Willox B, Bernhardt K, Liang J, et al. Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein super-enhancers control B cell growth. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17(2):205–16.
Kaneda A, Matsusaka K, Aburatani H, Fukayama M. Epstein-Barr virus infection as an epigenetic driver of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2012;72(14):3445–50.
Paschos K, Smith P, Anderton E, Middeldorp JM, White RE, Allday MJ. Epstein-barr virus latency in B cells leads to epigenetic repression and CpG methylation of the tumour suppressor gene Bim. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(6), e1000492.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2014;513(7517):202–9.
Küçük C, Hu X, Jiang B, Klinkebiel D, Geng H, Gong Q, et al. Global promoter methylation analysis reveals novel candidate tumor suppressor genes in natural killer cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(7):1699–711.
Fingeroth JD, Weis JJ, Tedder TF, Strominger JL, Biro PA, Fearon DT. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81(14):4510–4.
Nemerow GR, Wolfert R, McNaughton MW, Cooper NR. Identification and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus receptor on human B lymphocytes and its relationship to the C3d complement receptor (CR2). J Virol. 1985;55:347–51.
Li Q, Spriggs MK, Kovats S, Turk SM, Comeau MR, Nepom B, et al. Epstein-Barr virus uses HLA class II as a cofactor for infection of B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1997;71(6):4657–62.
Babcock GJ, Decker LL, Volk M, et al. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity. 1998;9:395–404.
Kurth J, Spieker T, Wustrow J, Strickler GJ, Hansmann LM, Rajewsky K, et al. EBV-infected B cells in infectious mononucleosis: viral strategies for spreading in the B cell compartment and establishing latency. Immunity. 2000;13(4):485–95.
Kieff E, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology, vol. 2. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 2603–54.
Kang MS, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent genes. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47, e131.
Price AM, Luftig MA. Dynamic Epstein-Barr virus gene expression on the path to B-cell transformation. Adv Virus Res. 2014;88:279–313.
Longnecker R, Kieff E, Cohen JI. Replication and Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2005. p. 1898–959.
Price AM, Luftig MA. To be or not IIb: a multi-step process for Epstein-Barr virus latency establishment and consequences for B cell tumorigenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11(3), e1004656.
Takacs M, Banati F, Koroknai A, Segesdi J, Salamon D, Wolf H, et al. Epigenetic regulation of latent Epstein-Barr virus promoters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1799(3–4):228–35.
Tempera I, Lieberman PM. Epigenetic regulation of EBV persistence and oncogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;26:22–9.
Roughan JE, Thorley-Lawson DA. The intersection of Epstein-Barr virus with the germinal center. J Virol. 2009;83(8):3968–76.
Küppers R. B cells under influence: transformation of B cells by Epstein-Barr virus. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(10):801–11.
Bienemann K, Borkhardt A, Klapper W, Oschlies I. High incidence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma-like B-cell lymphoproliferations with EBV latency profile 2 in children with interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase deficiency. Histopathology. 2015;24.
Lara J, Cohen M, De Matteo E, Aversa L, Preciado MV, Chabay P. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) association and latency profile in pediatric Burkitt’s lymphoma: experience of a single institution in Argentina. J Med Virol. 2014;86(5):845–50.
Gonzalez-Farre B, Rovira J, Martinez D, Valera A, Garcia-Herrera A, Marcos MA, et al. In vivo intratumoral Epstein-Barr virus replication is associated with XBP1 activation and early-onset post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders with prognostic implications. Mod Pathol. 2014;27(12):1599–611.
Ok CY, Li L, Xu-Monette ZY, Visco C, Tzankov A, Manyam GC, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of epstein-barr virus infection in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(9):2338–49.
Cohen M, De Matteo E, Narbaitz M, Carreño FA, Preciado MV, Chabay PA. Epstein-Barr virus presence in pediatric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reveals a particular association and latency patterns: analysis of viral role in tumor microenvironment. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(7):1572–80.
Montes-Moreno S, Odqvist L, Diaz-Perez JA, Lopez AB, de Villambrosía SG, Mazorra F, et al. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly is an aggressive post-germinal center B-cell neoplasm characterized by prominent nuclear factor-kB activation. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(7):968–82.
Nicolae A, Pittaluga S, Abdullah S, Steinberg SM, Pham TA, Davies-Hill T, et al. EBV-positive large B-cell lymphomas in young patients: a nodal lymphoma with evidence for a tolerogenic immune environment. Blood. 2015;126(7):863–72.
Menon MP, Pittaluga S, Jaffe ES. The histological and biological spectrum of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the World Health Organization classification. Cancer J. 2012;18(5):411–20.
Ok CY, Papathomas TG, Medeiros LJ, Young KH. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Blood. 2013;122(3):328–40.
Bollard CM, Rooney CM, Heslop HE. T-cell therapy in the treatment of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(9):510–9.
Khatri VP, Baiocchi RA, Peng R, Oberkircher AR, Dolce JM, Ward PM, et al. Endogenous CD8+ T cell expansion during regression of monoclonal EBV-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. J Immunol. 1999;163(1):500–6.
Porcu P, Eisenbeis CF, Pelletier RP, Davies EA, Baiocchi RA, Roychowdhury S, et al. Successful treatment of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) following renal allografting is associated with sustained CD8(+) T-cell restoration. Blood. 2002;100(7):2341–8.
Kroll J, Li S, Levi M, Weinberg A. Lytic and latent EBV gene expression in transplant recipients with and without post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. J Clin Virol. 2011;52(3):231–5.
Oertel SH, Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel MW, Jonas S, Riess HB. Identification of early antigen BZLF1/ZEBRA protein of Epstein-Barr virus can predict the effectiveness of antiviral treatment in patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Br J Haematol. 2002;118(4):1120–3.
Hartlage AS, Liu T, Patton JT, Garman SL, Zhang X, Kurt H, et al. The Epstein-Barr virus lytic protein BZLF1 as a candidate target antigen for vaccine development. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3(7):787–94.
Ma SD, Hegde S, Young KH, Sullivan R, Rajesh D, Zhou Y, et al. A new model of Epstein-Barr virus infection reveals an important role for early lytic viral protein expression in the development of lymphomas. J Virol. 2011;85(1):165–77.
Hsu M, Wu SY, Chang SS, Su IJ, Tsai CH, Lai SJ, et al. Epstein-Barr virus lytic transactivator Zta enhances chemotactic activity through induction of interleukin-8 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 2008;82(7):3679–88.
Mahot S, Sergeant A, Drouet E, Gruffat H. A novel function for the Epstein-Barr virus transcription factor EB1/Zta: induction of transcription of the hIL-10 gene. J Gen Virol. 2003;84(Pt 4):965–74.
Tsai SC, Lin SJ, Chen PW, Luo WY, Yeh TH, Wang HW, et al. EBV Zta protein induces the expression of interleukin-13, promoting the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Blood. 2009;114(1):109–18.
Grömminger S, Mautner J, Bornkamm GW. Burkitt lymphoma: the role of Epstein-Barr virus revisited. Br J Haematol. 2012;156(6):719–29.
Thorley-Lawson DA, Allday MJ. The curious case of the tumour virus: 50 years of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6(12):913–24.
Kelly GL, Long HM, Stylianou J, Thomas WA, Leese A, Bell AI, et al. An Epstein-Barr virus anti-apoptotic protein constitutively expressed in transformed cells and implicated in burkitt lymphomagenesis: the Wp/BHRF1 link. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(3), e1000341.
Navari M, Fuligni F, Laginestra MA, Etebari M, Ambrosio MR, Sapienza MR, et al. Molecular signature of Epstein Barr virus-positive Burkitt lymphoma and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder suggest different roles for Epstein Barr virus. Front Microbiol. 2014;5:728.
Kanemitsu N, Isobe Y, Masuda A, Momose S, Higashi M, Tamaru J, et al. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in extranodal NK/T-cell Lymphoma, nasal type (ENKL): differences in biologic and clinical behaviors of LMP1-positive and -negative ENKL. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(8):2164–72.
Tsao SW, Tsang CM, To KF, Lo KW. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in epithelial malignancies. J Pathol. 2015;235(2):323–33.
Fox CP, Haigh TA, Taylor GS, Long HM, Lee SP, Shannon-Lowe C, et al. A novel latent membrane 2 transcript expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-positive NK- and T-cell lymphoproliferative disease encodes a target for cellular immunotherapy. Blood. 2010;116(19):3695–704.
Delecluse HJ, Marafioti T, Hummel M, Dallenbach F, Anagnostopoulos I, Stein H. Disappearance of the Epstein-Barr virus in a relapse of Hodgkin’s disease. J Pathol. 1997;182(4):475–9.
Green MR, Rodig S, Juszczynski P, Ouyang J, Sinha P, O’Donnell E, et al. Constitutive AP-1 activity and EBV infection induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin lymphomas and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: implications for targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(6):1611–8.
Hudnall SD, Ge Y, Wei L, et al. Distribution and phenotype of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in human pharyngeal tonsils. Modern Pathol: Off J US Can Acad Pathol, Inc. 2005;18:519–27.
Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel M, Kreschel C, et al. Morphology, immunophenotype, and distribution of latently and/or productively Epstein–Barr virus-infected cells in acute infectious mononucleosis: implications for the interindividual infection route of Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1995;85:744–50.
Trempat P, Tabiasco J, Andre P, et al. Evidence for early infection of non-neoplastic natural killer cells by Epstein–Barr virus. J Virol. 2002;76:11139–42.
Tabiasco J, Vercellone A, Meggetto F, et al. Acquisition of viral receptor by NK cells through immunological synapse. J Immunol. 2003;170:5993–8.
Jones JF, Shurin S, Abramowsky C, Tubbs RR, Sciotto CG, Wahl R, et al. T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA in patients with chronic Epstein-Barr virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(12):733–41.
Kikuta H, Taguchi Y, Tomizawa K, et al. Epstein–Barr virus genome-positive T lymphocytes in a boy with chronic active EBV infection associated with Kawasaki-like disease. Nature. 1988;333:455–7.
Imai S, Sugiura M, Oikawa O, Koizumi S, Hirao M, Kimura H, et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-carrying and -expressing T-cell lines established from severe chronic active EBV infection. Blood. 1996;87(4):1446–57.
Kanegane H, Bhatia K, Gutierrez M, Kaneda H, Wada T, Yachie A, et al. A syndrome of peripheral blood T-cell infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) followed by EBV-positive T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1998;91(6):2085–91.
Ishihara S, Okada S, Wakiguchi H, Kurashige T, Hirai K, Kawa-Ha K. Clonal lymphoproliferation following chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection and hypersensitivity to mosquito bites. Am J Hematol. 1997;54(4):276–81.
Kawa-Ha K, Ishihara S, Ninomiya T, Yumura-Yagi K, Hara J, Murayama F, et al. CD3-negative lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA. J Clin Invest. 1989;84(1):51–5.
Kimura H, Hoshino Y, Kanegane H, Tsuge I, Okamura T, Kawa K, et al. Clinical and virologic characteristics of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Blood. 2001;98(2):280–6.
Kasahara Y, Yachie A, Takei K, Kanegane C, Okada K, Ohta K, et al. Differential cellular targets of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection between acute EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and chronic active EBV infection. Blood. 2001;98(6):1882–8.
Kimura H, Hoshino Y, Hara S, Sugaya N, Kawada J, Shibata Y, et al. Differences between T cell-type and natural killer cell-type chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infect Dis. 2005;191(4):531–9.
Cohen JI, Jaffe ES, Dale JK, et al. Characterization and treatment of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease: a 28-year experience in the United States. Blood. 2011;117:5835–49.
Zhou XG, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Yan QH, Pallesen G. High frequency of Epstein-Barr virus in Chinese peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Histopathology. 1994;24:115–22.
Lee SH, Su IJ, Chen RL, Lin KS, Lin DT, Chuu WM. A pathologic study of childhood lymphoma in Taiwan with special reference to peripheral T-cell lymphoma and the association with Epstein-Barr viral infection. Cancer. 1991;68:1954–62.
Ohshima K, Kikuchi M, Eguchi F, et al. Analysis of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in lymphoid malignancy using Southern blotting, polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;59:383–90.
Teramoto N, Sarker AB, Tonoyama Y, et al. Epstein-Barr virus infection in the neoplastic and nonneoplastic cells of lymphoid malignancies. Cancer. 1996;77:2339–47.
Huh J, Cho K, Heo DS, Kim JE, Kim CW. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in Korean peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 1999;60:205–14.
Hirose Y, Masaki Y, Sawaki T, et al. Association of Epstein-Barr virus with human immunodeficiency virus-negative peripheral T-cell lymphomas in Japan. Eur J Haematol. 2006;76:109–18.
Su IJ, Lin KH, Chen CJ, Tien HF, Hsieh HC, Lin DT, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated peripheral T-cell lymphoma of activated CD8 phenotype. Cancer. 1990;66(12):2557–62.
Cho EY, Kim KH, Kim WS, Yoo KH, Koo HH, Ko YH. The spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease in Korea: incidence of disease entities by age groups. J Korean Med Sci. 2008;23(2):185–92.
Yoon SO, Suh C, Lee DH, Chi HS, Park CJ, Jang SS, et al. Distribution of lymphoid neoplasms in the Republic of Korea: analysis of 5318 cases according to the World Health Organization classification. Am J Hematol. 2010;85(10):760–4.
Au WY, Ma SY, Chim CS, Choy C, Loong F, Lie AK, et al. Clinicopathologic features and treatment outcome of mature T-cell and natural killer-cell lymphomas diagnosed according to the World Health Organization classification scheme: a single center experience of 10 years. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(2):206–14.
Arber DA, Weiss LM, Albujar PF, Chen YY, Jaffe ES. Nasal lymphomas in Peru. High incidence of T-cell immunophenotype and Epstein-Barr virus infection. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17(4):392–9.
Barrionuevo C, Zaharia M, Martinez MT, Taxa L, Misad O, Moscol A, et al. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: study of clinicopathologic and prognosis factors in a series of 78 cases from Peru. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2007;15(1):38–44.
Coleman CB, Wohlford EM, Smith NA, et al. Epstein-Barr virus type 2 latently infects T cells, inducing an atypical activation characterized by expression of lymphotactic cytokines. J Virol. 2015;89:2301–12.
Asano N, Kato S, Nakamura S. Epstein-Barr virus-associated natural killer/T-cell lymphomas. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2013;26:15–21.
Chan JKC, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ferry JA, Peh SC. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2007. p. 285–8.
Harabuchi Y, Yamanaka N, Kataura A, Imai S, Kinoshita T, Mizuno F, et al. Epstein-Barr virus in nasal T-cell lymphomas in patients with lethal midline granuloma. Lancet. 1990;335(8682):128–30.
Kanavaros P, Lescs MC, Briere J, Divine M, Galateau F, Joab I, et al. Nasal T-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic entity associated with peculiar phenotype and with Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1993;81(10):2688–95.
Jaffe ES. Nasal and nasal-type T/NK cell lymphoma: a unique form of lymphoma associated with the Epstein-Barr virus. Histopathology. 1995;27(6):581–3.
Chan JK, Yip TT, Tsang WY, Ng CS, Lau WH, Poon YF, et al. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral RNA in malignant lymphomas of the upper aerodigestive tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18(9):938–46.
Tao Q, Ho FC, Loke SL, Srivastava G. Epstein-Barr virus is localized in the tumour cells of nasal lymphomas of NK, T or B cell type. Int J Cancer. 1995;60(3):315–20.
Minarovits J, Hu LF, Imai S, Harabuchi Y, Kataura A, Minarovits-Kormuta S, et al. Clonality, expression and methylation patterns of the Epstein-Barr virus genomes in lethal midline granulomas classified as peripheral angiocentric T cell lymphomas. J Gen Virol. 1994;75(Pt 1):77–84.
Hsieh PP et al. EBV viral load in tumor tissue is an important prognostic indicator for nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128(4):579–84.
Suzuki R, Yamaguchi M, Izutsu K, Yamamoto G, Takada K, Harabuchi Y, et al. Prospective measurement of Epstein-Barr virus-DNA in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood. 2011;118(23):6018–22.
Chan JKC, Jaffe E, Ralfkiaer E, Ko Y-H. Aggressive NK-cell leukaemia. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2007. p. 276–7.
Akashi K, Mizuno S. Epstein-Barr virus-infected natural killer cell leukemia. Leukemia lymphoma. 2000;40:57–66.
Ruskova A, Thula R, Chan G. Aggressive natural killer-cell leukemia: report of five cases and review of the literature. Leukemia lymphoma. 2004;45:2427–38.
Iwatsuki K, Xu Z, Takata M, Iguchi M, Ohtsuka M, Akiba H, et al. The association of latent Epstein-Barr virus infection with hydroa vacciniforme. Br J Dermatol. 1999;140(4):715–21.
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ridaura C, Nagl F, et al. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma: a chronic EBV+ lymphoproliferative disorder with risk to develop a systemic lymphoma. Blood. 2013;122:3101–10.
Barrionuevo C, Anderson VM, Zevallos-Giampietri E, et al. Hydroa-like cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic and molecular genetic study of 16 pediatric cases from Peru. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2002;10:7–14.
Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Barrionuevo C, Garcia J, et al. EBV-associated cutaneous NK/T-cell lymphoma: review of a series of 14 cases from Peru in children and young adults. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:1773–82.
d’Amore F, Johansen P, Houmand A, et al. Epstein-Barr virus genome in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas occurring in immunocompetent patients: highest prevalence in nonlymphoblastic T-cell lymphoma and correlation with a poor prognosis. Danish Lymphoma Study Group, LYFO. Blood. 1996;87:1045–55.
de Bruin PC, Jiwa M, Oudejans JJ, et al. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus in extranodal T-cell lymphomas: differences in relation to site. Blood. 1994;83:1612–8.
De Bruin PC, Jiwa NM, Van der Valk P, Van Heerde P, Gordijn R, Ossenkoppele GJ, et al. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus nucleic acid sequences and protein in nodal T-cell lymphomas: relation between latent membrane protein-1 positivity and clinical course. Histopathology. 1993;23(6):509–18.
Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Pallesen G. A survey of Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in sporadic non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in a subset of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1992;140:1315–25.
Herreman A, Dierickx D, Morscio J, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders of T-cell origin: single-center series of nine cases and meta-analysis of 147 reported cases. Leuk lymphoma. 2013;54:2190–9.
Korbjuhn P, Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel M, et al. Frequent latent Epstein-Barr virus infection of neoplastic T cells and bystander B cells in human immunodeficiency virus-negative European peripheral pleomorphic T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 1993;82:217–23.
Ott G, Ott MM, Feller AC, Seidl S, Muller-Hermelink HK. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in different T-cell lymphoma entities in a European population. Int J Cancer. 1992;51:562–7.
Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel M, Finn T, et al. Heterogeneous Epstein-Barr virus infection patterns in peripheral T-cell lymphoma of angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy type. Blood. 1992;80:1804–12.
Ahearne MJ, Allchin RL, Fox CP, Wagner SD. Follicular helper T-cells: expanding roles in T-cell lymphoma and targets for treatment. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(3):326–35.
Federico M, Rudiger T, Bellei M, Nathwani BN, Luminari S, Coiffier B, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: analysis of the international peripheral T-cell lymphoma project. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(2):240–6.
Willenbrock K, Bräuninger A, Hansmann ML. Frequent occurrence of B-cell lymphomas in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in early cases. Br J Haematol. 2007;138(6):733–9.
Zettl A, Lee SS, Rüdiger T, Starostik P, Marino M, Kirchner T, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in angloimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;117(3):368–79.
Xu Y, McKenna RW, Hoang MP, Collins RH, Kroft SH. Composite angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;118(6):848–54. Review.
Bräuninger A, Spieker T, Willenbrock K, Gaulard P, Wacker HH, Rajewsky K, et al. Survival and clonal expansion of mutating “forbidden” (immunoglobulin receptor-deficient) epstein-barr virus-infected b cells in angioimmunoblastic t cell lymphoma. J Exp Med. 2001;194(7):927–40.
Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Vose JM, McKeithan T, Kucuk C, et al. Molecular signatures to improve diagnosis in peripheral T-cell lymphoma and prognostication in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2010;115(5):1026–36.
Tan BT, Warnke RA, Arber DA. The frequency of B- and T-cell gene rearrangements and Epstein-Barr virus in T-cell lymphomas: a comparison between angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified with and without associated B-cell proliferations. J Mol Diagn. 2006;8(4):466–75.
Weisenburger DD, Savage KJ, Harris NL, Gascoyne RD, Jaffe ES, MacLennan KA, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: a report of 340 cases from the International Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Project. Blood. 2011;117(12):3402–8.
Chen YP, Jones D, Chen TY, Chang KC. Epstein-Barr virus present in T cells or B cells shows differential effects on hemophagocytic symptoms associated with outcome in T-cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014;55(9):2038–47.
Ha SY, Sung J, Ju H, Karube K, Kim SJ, Kim WS, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-positive nodal peripheral T cell lymphomas: clinicopathologic and gene expression profiling study. Pathol Res Pract. 2013;209(7):448–54.
Nicolae A, Pittaluga S, Venkataraman G, Vijnovich-Baron A, Xi L, Raffeld M, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas of follicular T-helper cell derivation with Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells of B-cell lineage: both EBV-positive and EBV-negative variants exist. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37(6):816–26.
Kato S, Takahashi E, Asano N, Tanaka T, Megahed N, Kinoshita T, et al. Nodal cytotoxic molecule (CM)-positive Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL): a clinicopathological study of 26 cases. Histopathology. 2012;61(2):186–99.
Haverkos B, Huang Y, Gru AA, Baiocchi RA, Porcu P. Elevated levels of plasma EBV DNA at diagnosis predict a poor prognosis in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2015;15 Suppl 2:S67. abstr. 912.
Boussiotis VA, Chatterjee P, Li L. Biochemical signaling of PD-1 on T cells and its functional implications. Cancer J. 2014;20(4):265–71.
Ribas A. Adaptive immune resistance: how cancer protects from immune attack. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(9):915–9.
Fang W, Zhang J, Hong S, Zhan J, Chen N, Qin T, et al. EBV-driven LMP1 and IFN-γ up-regulate PD-L1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: implications for oncotargeted therapy. Oncotarget. 2014;5(23):12189–202.
Chen BJ, Chapuy B, Ouyang J, Sun HH, Roemer MG, Xu ML, et al. PD-L1 expression is characteristic of a subset of aggressive B-cell lymphomas and virus-associated malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(13):3462–73.
Siemer D, Kurth J, Lang S, Lehnerdt G, Stanelle J, Küppers R. EBV transformation overrides gene expression patterns of B cell differentiation stages. Mol Immunol. 2008;45(11):3133–41.
Lin TC et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART20-5p inhibits T-bet translation with secondary suppression of p53 in invasive nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(5):1865–75.
Iqbal J, Wright G, Wang C, Rosenwald A, Gascoyne RD, Weisenburger DD, et al. Gene expression signatures delineate biological and prognostic subgroups in peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2014;123(19):2915–23.
Glaser SL, Clarke CA, Chang ET, Yang J, Gomez SL, Keegan TH. Hodgkin lymphoma incidence in California Hispanics: influence of nativity and tumor Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25(6):709–25.
Peh SC. Host ethnicity influences non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma subtype frequency and Epstein-Barr virus association rate: the experience of a multi-ethnic patient population in Malaysia. Histopathology. 2001;38(5):458–65.
Zallio F, Primon V, Tamiazzo S, Pini M, Baraldi A, Corsetti MT, et al. Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in allogeneic stem cell transplantation is highly related to cytomegalovirus reactivation. Clin Transplant. 2013;27(4):E491–7.
Rickinson AB. Co-infections, inflammation and oncogenesis: future directions for EBV research. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;26:99–115.
Tsai MH, Raykova A, Klinke O, Bernhardt K, Gärtner K, Leung CS, et al. Spontaneous lytic replication and epitheliotropism define an Epstein-Barr virus strain found in carcinomas. Cell Rep. 2013;5(2):458–70.
Draborg AH, Duus K, Houen G. Epstein-Barr virus in systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:535738.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of Topical Collection on T-Cell and Other Lymphoproliferative Malignancies
A. A. Gru and B. H. Haverkos contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gru, A.A., Haverkos, B.H., Freud, A.G. et al. The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) in T Cell and NK Cell Lymphomas: Time for a Reassessment. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 10, 456–467 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11899-015-0292-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11899-015-0292-z