Abstract
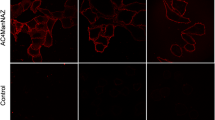
The terminal monosaccharide of glycoconjugates on a eukaryotic cell surface is typically a sialic acid (Neu5Ac). Increased sialylation usually indicates progression and poor prognosis of most carcinomas. Here, we utilize two human mammary epithelial cell lines, HB4A (breast normal cells) and T47D (breast cancer cells), as a model system to demonstrate differential surface glycans when treated with sialic acid under nutrient deprivation. Under a starved condition, sialic acid treatment of both cells resulted in increased activities of α2→3/6 sialyltransferases as demonstrated by solid phase assay using lectin binding. However, a very strong Maackia amurensis agglutinin I (MAL-I) staining on the membrane of sialic acid-treated T47D cells was observed, indicating an increase of Neu5Acα2→3Gal on the cell surface. To our knowledge, this is a first report showing the utility of lectins, particularly MAL-I, as a means to discriminate between normal and cancer cells after sialic acid treatment under nutrient deprivation. This method is sensitive and allows selective detection of glycan sialylation on a cancer cell surface.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varki, A. (2007). Nature, 446, 1023–1029.
Ohtsubo, K., & Marth, J. D. (2006). Cell, 126, 855–867.
Service, R. F. (2012). Science, 338, 321–323.
Varki, A., Cummings, R. D., Esko, J. D., Freeze, H. H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, C. R., et al. (2009). Essential of glycobiology (2nd ed.). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Du, J., Meledeo, M. A., Wang, Z., Khanna, H. S., Paruchuri, V. D. P., & Yarema, K. J. (2009). Glycobiology, 12, 1382–1401.
Agard, N. J., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2009). Accounts of Chemical Research, 42, 788–797.
Mariño, K., Bones, J., Kattla, J. J., & Rudd, P. M. (2010). Nature Chemical Biology, 6, 713–723.
Prescher, J. A., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2006). Cell, 126, 851–854.
Boyce, M., & Bertozzi C. R. (2011). Nature Methods, 8, 638–642.
Paulson, J. C., & Rademacher, C. (2009). Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 16, 1121–1122.
Dube, D. H., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2005). Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 4, 477–488.
Ghaderi, D., Zhang, M., Hurtado-Ziola, N., & Varki, A. (2012). Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, 28, 147–75.
Lau, K. S., Partridge, E. A., Grigorian, A., Silvescu, C. I., Reinhold, V. N., Demetriou, M., et al. (2007). Cell, 129, 123–134.
DeBerardinis, R. J., & Thompson, C. B. (2012). Cell, 148, 1132–1144.
Chandrasekaran, E. V., Xue, J., Xia, J., Locke, R. D., Patil, S. A., Neelamegham, S., et al. (2012). Journal of Proteome Research, 11, 2609–2618.
Ramessur, K. T., Greenwell, P., Nash, R., & Dwek, M. V. (2010). British Journal of Biomedical Science, 67, 189–96.
Ghaderi, D., Taylor, R. E., Karavani, V. P., Diaz, S., & Varki, A. (2010). Nature Biotechnology, 28, 863–867.
Qiani, J., Zhu, C., Tang, S., Shen, A., Ai, J., Li, J., et al. (2009). Acta Pharmaceutica Sinic, 30, 1039–1045.
Recchi, M. A., Lepers, A. H., Marer, Y. B., Verbert, A., & Delannoy, P. (1998). Glycoconjugate Journal, 15, 19–27.
Vander Heiden, M. G. (2011). Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 10, 671–684.
Liu, C., Lei, T., Kosuke, I., Matsue, T., Tao, N., & Li, C.-Z. (2012). Chemical Communications, 48, 10389–10391.
Meany, D. L., & Chan, D. W. (2011). Clinical Proteomics, 8, 1–14.
Paulson, J. C., Blixt, O., & Collins, B. E. (2006). Nature Chemical Biology, 2, 238–248.
Picco, G., Julien, S., Brockhausen, I., Beatson, R., Antonopoulos, A., Haslam, S., et al. (2010). Glycobiology, 20, 1241–1250.
Julien, S., Adriaenssens, E., Ottenberg, K., Furlan, A., Courtand, G., Vercoutter-Edouart, A. S., et al. (2006). Glycobiology, 16, 54–64.
Varki, N. M., & Varki, A. (2007). Laboratory Investigation, 87, 851–857.
Geisler, C., & Jarvis, D. L. (2011). Glycobiology, 21, 988–993.
Schwefel, D., Maierhofer, C., Beck, J. G., Seeberger, S., Diederichs, K., Moller, H. M., et al. (2010). Journal of the American Chemical Society, 25, 8704–8719.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant 0068GF for Scientific Research on Priority Areas Cancer from the Ministry of Science and Education (Science and Technology Program Kazakhstan) to L.B.D. and grants R15ES021079-01 and R41CA141970-01A2 from the National Institute of Health (USA) to C.-Z.L. and H.A., respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 298 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badr, H.A., ElSayed, A.I., Ahmed, H. et al. Preferential Lectin Binding of Cancer Cells upon Sialic Acid Treatment Under Nutrient Deprivation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171, 963–974 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0409-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0409-6