Abstract
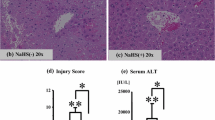
Thioacetamide (TAA) administration is widely used for induction of liver cirrhosis in rats, where reactive oxygen radicals (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) participate in development of liver damage. Cardiac dysfunction is an important complication of liver cirrhosis, but the role of ROS or NO in cardiac abnormalities during liver cirrhosis is not well understood. This was investigated in animals after TAA-induced liver cirrhosis and temporal changes in oxidative stress, NO and mitochondrial function in the heart evaluated. TAA induced elevation in cardiac levels of nitrate before development of frank liver cirrhosis, without gross histological alterations. This was accompanied by an early induction of P38 MAP kinase, which is influenced by ROS and plays an important signaling role for induction of iNOS. Increased nitrotyrosine, protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation in the heart and cardiac mitochondria, suggestive of oxidative stress, also preceded frank liver cirrhosis. However, compromised cardiac mitochondrial function with a decrease in respiratory control ratio and increased mitochondrial swelling was seen later, when cirrhosis was evident. In conclusion, TAA induces elevations in ROS and NO in the heart in parallel to early liver damage. This leads to later development of functional deficits in cardiac mitochondria after development of liver cirrhosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, T., Shankar, K., Ronis, M. J., & Mehendale, H. M. (2000). Potentiation of thioacetamide liver injury in diabetic rats is due to induced CYP2E1. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 294, 473–479.
Ambrose, A. M., De, E. F., & Rather, L. J. (1949). Toxicity of thioacetamide in rats. The Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 31, 158–161.
Fitzhugh, O. G., & Nelson, A. A. (1948). Liver tumors in rats fed thiourea or thioacetamide. Science, 108, 626–628.
Rather, L. J. (1951). Experimental alteration of nuclear and cytoplasmic components of the liver cell with thioacetamide. I. Early onset and reversibility of volume changes of the nucleolus, nucleus and cytoplasm. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital, 88, 38–58.
Al-Hamoudi, W. K. (2010). Cardiovascular changes in cirrhosis: Pathogenesis and clinical implications. Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology, 16, 145–153.
Fattouh, A. M., El-Shabrawi, M. H., Mahmoud, E. H., & Ahmed, W. O. (2016). Evaluation of cardiac functions of cirrhotic children using serum brain natriuretic peptide and tissue Doppler imaging. Annals of Pediatric Cardiology, 9, 22–28.
Milic, S., Lulic, D., Stimac, D., Ruzic, A., & Zaputovic, L. (2016). Cardiac manifestations in alcoholic liver disease. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 92, 235–239.
Naschitz, J. E., Slobodin, G., Lewis, R. J., Zuckerman, E., & Yeshurun, D. (2000). Heart diseases affecting the liver and liver diseases affecting the heart. American Heart Journal, 140, 111–120.
Such, J., Frances, R., & Perez-Mateo, M. (2002). Nitric oxide in patients with cirrhosis and bacterial infections. Metabolic Brain Disease, 17, 303–309.
Liu, H., Ma, Z., & Lee, S. S. (2000). Contribution of nitric oxide to the pathogenesis of cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in bile duct-ligated rats. Gastroenterology, 118, 937–944.
Garcia-Estan, J., Ortiz, M. C., & Lee, S. S. (2002). Nitric oxide and renal and cardiac dysfunction in cirrhosis. Clinical Science (Lond), 102, 213–222.
Sumida, Y., Niki, E., Naito, Y., & Yoshikawa, T. (2013). Involvement of free radicals and oxidative stress in NAFLD/NASH. Free Radical Research, 47, 869–880.
Ramachandran, A., Prabhu, R., Thomas, S., Reddy, J. B., Pulimood, A., & Balasubramanian, K. A. (2002). Intestinal mucosal alterations in experimental cirrhosis in the rat: Role of oxygen free radicals. Hepatology, 35, 622–629.
Natarajan, S. K., Ramamoorthy, P., Thomas, S., Basivireddy, J., Kang, G., Ramachandran, A., et al. (2006). Intestinal mucosal alterations in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis: Changes in glycosylation and luminal bacteria. Hepatology, 43, 837–846.
Natarajan, S. K., Basivireddy, J., Ramachandran, A., Thomas, S., Ramamoorthy, P., Pulimood, A. B., et al. (2006). Renal damage in experimentally-induced cirrhosis in rats: Role of oxygen free radicals. Hepatology, 43, 1248–1256.
Yang, Y. Y., Liu, H., Nam, S. W., Kunos, G., & Lee, S. S. (2010). Mechanisms of TNFalpha-induced cardiac dysfunction in cholestatic bile duct-ligated mice: Interaction between TNFα and endocannabinoids. Journal of Hepatology, 53, 298–306.
Ljubuncic, P., Tanne, Z., & Bomzon, A. (2000). Evidence of a systemic phenomenon for oxidative stress in cholestatic liver disease. Gut, 47, 710–716.
Hori, N., Okanoue, T., Sawa, Y., Mori, T., & Kashima, K. (1993). Hemodynamic characterization in experimental liver cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide administration. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 38, 2195–2202.
Sastry, K. V., Moudgal, R. P., Mohan, J., Tyagi, J. S., & Rao, G. S. (2002). Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper-cadmium alloy. Analytical Biochemistry, 306, 79–82.
Ohkawa, H., Ohishi, N., & Yagi, K. (1979). Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Analytical Biochemistry, 95, 351–358.
Chan, H. W., & Levett, G. (1977). Autoxidation of methyl linoleate. Separation and analysis of isomeric mixtures of methyl linoleate hydroperoxides and methyl hydroxylinoleates. Lipids, 12, 99–104.
Sohal, R. S., Agarwal, S., Dubey, A., & Orr, W. C. (1993). Protein oxidative damage is associated with life expectancy of houseflies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 90, 7255–7259.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Takeyama, N., Matsuo, N., & Tanaka, T. (1993). Oxidative damage to mitochondria is mediated by the Ca2+-dependent inner-membrane permeability transition. Biochemical Journal, 294(Pt 3), 719–725.
Madesh, M., & Balasubramanian, K. A. (1997). Nitric oxide inhibits enterocyte mitochondrial phospholipase D. FEBS Letters, 413, 269–272.
Zhao, T. C., Taher, M. M., Valerie, K. C., & Kukreja, R. C. (2001). p38 Triggers late preconditioning elicited by anisomycin in heart: Involvement of NF-κB and iNOS. Circulation Research, 89, 915–922.
Clerk, A., Fuller, S. J., Michael, A., & Sugden, P. H. (1998). Stimulation of “stress-regulated” mitogen-activated protein kinases (stress-activated protein kinases/c-Jun N-terminal kinases and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinases) in perfused rat hearts by oxidative and other stresses. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 7228–7234.
van Obbergh, L., Vallieres, Y., & Blaise, G. (1996). Cardiac modifications occurring in the ascitic rat with biliary cirrhosis are nitric oxide related. Journal of Hepatology, 24, 747–752.
Sarma, D., Hajovsky, H., Koen, Y. M., Galeva, N. A., Williams, T. D., Staudinger, J. L., & Hanzlik, R. P. (2012). Covalent modification of lipids and proteins in rat hepatocytes and in vitro by thioacetamide metabolites. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 25, 1868–1877.
Metze, K., & Brandt, G. (1981). Copper and zinc content of liver, heart, skeletal muscle, and brain, in acute thioacetamide intoxication of rats. Hepato-Gastroenterology, 28, 99–101.
Liao, P., Georgakopoulos, D., Kovacs, A., Zheng, M., Lerner, D., Pu, H., et al. (2001). The in vivo role of p38 MAP kinases in cardiac remodeling and restrictive cardiomyopathy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 98, 12283–12288.
Shimizu, M., Ogura, K., Mizoguchi, I., Chiba, Y., Higuchi, K., Ohtsuka, H., et al. (2012). IL-27 promotes nitric oxide production induced by LPS through STAT1, NF-κB and MAPKs. Immunobiology, 218, 628–634.
Shiva, S., Moellering, D., Ramachandran, A., Levonen, A. L., Landar, A., Venkatraman, A., et al. (2004). Redox signalling: From nitric oxide to oxidized lipids. Biochemical Society Symposia, 71, 107–120.
Shafaroodi, H., Ebrahimi, F., Moezi, L., Hashemi, M., Doostar, Y., Ghasemi, M., & Dehpour, A. R. (2010). Cholestasis induces apoptosis in mice cardiac cells: The possible role of nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Liver International, 30, 898–905.
Beckman, J. S., & Koppenol, W. H. (1996). Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. American Journal of Physiology, 271, C1424–C1437.
Mani, A. R., Ippolito, S., Ollosson, R., & Moore, K. P. (2006). Nitration of cardiac proteins is associated with abnormal cardiac chronotropic responses in rats with biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology, 43, 847–856.
Dai, D. F., Johnson, S. C., Villarin, J. J., Chin, M. T., Nieves-Cintron, M., Chen, T., et al. (2011). Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and Galphaq overexpression-induced heart failure. Circulation Research, 108, 837–846.
Montaigne, D., Marechal, X., Coisne, A., Debry, N., Modine, T., Fayad, G., et al. (2014). Myocardial contractile dysfunction is associated with impaired mitochondrial function and dynamics in type 2 diabetic but not in obese patients. Circulation, 130, 554–564.
Sharov, V. G., Todor, A. V., Silverman, N., Goldstein, S., & Sabbah, H. N. (2000). Abnormal mitochondrial respiration in failed human myocardium. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 32, 2361–2367.
Pham, T., Loiselle, D., Power, A., & Hickey, A. J. (2014). Mitochondrial inefficiencies and anoxic ATP hydrolysis capacities in diabetic rat heart. American Journal of Physiology: Cell Physiology, 307, C499–C507.
Lemasters, J. J., Theruvath, T. P., Zhong, Z., & Nieminen, A. L. (2009). Mitochondrial calcium and the permeability transition in cell death. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1787, 1395–1401.
Kajander, O. A., Karhunen, P. J., & Jacobs, H. T. (2002). The relationship between somatic mtDNA rearrangements, human heart disease and aging. Human Molecular Genetics, 11, 317–324.
Zavodnik, I. B., Dremza, I. K., Cheshchevik, V. T., Lapshina, E. A., & Zamaraewa, M. (2013). Oxidative damage of rat liver mitochondria during exposure to t-butyl hydroperoxide. Role of Ca2+ ions in oxidative processes. Life Sciences, 92, 1110–1117.
Murphy, M. P., Echtay, K. S., Blaikie, F. H., Asin-Cayuela, J., Cocheme, H. M., Green, K., et al. (2003). Superoxide activates uncoupling proteins by generating carbon-centered radicals and initiating lipid peroxidation: Studies using a mitochondria-targeted spin trap derived from alpha-phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 48534–48545.
Ide, T., Tsutsui, H., Hayashidani, S., Kang, D., Suematsu, N., Nakamura, K., et al. (2001). Mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction associated with oxidative stress in failing hearts after myocardial infarction. Circulation Research, 88, 529–535.
Acknowledgments
G. J. A. was funded by a Senior Research Fellowship from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India. Funding from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirtharaj, G.J., Natarajan, S.K., Pulimood, A. et al. Role of Oxygen Free Radicals, Nitric Oxide and Mitochondria in Mediating Cardiac Alterations During Liver Cirrhosis Induced by Thioacetamide. Cardiovasc Toxicol 17, 175–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-016-9371-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-016-9371-1