Abstract
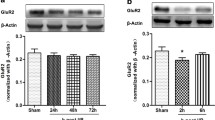
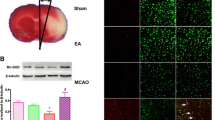
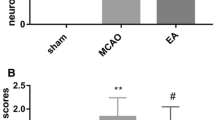
We have previously shown that electroacupuncture (EA) pretreatment produces neuroprotective effects, which were mediated through an endocannabinoid signal transduction mechanism. Herein, we have studied the possible contribution of the phosphorylated form of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) in EA pretreatment-induced neuroprotection via the cannabinoid CB1 receptor (CB1R). Focal transient cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Phosphorylation of GSK-3β at Ser-9 [p-GSK-3β (Ser-9)] was evaluated in the penumbra tissue following reperfusion. Infarct size and neurological score were assessed in the presence of either PI3K inhibitors or a GSK-3β inhibitor 72 h after reperfusion. Cellular apoptosis was evidenced by TUNEL staining and determination of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio 24 h after reperfusion. The present study showed that EA pretreatment increased p-GSK-3β(Ser-9) 2 h after reperfusion in the ipsilateral penumbra. Augmented phosphorylation of GSK-3β induced similar neuroprotective effects as did EA pretreatment. By contrast, inhibition of PI3K dampened the levels of p-GSK-3β(Ser-9), and reversed not only the neuroprotective effect but also the anti-apoptotic effect following EA pretreatment. Regulation of GSK-3β by EA pretreatment was abolished following treatment with a CB1R antagonist and CB1R knockdown, whereas two CB1R agonists enhanced the phosphorylation of GSK-3β. Therefore we conclude that EA pretreatment protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through CB1R-mediated phosphorylation of GSK-3β.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM et al (2012) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 125:e2–e220
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Nie H, Xiong L, Lao N, Chen S, Xu N, Zhu Z (2006) Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning induces tolerance against spinal cord ischemia by upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in rabbits. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:666–674
Assad AR, Delou JM, Fonseca LM et al (2009) The role of KATP channels on propofol preconditioning in a cellular model of renal ischemia–reperfusion. Anesth Analg 109:1486–1492
Raphael J, Zuo Z, Abedat S, Beeri R, Gozal Y (2008) Isoflurane preconditioning decreases myocardial infarction in rabbits via up-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 that is mediated by mammalian target of rapamycin. Anesthesiology 108:415–425
Xiong L, Lu Z, Hou L et al (2003) Pretreatment with repeated electroacupuncture attenuates transient focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats. Chin Med J (Engl) 116:108–111
Shukla S, Torossian A, Duann JR, Leung A (2011) The analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on acute thermal pain perception—a central neural correlate study with fMRI. Mol Pain 7:45
Liu W, Mukherjee M, Sun C, Liu H, McPeak LK (2008) Electroacupuncture may help motor recovery in chronic stroke survivors: a pilot study. J Rehabil Res Dev 45:587–595
Wang Q, Peng Y, Chen S et al (2009) Pretreatment with electroacupuncture induces rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia through regulation of endocannabinoid system. Stroke 40:2157–2164
Du J, Wang Q, Hu B et al (2010) Involvement of ERK 1/2 activation in electroacupuncture pretreatment via cannabinoid CB1 receptor in rats. Brain Res 1360:1–7
Wang Q, Li X, Chen Y et al (2011) Activation of epsilon protein kinase C-mediated anti-apoptosis is involved in rapid tolerance induced by electroacupuncture pretreatment through cannabinoid receptor type 1. Stroke 42:389–396
Ozaita A, Puighermanal E, Maldonado R (2007) Regulation of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 pathway by cannabinoids in the brain. J Neurochem 102:1105–1114
Doble BW, Woodgett JR (2003) GSK-3: tricks of the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci 116:1175–1186
Kockeritz L, Doble B, Patel S, Woodgett JR (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3—an overview of an over-achieving protein kinase. Curr Drug Targets 7:1377–1388
Dash PK, Johnson D, Clark J et al (2011) Involvement of the glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling pathway in TBI pathology and neurocognitive outcome. PLoS One 6:e24648
Simao F, Matte A, Pagnussat AS, Netto CA, Salbego CG (2012) Resveratrol prevents CA1 neurons against ischemic injury by parallel modulation of both GSK-3beta and CREB through PI3-K/Akt pathways. Eur J Neurosci 36:2899–2905
Wang JK, Yu LN, Zhang FJ et al (2010) Postconditioning with sevoflurane protects against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt pathway. Brain Res 1357:142–151
Zhao H, Shimohata T, Wang JQ et al (2005) Akt contributes to neuroprotection by hypothermia against cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci 25:9794–9806
Collino M, Thiemermann C, Mastrocola R et al (2008) Treatment with the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibitor, TDZD-8, affects transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat hippocampus. Shock 30:299–307
Zoppi S, Perez NB, Madrigal JL, Manzanares J, Leza JC, Garcia-Bueno B (2011) Regulatory role of cannabinoid receptor 1 in stress-induced excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation. Neuropsychopharmacol 36:805–818
Wang Q, Wang F, Li X et al (2012) Electroacupuncture pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury through alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 release in rats. J Neuroinflammation 9:24
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ (1995) Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke 26(627–634):635
Hu B, Wang Q, Chen Y et al (2010) Neuroprotective effect of WIN 55,212-2 pretreatment against focal cerebral ischemia through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 645:102–107
Zhao ZQ (2008) Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 85:355–375
Chao LF, Zhang AL, Liu HE, Cheng MH, Lam HB, Lo SK (2009) The efficacy of acupoint stimulation for the management of therapy-related adverse events in patients with breast cancer: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118:255–267
Wang Q, Xiong L, Chen S, Liu Y, Zhu X (2005) Rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia in rats is induced by preconditioning with electroacupuncture: window of protection and the role of adenosine. Neurosci Lett 381:158–162
Xiong LZ, Yang J, Wang Q, Lu ZH (2007) Involvement of delta- and mu-opioid receptors in the delayed cerebral ischemic tolerance induced by repeated electroacupuncture preconditioning in rats. Chin Med J (Engl) 120:394–399
Salcedo-Tello P, Ortiz-Matamoros A, Arias C (2011) GSK3 function in the brain during development, neuronal plasticity, and neurodegeneration. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:189728
Song B, Lai B, Zheng Z et al (2010) Inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3 by CaMKII couples depolarization to neuronal survival. J Biol Chem 285:41122–41134
Wang Y, Feng W, Xue W et al (2009) Inactivation of GSK-3beta by metallothionein prevents diabetes-related changes in cardiac energy metabolism, inflammation, nitrosative damage, and remodeling. Diabetes 58:1391–1402
Rahman S, Li J, Bopassa JC et al (2011) Phosphorylation of GSK-3beta mediates intralipid-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Anesthesiology 115:242–253
Zhai P, Sciarretta S, Galeotti J, Volpe M, Sadoshima J (2011) Differential roles of GSK-3beta during myocardial ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion. Circ Res 109:502–511
Krafft PR, Altay O, Rolland WB et al (2012) alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonism confers neuroprotection through GSK-3beta inhibition in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 43:844–850
Kanninen K, White AR, Koistinaho J, Malm T (2011) Targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3beta for therapeutic benefit against oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: involvement of the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:985085
Wang MJ, Huang HY, Chen WF, Chang HF, Kuo JS (2010) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inactivation inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in microglia by modulating nuclear factor kappaB and MLK3/JNK signaling cascades. J Neuroinflammation 7:99
Li J, Xuan W, Yan R et al (2011) Remote preconditioning provides potent cardioprotection via PI3K/Akt activation and is associated with nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin. Clin Sci (Lond) 120:451–462
Guo W, Murthy AC, Zhang L et al (2012) Inhibition of GSK3beta improves hippocampus-dependent learning and rescues neurogenesis in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 21:681–691
Lin D, Li G, Zuo Z (2011) Volatile anesthetic post-treatment induces protection via inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in human neuron-like cells. Neuroscience 179:73–79
Yin W, Signore AP, Iwai M et al (2007) Preconditioning suppresses inflammation in neonatal hypoxic ischemia via Akt activation. Stroke 38:1017–1024
Collino M, Aragno M, Castiglia S et al (2009) Insulin reduces cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the hippocampus of diabetic rats: a role for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Diabetes 58:235–242
Sasaki T, Han F, Shioda N et al (2006) Lithium-induced activation of Akt and CaM kinase II contributes to its neuroprotective action in a rat microsphere embolism model. Brain Res 1108:98–106
Miura T, Tanno M, Sato T (2010) Mitochondrial kinase signalling pathways in myocardial protection from ischaemia/reperfusion-induced necrosis. Cardiovasc Res 88:7–15
Brooks C, Wei Q, Feng L et al (2007) Bak regulates mitochondrial morphology and pathology during apoptosis by interacting with mitofusins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11649–11654
Wang Z, Havasi A, Gall J et al (2010) GSK3beta promotes apoptosis after renal ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:284–294
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 30930091), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (grant 2010 CXTD01), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 81072888, 81035375), and the Overseas, Hong Kong and Macao Scholars Collaborated Researching Fund (grant 81228022).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Haidong Wei, Xi Yao, and Lifang Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Yao, X., Yang, L. et al. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Is Involved in Electroacupuncture Pretreatment via the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor in Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol 49, 326–336 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8524-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8524-5