Abstract
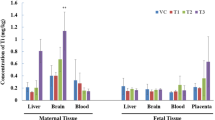
Recent toxicity studies of zinc oxide nanoparticles by oral administration showed relatively low toxicity, which may be resulted from low bioavailability. So, the intrinsic toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles needs to be evaluated in the target organs by intravenous injection for full systemic concentration of the administered dosage. Although the exposure chance of injection route is low compared to oral and/or inhalation route, it is important to see the toxicity with different exposure routes to get better risk management tool. In this study, the effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on dams and fetuses were investigated in rats after intravenous injection (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg) from gestation day 6 to 20. Two of 20 dams in the 20 mg/kg treatment group died during the treatment period. Hematological examination and serum biochemistry showed dose-dependent toxicity in treated dams. Histopathological analysis of treated dams revealed multifocal mixed cell infiltration and thrombosis in lung, tubular dilation in kidneys, and extramedullary hemopoiesis in liver. Total dead fetuses (post-implantation loss) were increased and the body weight of fetus was decreased in the 20 mg/kg treatment group. Statistical differences in corpora lutea, resorption, placental weight, morphological alterations including external, visceral and skeletal malformations were not observed in treated groups. Based on the data, lowest observed adverse effect level of injection route was suggested to be 5 mg/kg in dams and no observed adverse effect level was suggested to be 10 mg/kg in fetal developmental toxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzouz I, Trabelsi H, Hanini A, Ferchichi S, Tebourbi O, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2014) Interaction between nanoparticles generated by zinc chloride treatment and oxidative responses in rat liver. Int J Nanomed 9:223–229
Chahoud I, Buschman J, Clark R, Druga A, Falke H, Faqi A, Hansen E, Heinrich-Hirsch B, Hellwig J, Lingk W, Parkinson M, Paumgartten F, Pfeil R, Platzek T, Scialli AR, Seed J, Stahlmann R, Elbrich B, Wu X, Yasuda M, Younes M, Solecki R (1999) Classification terms in developmental toxicology: need for harmonization. Reprod Toxicol 13:77–82
Choi J, Kim H, Kim P, Jo E, Kim HM, Lee MY, Jin SM, Park K (2015) Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats treated by two different routes: single intravenous injection and single oral administration. J Toxicol Environ Health Park A 78:226–243
Chu M, Wu Q, Yang H, Yuan R, Hou S, Yang Y, Zou Y, Xu S, Xu K, Ji A, Sheng L (2010) Transfer of quantum dots from pregnant mice to pups across the placental barrier. Small 6(5):670–678
Davalos D, Akassoglou K (2012) Fibrinogen as a key regulator of inflammation in disease. Semin Immunopathol 34(1):43–62
Heng BC, Zhao Z, Xiong S, Ng KW, Boey FW, Loo JS (2010) Toxicity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) is accentuated by oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1762–1766
Ho M, Wu KY, Chein HM, Chen LC, Cheng TJ (2011) Pulmonary toxicity of inhaled nanoscale and fine zinc oxide particles: mass and surface area as an exposure metric. Inhal Toxicol 23:947–956
Hong JS, Park MK, Kim MS, Lim JH, Park GJ, Maeng EH, Shin JH, Kim YR, Kim MK, Lee JK, Park JA, Kim JC, Shin HC (2014a) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on dams and embryo-fetal development in rats. Int J Nanomed 9(Suppl 2):145–157
Hong JS, Park MK, Kim MS, Lim JH, Park GJ, Maeng EH, Shin JH, Kim MK, Jeong J, Park JA, Kim JC, Shin HC (2014b) Prenatal development toxicity study of zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats. Int J Nanomed 9(suppl 2):159–171
Inouye M (1976) Differential staining of cartilage and bone in fetal mouse skeleton by alcian blue and alizarin red. Congenit Anom 16:171–173
Jo E, Seo G, Kwon JT, Lee M, Lee BC, Eom I, Kim P, Choi K (2013) Exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles affects reproductive development and biodistribution in offspring rats. J Toxicol Sci 38(4):525–530
Kaluza J, Madej D, Brzozowska A (2013) The effect of iron and zinc supplementation and discontinuation of this practice on iron and zinc level in tissues in rats fed deficient diets. J Trace Elem Med Biol 27(4):334–338
Kim YR, Park JI, Lee EJ, Park SH, Seong NW, Kim JH, Kim GY, Meang EH, Hong JS, Kim SH, Koh SB, Kim MS, Kim CS, Kim SK, Son SW, Seo YR, Kang BH, Han BS, An SS, Yun HI, Kim MK (2014) Toxicity of 100 nm zinc oxide nanoparticles: a report of 90 days repeated oral administration in Sprague Dawley rats. Int J Nanomed 9(Suppl 2):109–126
Lee Y, Choi J, Kim P, Choi K, Kim S, Shon W, Park K (2012) A transfer of silver nanoparticles from pregnant rat to offspring. Toxicol Res 28(3):139–141
Ludi B, Niederberger M (2013) Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Chemical mechanisms and classical and non-classical crystallization. Dalton Trans 42:12554–12568
Ma H, Williams PL, Diamond SA (2013) Ecotoxicity of manufactured ZnO nanoparticles-a review. Environ Pollut 172:76–85
Makris SL, Solomon HM, Clark R, Shiota K, Barbellion S, Buschmann J, Ema M, Fujiwara M, Grote K, Hazelden KP, Hew KW, Horimoto M, Ooshima Y, Parkinson M, Wise LD (2009) Terminology of developmental abnormalities in common laboratory mammals (version 2). Birth Defects Res B 86:227–327
Nemmar A, Albarwani S, Beegam S, Yuvaraju P, Yasin J, Attoub S, Ali BH (2014) Amorphous silica nanoparticles impair vascular homeostasis and induce systemic inflammation. Int J Nanomed 9:2779–2789
Nishimura K (1974) Microdissection method for detecting thoracic visceral malformations in mouse and rat fetuses. Cong Anom 14:23–40
OECD (2001) OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4. Test No. 414, Prenatal Development Toxicity Study. doi: 10.1787/9789264070820-en
Osmond MJ, McCall MJ (2010) Zinc oxide nanoparticles in modern sunscreens: an analysis of potential exposure and hazard. Nanotoxicology 4:15–41
Park HS, Kim SJ, Lee TJ, Kim GY, Meang E, Hong JS, Kim SH, Koh SB, Hong SG, Sun YS, Kang JS, Kim YR, Kim MK, Jeong J, Lee JK, Son WC, Park JH (2014a) A 90 days study of sub-chronic oral toxicity of 20 nm positively charged zinc oxide nanoparticles in Sprague Dawley rats. Int J Nanomed 9(Suppl 2):93–107
Park HS, Shin SS, Meang EH, Hong JS, Park JI, Kim SH, Koh SB, Lee SY, Jang DH, Lee JY, Sun YS, Kang JS, Kim YR, Kim MK, Jeong J, Lee JK, Son WC, Park JH (2014b) A 90-day study of subchronic oral toxicity of 20 nm, negatively charged zinc oxide nanoparticles in Sprague Dawley rats. Int J Nanomed 9(Suppl 2):79–92
Roy R, Tripathi A, Das M, Dwivedi PD (2011) Cytotoxicity and uptake of zinc oxide nanoparticles leading to enhanced inflammatory cytokines levels in murine macrophages: Comparison with bulk zinc oxide. J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:110–111
Ryu HJ, Seong NW, So BJ, Seo HS, Kim JH, Hong JS, Park MK, Kim MS, Kim YR, Cho KB, Seo MY, Kim MK, Maeng EH, Son SW (2014) Evaluation of silica nanoparticle toxicity after topical exposure for 90 days. Int J Nanomed 9(Suppl 2):127–136
Salewski E (1964) Farbemethode zum makroscopischen nachweis von implantations stellen am uterus der ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pathol Exp Pharmakol 247:367
Sattarahmady N, Zare T, Mehdizadeh AR, Azarpira N, Heidari M, Lotfi M, Heli H (2015) Dextrin-coated zinc substituted cobalt-ferrite nanoparticles as an MRI contrast agent: in vitro and in vivo imaging studies. Colloids Surf B 129:15–20
Semmler-Behnke M, Lipka J, Wenk A, Hirn S, Schäffler M, Tian F, Schmid G, Oberdörster G, Kreyling WG (2013) Size dependent translocation and fetal accumulation of gold nanoparticles from maternal blood in the rat. Part Fibre Toxicol 11:33
Sharma V, Singh SK, Anderson D, Tobin DJ, Dhawan A (2011a) Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced genotoxicity in primary human epidermal keratinocytes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:3782–3788
Sharma V, Anderson D, Dhawan A (2011b) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human liver cells (HepG2). J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:98–99
Sharma V, Singh P, Pandey AK, Dhawan A (2012) Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse liver after sub-acute oral exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mutat Res 745:84–91
Solomon C, Hagl C, Rahe-Meyer N (2013) Time course of haemostatic effects of fibrinogen concentrate administration in aortic surgery. Br J Anaesth 110(6):947–956
Surekha P, Kishore AS, Srinivas A, Selvam G, Goparaju A, Reddy PN, Murthy PB (2012) Repeated dose dermal toxicity study of nano zinc oxide with Sprague-Dawley rats. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 31:26–32
Tian X, Zheng Y, Li Y, Shen Z, Tao L, Dou X, Qian J, Shen H (2014) Psychological stress induced zinc accumulation and up-regulation of ZIP14 and metallothionein in rat liver. BMC Gastroenterol 14:32
Tsyganova NA, Khairullin RM, Terentyuk GS, Khlebtsov BN, Bogatyrev VA, Dykman LA, Erykov SN, Khlebtsov NG (2014) Penetration of pegylated gold nanoparticles through rat placental barrier. Bull Exp Biol Med 157(3):383–385
Wilson JG (1965) Methods for administering agents and detecting malformations in experimental animals. In: Wilson JG, Warkany J (eds) Teratology: principles and techniques. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 262–277
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institute of Environmental Research, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Yu, WJ., Song, J. et al. Developmental toxicity of intravenously injected zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 1682–1692 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0767-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0767-z