Abstract
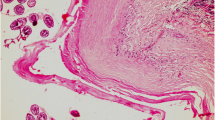
Hydatidosis, an important parasitic zoonoses is a major public health as well as economic concern throughout the world. A total of 2100, sheep (2052) and goats (48), slaughtered or spontaneously dead, from various areas of Kashmir valley were screened for the presence of hydatidosis. Out of 2100 cases, 85 were positive for hydatidosis. The frequently infected organs were lungs and liver. The liver was observed to be the most frequently infected organ with relative prevalence of 61.17% followed by lungs (38.82%). The pulmonary cysts were more fertile (55%) compared to hepatic cysts (45%). Histopathologicallly, the cyst wall consisted of the inner germinal, middle lamellated/laminated, and outer fibrous layer. Inflammatory reaction around the cyst was variable and was characterized by an inner zone of loosely arranged fibroblasts infiltrated with mononuclear cells, followed by densely arranged fibroblasts along with mononuclear cells; and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. Fibroplasia and calcification were noted at places. In liver besides the cellular reaction against the expanding cyst, hepatocellular degeneration and cirrhosis were observed, the severity of which was inversely related to the distance from the cyst. The structural details of the protoscolices were clearly discernable.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar Z, Tanveer A, Bashir S (1999) Echinococcus granulosus: histopathology of naturally infected sheep liver. Punjab Univ J Zool 14:105–111
Barnes TS, Hinds LA, Jenkins DJ, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Lightowlers MW, Coleman GT (2011) Comparative pathology of pulmonary hydatid cysts in macropods and sheep. J Comp Pathol 144:113–122
Canda MS, Ray MG, Canda TL, Astarcioúlu HS (2003) The pathology of echinococcosis and the current echinococcosis problem in Western Turkey (A report of pathologic features in 80 cases). Turk J Med Sci 33:369–374
da Silva A (2010) Human echinococcosis: a neglected disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 6:1–9
Ernest E, Nonga HE, Kassuku AA, Kazwala RR (2009) Echinococcosis of slaughtered animals in Ngorongoro district of Arusha region, Tanzania. Trop Anim Health Prod 41:1179–1185
Fakhar M, Sadjjadi SM (2007) Prevalence of hydatidosis in slaughtered herbivores in Qom Province, Central Part of Iran. Vet Res Com 31:993–997
Hansen B (1991) New York City epidemics and history for the public. In: Harden VA, Risse GB (eds) AIDS and the historian. Bethesda, National Institutes of Health, pp 21–28
Huttner M, Nakao M, Wassermann T, Siefert L, Boomker JD (2008) Genetic characterization and phylogenetic position of Echinococcus felidis (Cestoda: Taeniidae) from the African lion. Int J Parasitol 7:861–868
Ibrahim SEA, Gameel AA (2014) Pathological, histochemical and Immunohistochemical studies of lungs and livers of cattle and sheep infected with hydatid disease. In: Proceedings of 5th annual conference-agricultural and veterinary research–February 2014, Khartoum, Sudan, vol 2, pp 1–17
Johannes E, Deplazes P (2004) Biological, Epidemio-logical, and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin Microbio Rev 17:107–135
Kebede N, Mitiku A, Tilahun G (2009) Echinococcosis of slaughtered animals in Bahir Dar Abattoir, Northwestern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 41:43–50
Khadidja H, Achour Y, Houcin B, Vasile C (2014) Histological Appearance of Echinococcus Granulosus in the Camel Species in Algeria. Bulletin UASVM Vet Med 71:79–84
Kul O, Yildiz K (2010) Multivesicular cysts in cattle: Characterisation of unusual hydatid cyst morphology caused by Echinococcus granulosus. Vet Parasitol 170:162–166
Lahmar S, Trifi S M, Ben-Naceur S, Bouchhima T, Lahouar N, Lamouchi I, Maamouri N, Selmi R, Dhibi M, Torgerson PR (2012) Cystic echinococcosis in slaughtered domestic ruminnats from Tunisia. J Helminthol 87:1–8
Luna LG (1968) Manual of histologic staining methods of the Armed forces, Institute of Pathology, 3rd edn. Mc Graw Hill Book Company, New York
Mitrea IL (1998) Research regarding immunodiagnostics, immune response and immune prophylaxis in hydatidosis in ruminants [In Romanian]. PhD thesis, USAMV Bucharest, Romania
Njoroge EM, Mbithi PM, Gathuma JM, Wachira TM, Magambo JK, Zeyhle EA (2002) Study of cystic echinococcosis in slaughter animals in three selected areas of northern Turkana, Kenya. Vet Parasitol 104:85–91
OIE (2008) Echinococcosis/hydatidosis. OIE terrestrial manual pp 175–190
Ould CB, Schneegans F, Chollet JY, Jemli MH (2010) Prevalence and aspects of lesions of echinococcosis in camel in Northern Mauritania. Revue Elev Méd Vét Pays Trop 63:23–28
Pedro M, Peter MS (2009) Echinococcosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis 13:125–133
Rashed AA, Omer HM, Fouad MAH, Al-Shareef AMF (2004) The effect of severe cystic hydatidosis on the liver of a Najdi sheep with special reference to the cyst histology and histochemistry. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 34:297–304
Sakamoto T, Gutierrez C (2005) Pulmonary complications of cystic echinococcosis in children in Uruguay. Pathol Int 55:497–503
Seadawy MAH, Al-Kaled MJA (2012) Gross and histological comparison of hydatid cyst infection in livers of sheep and cows. AL-Qadisiya J Vet Med Sci 11(2):1643–1646
Singh BB, Sharma R, Sharma JK, Mahajan V, Gill JPS (2014) Histopathological changes associated with E. granulosus echinococcosis in food producing animals in Punjab (India). J Parasit Dis 40:1–3
Solcan C, Solcan G, Ioniţă M, Hristescu DV, Mitrea IL (2010) Histological aspects of cystic echinococcosis in goats. Sci Parasitol 11:191–198
Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ (1988) The nature, extent and significance of variation within the genus Echinococcus. Adv Parasitol 27:209–258
Tilahun A, Terefe Y (2013) Echinococcosis: prevalence, cyst distribution and economic significance in cattle slaughtered at Arbaminch municipality abattoir, Southern Ethiopia. Glob Vet 11:329–334
Torgerson PR (2003) The economic effects of echinococcosis. Acta Trop 85:113–118
Verma Y, Swamy M (2009) Prevalence and pathology of hydatidosis in buffalo liver. Buffalo Bull 28:207–211
Xiao N, Qiu JM, Nakao M, Li TY, Yang W (2005) Echinococcus shiquicus n.sp., a taeniid cestod from Tibetan fox and plateau pika in China. Int J Parasitol 35:693–701
Young ED (2005) Brucella species. In: Mandell GL, Douglos RG, Bennett JE (eds) Principles and practice of infectious disease, 6th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Pensylvania, pp 3290–3292
Zhang T, Yang D, Zeng Z, Zhao W, Liu A, Piao D, Jiang T, Cao J, Shen Y, Liu H, Zhang W (2014) Genetic characterization of human-derived hydatid cysts of Echinococcus granulosus Sensu Lato in Heilongjiang Province and the first report of G7 genotype of E. canadensis in humans in China. PLoS ONE 9:10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: A. B. Beigh, M.M. Darzi. Acquisition of data: A. B. Beigh. Analysis and interpretation of data: B. kashani, A. Shah. Drafting of manuscript: S. Bashir. Critical revision: S. Shah.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no personal or financial relationships between the authors and other people or organizations which have inappropriately influenced this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beigh, A.B., Darzi, M.M., Bashir, S. et al. Gross and histopathological alterations associated with cystic echinococcosis in small ruminants. J Parasit Dis 41, 1028–1033 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-017-0929-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-017-0929-z