Abstract
To evaluate the efficacy of autologous platelet rich fibrin in soft tissue healing and bone regeneration in mandibular third molar extraction sockets.
Method
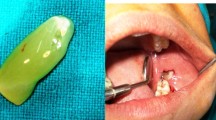
The study was conducted in 20 patients visiting in outpatient department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, requiring extraction of bilateral mandibular third molar, following extraction platelet rich fibrin (PRF) was placed in one extraction sockets, the other socket was studied as the control sites with no PRF. The patient were assessed for post operative pain, soft tissue healing and trabecular pattern in healing bone. Radiological assessment of the extraction site was done for period of 3 months to evaluate the change in bone density.
Results
Pain was less in study side compare to control site soft tissue was healing was better in study site. Evaluation of trabecular bone formation started earlier in PRF site compare to control site. The evaluation of bone density by radiological assessment showed the grey level value calculated after 3 months at the PRF site well comparatively higher than the average baseline value of the bone density at the extraction site in control site.
Conclusion
The study showed that autologous PRF is biocompatible and has significantly improved soft tissue healing. Bone regeneration and increase in bone density in extraction sockets. However, a more elaborate study with a large number of clinical cases is essential to be more conclusive regarding its efficacy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gassling VL, Acil Y, Springer IN et al (2009) Platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin in human cell culture. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108:48–55
Vivek Gk, Sripathi Rao BH (2009) Potential for osseous regeneration of platelet rich plasma: a comparative study in mandibular third molar sockets. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 8(4):308–311
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:E37–E44
Brown LF, Lanir N, McDonagh J (1993) Fibroblast migration in fibrin gel matrices. Am J Pathol 142:273–283
Van Hinsbergh VW, Collen A, Koolwijk P (2001) Role of fibrin matrix in angiogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci 936:426–437
Nehls V, Herrmann R (1996) The configuration of fibrin clots determines capillary morphogenesis and endothelial cell migration. Microvasc Res 51:347–364
Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:E56–E60
Kazura JW, Wenger JD, Salata RA, Budzynski AZ, Goldsmith GH (1989) Modulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte microbicidal activity and oxidative metabolism by fibrinogen degradation products D and E. J Clin Invest 83:1916–1924
Gassling V, Douglas T, Warnke PH (2010) Platelet-rich fibrin membranes as scaffolds for periosteal tissue engineering. Clin Oral Implant Res 21:543–549
Landry RG, Turnbull RS, Howley T (1988) Effectiveness of benzydamyne HC1 in the treatment of periodontal post-surgical patients. Res Clin Forum 10:105–118
Sunitha Raja V, Munirathnam Naidu E (2008) Platelet-rich fibrin: evolution of a second-generation platelet concentrate. Indian J Dent Res 19(1):42–46
Anil Kumar K, Geetha A, Unasudhakar (2009) Platelet-rich fibrin: a novel root coverage approach. J Indian Soc Periodontol 13(1):50–54
Bensaid W, Triffitt JT, Blanchat C (2003) A biodegradable fibrin scaffold for mesenchymal stem cells transplantation. Biomaterials 24:2497–2502
Boo JS, Yamada Y, Okazaki Y, Hibino Y, Okada K, Hata K et al (2002) Tissue-engineered bone using mesenchymal stem cells an a biodegradable scaffold. J Craniofac Surg 13:231–239
Lozada JL, Caplanis N, Proussaefs P, Willardsen J, Kammeyer G (2001) Platelet-rich plasma application in sinus graft surgery: part I-background and processing techniques. J Oral Implantol 27:38–42
Vinazzer H (1985) Fibrin sealing: physiologic and biochemical background. Facial Plast Surg 2:291–295
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL et al (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second generation platelet concentrate, part II: platelet related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:E45–E50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Kohli, M. & Gupta, N. Platelet Rich Fibrin: A Novel Approach for Osseous Regeneration. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 11, 430–434 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-012-0351-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-012-0351-0