Abstract
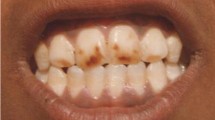
Fluoride (F) toxicosis in the forms of dental, skeletal and non-skeletal fluorosis were investigated in 996 tribal individuals (503 males and 493 females) above 10 years of age living in nine F endemic villages of Dungarpur district of Rajasthan, India. Drinking water sources of these villages contained F in the range of 1.5–4.4 ppm. Of these tribals, 735 (73.8 %) and 294 (29.5 %) were found to be afflicted with mild to severe dental and skeletal fluorosis, respectively. At 1.5 ppm F concentration the prevalence of dental and skeletal fluorosis was 33.9 and 10.7 %, respectively. A polymorphism of dental fluorosis in the form of brown to deep yellowish bilaterally stratified horizontal lines, pits or patches, and fine dots or granules was noted on anterior teeth of tribal individuals. Irregular wearing, excessive corrosions (abrasions), dark-yellowish pigmentation of exposed cementum and dentine material, diastemas between teeth, pronounced loss of tooth supporting bone with recession, and bulging of gingiva (gum) were also present. Among the adult and old tribal individuals, the following mild to severe manifestations of skeletal fluorosis such as crippling, kyphosis, invalidism and genu-varum syndrome were found. Sporadic cases of paraplegia and quadriplegia were also found. None of the fluorotic tribals showed evidence of genu-valgum syndrome. Radiological changes were also observed in these individuals. Other signs of chronic F intoxication in soft tissues (non-skeletal fluorosis) included colic, intermittent diarrhoea or constipation, bloating, urticaria, polyurea, polydipsia, repeated abortions, still birth and sterility. Data pertaining to prevalence of osteo-dental fluorosis in relation to age and F concentration exhibited statistically significant correlation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (1970) Fluorides and human health, monograph series, vol 59. World Health Organization, Geneva
Swarup D, Dwivedi SK (2002) Environmental pollution and effects of lead and fluoride and animal health. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
Choubisa SL (1999) Chronic fluoride intoxication (fluorosis) in tribes and their domestic animals. Int J Environ Stud 56(5):703–716
Choubisa SL (1999) Some observations on endemic fluorosis in domestic animals of southern Rajasthan. Vet Res Commun 23(7):457–465
Choubisa SL (2007) Fluoridated ground water and its toxic effects on domesticated animals residing in rural areas of Rajasthan. (India). Int J Environ Stud 64(2):151–159
Choubisa SL, Mishra GV, Sheikh Z, Bhardwaj B, Mali P, Jaroli VJ (2011) Toxic effects of fluoride in domestic animals. Adv Pharmacol Toxicol 12(2):29–37
Choubisa SL (2010) Osteo-dental fluorosis in horses and donkeys of Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 43(1):5–12
Choubisa SL (2010) Fluorosis in dromedary camels, Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 43(3):194–199
Thergaonkar VP, Bhargava RK (1974) Water quality and incidence of fluorosis in Jhunjhunu of Rajasthan: preliminary observations. Indian J Environ Health 16:168–180
Choubisa SL, Choubisa L, Choubisa D (2009) Osteo-dental fluorosis in relation to nutritional status, living habits and occupation in rural tribal areas of Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 42(3):210–215
Choubisa SL (2010) Natural amelioration of fluoride toxicity (fluorosis) in goats and sheep. Curr Sci 99(10):1331–1332
Choubisa SL, Mishra GV, Sheikh Z, Bharadwaj B, Mali P, Jaroli VJ (2011) Food, fluoride, and fluorosis in domestic ruminants in the Dungarpur district of Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 43(2):70–76
Choubisa SL (2001) Endemic fluorosis in southern Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 34(1):61–70
Hussain J, Hussain I, Sharma KC (2010) Fluoride and health hazards: community perception in a fluorotic area of central Rajasthan (India): an arid environment. Environ Monit Assess 162:1–14
Mathur M, Tamboli BL, Mathur RH et al (1976) Preliminary epidemiological investigation of fluorosis in Surajpura and Pratappura villages of Sarwar Tehsil, Ajmer district (Rajasthan). Indian J Prev Soc Med 7:90–93
Choubisa SL (1998) Fluorosis in some tribal villages of Udaipur district (Rajasthan). J Environ Bio 19(4):341–352
Maithani PB, Gurjar R, Banerjee R, Balaji BK, Ramachandran S, Singh R (1998) Anomalous fluoride in ground water from western part of Sirohi district, Rajasthan and its crippling effects on human health. Curr Sci 4(9):773–777
Choubisa SL (1996) An epidemiological study on endemic fluorosis in tribal area of southern Rajasthan [a technical report]. Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi
Choubisa SL (1996) Radiological skeletal changes due to fluoride intoxication in Udaipur district (Rajasthan). Poll Res 15:227–229
Choubisa SL, Sompura K (1996) Dental fluorosis in tribal villages of Dungarpur district (Rajasthan). Poll Res 15:45–47
Choubisa SL, Verma R (1996) Skeletal fluorosis in bone injury case. J Environ Biol 17(1):17–20
Mahajan BK (1984) Methods in biostatistics. Jaypee Brothers, Medical Publisher Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi
Venkateswarlu P, Rao DN, Rao KR (1952) Studies in endemic fluorosis in Visakhapatnam and Sub urban areas. Indian J Med Res 40:353–362
Ray SK, Ghosh S, Nagchaudhary J, Tiwari IC, Kaur P (1981) Prevalence of fluorosis in rural community near Varanasi. Fluoride 14:86–90
Subbareddy VV, Tiwari A (1985) Enamel mottling at different levels of fluoride in drinking water: in an endemic areas. J Indian Dent Assoc 57:205–212
Choubisa SL, Choubisa L, Sompura K, Choubisa D (2007) Fluorosis in subjects belonging to different ethnic groups of Rajasthan (India). J Commun Dis 39(3):171–177
Choubisa SL, Choubisa L and Choubisa D (2011) Osteo-dental fluorosis in relation to chemical constituents of drinking waters. J Environ Sci Eng (in press)
Krishnamachari KAVP, Krishnaswamy K (1976) An epidemiological study of the syndrome of genu valgum among residents of endemic areas for fluorosis in Andhra Pradesh. Indian J Med Res 62(9):1415–1423
Chakma T, Singh SB, Godbole S, Tiwary RS (1997) Endemic fluorosis with genu valgum syndrome in a village of district Mandala, Madhya Pradesh. Indian Pediatr 34:232–236
Choubisa SL, Choubisa L, Choubisa DK (2001) Endemic fluorosis in Rajasthan. Indian J Environ Health 43(4):177–189
Susheela AK, Das TK, Gupta IP, Tondon RK, Kacker SK, Ghosh P, Deka RC (1992) Fluoride ingestion and its correlation with gastro-intestinal discomfort. Fluoride 25(1):5–22
Sharma JD, Sohu D, Jain P (2009) Prevalence of neurological manifestations in a human population exposed to fluoride in drinking water. Fluoride 42:127–132
Sharma JD, Jain P, Sohu D (2009) Gastric discomforts from fluoride in drinking water in Sanganer Tehsil, Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 42(4):286–291
Justus C, Krook LP (2006) Allergy in horses from artificially fluoridated water. Fluoride 39(2):89–94
Acknowledgments
Author thanks the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India for financial assistance. Author is also thankful to Dr. H. Jain (Orthopaedician), Dr. Darshana Choubisa (Dentist) and Dr. Zulfiya Sheikh (Asst. Prof. of Zoology) for their cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choubisa, S.L. Fluoride in Drinking Water and its Toxicosis in Tribals of Rajasthan, India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 82, 325–330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0047-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0047-8