Abstract
The blockchain technology is one of the grand challenges for the governance of new entrepreneurial projects. Thanks to this decentralized mechanism of certification, teams are now able to organize Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and raise money on the Internet offering digital tokens, bypassing any screening or control from central entities and independent auditors. While many of the governance mechanisms applied in traditional venture financing do not apply to ICOs, contributors may rely ex ante on the quality of the team and on unaudited information disclosed in a ‘white paper’, ex post on the development on enforcing digital ‘smart contracts’. In this work we study the governance signals of ICO-backed projects (token rights, institutional setting, team quality), analyzing a sample of 935 offerings. We examine the relationship between governance issues and the fundraising success and we find that both the project team and advisory committee size is positively and significantly correlated with the success. When the fraction of tokens retained by insiders and managers is larger, the probability of fundraising success is also larger, but to a lower extent if the token gives access to a service (‘utility token’). Specific provisions about the future jurisdiction and incorporation of the project are not considered as a credible governance signal. On the contrary, past managerial experience of the proponents is a valuable asset for contributors.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Smart contracts are programmable contractual tools embedded in a software code. Thus, a smart contract can include the governance arrangement itself, stating the preconditions necessary for the contractual obligations to take place and the actual execution of the contract (Koulu 2016).
Sources: National Venture Capital Association and Invest Europe.
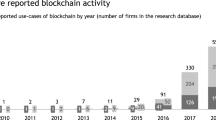
Sources: platform web sites.
An Initial Exchange Offering relies on an exchange as the counter-party of the offering. Developers mint the digital tokens and send them to the exchange, which will place the tokens to individual contributors. A Security Token Offering represents an investment contract into an underlying asset and complies with the regulation of security placements, as in a standard public offering.
Following Adhami et al. (2018), we use TokenData.io as the starting point for the ICO list creation as it proved to be reliable since the onset of the ICO phenomenon. Surely, ICOBench.com and other aggregators provide more information regarding each single issue (and this information is also used by our sample) but we find that they are less accurate or complete when defining ‘failed’ ICOs.
E.g., see the report by PWC and Cripto Valley “Initial Coin Offerings: a Strategic Perspective”, June 2018.
Sources: http://www.kickstarter.com and http://www.crowdcube.com.
In Vietnam 32,000 pledgers in two allegedly fraudulent initial coin offerings lost $660 million, according to news agencies. See also Zetzsche et al. (2017).
In September 2017, the US SEC charged two ICOs that allegedly placed unregistered securities. Many other episodes followed up.
References
Adhami, S., Giudici, G., & Martinazzi, S. (2018). Why do businesses go crypto? An empirical analysis of initial coin offerings. Journal of Economics and Business, 100, 64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconbus.2018.04.001.
Ahlers, G. K., Cumming, D., Günther, C., & Schweizer, D. (2015). Signaling in equity crowdfunding. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 39(4), 955–980. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12157.
Ahlstrom, D., Cumming, D. J., & Vismara, S. (2018). New methods of entrepreneurial firm financing: Fintech, crowdfunding and corporate governance implications. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 26(5), 310–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/corg.12258.
Amsden, R., & Schweizer, D. (2018). Are blockchain crowdsales the new ‘Gold Rush’? Success determinants of initial coin offerings. Available at SSRN. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3163849.
Backes-Gellner, U., & Werner, A. (2007). Entrepreneurial signaling via education: A success factor in innovative start-ups. Small Business Economics, 29, 173–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-006-0016-9.
Barone, R., & Masciandaro, D. (2019). Cryptocurrency or usury? Crime and alternative money laundering techniques. European Journal of Law and Economics, 47(2), 233–254.
Bartoletti, M., & Pompianu, L. (2017). An empirical analysis of smart contracts: Platforms, applications, and design patterns. In International conference on financial cryptography and data security (pp. 494–509). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70278-0_31.
Baum, J. A., & Silverman, B. S. (2004). Picking winners or building them? Alliance, intellectual, and human capital as selection criteria in venture financing and performance of biotechnology startups. Journal of Business Venturing, 19(3), 411–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-9026(03)00038-7.
Bebchuk, L. A., & Weisbach, M. S. (2010). The state of corporate governance research. The Review of Financial Studies, 23(3), 939–961. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhp121.
Becker, G. S. (1964). Human capital: A theoretical and empirical analysis, with special reference to education. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Bhagat, S., & Bolton, B. (2008). Corporate governance and firm performance. Journal of Corporate Finance, 14(3), 257–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2008.03.006.
Block, J. H., Cumming, D. J., & Vismara, S. (2017). International perspectives on venture capital and bank finance for entrepreneurial firms. Economia e Politica Industriale—Journal of Industrial & Business Economics, 44(1), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40812-017-0069-6.
Bonzanini, D., Giudici, G., & Patrucco, A. (2015). The crowdfunding of renewable energy projects. In V. Ramiah, & G. N. Grogoriou (Eds.), Handbook of Environmental and Sustainable Finance. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803615-0.00021-2.
Brown, P., Beekes, W., & Verhoeven, P. (2011). Corporate governance, accounting and finance: A review. Accounting & Finance, 51(1), 96–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-629X.2010.00385.x.
Chen, Y. (2018). Blockchain tokens and the potential democratization of entrepreneurship and innovation. Business Horizons, 61(4), 567–575.
Cheung, S. N. S. (1983). The contractual nature of the firm. The Journal of Law and Economics, 26(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1086/467023.
Christidis, K., & Devetsikiotis, M. (2016). Blockchains and smart contracts for the internet of things. IEEE Access, 4, 2292–2303. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2566339.
Chung, S., Singh, H., & Lee, K. (2000). Complementarity, status similarity and social capital as drivers of alliance formation. Strategic Management Journal, 21(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(200001)21:1%3C1:AID-SMJ63%3E3.0.CO;2-P.
Condos, J., Sorrell, W., & Donegan, S. (2016). Blockchain technology: Opportunities and risks. State of Vermont. https://legislature.vermont.gov/assets/Legislative-Reports/blockchain-technology-report-final.pdf
Cong, L. W., Edmans, A., Park, A., & Hara, M. O. (2018). Block chain disruption and smart contracts. Cambridge, MA. https://doi.org/10.3386/w24399, http://www.zhiguohe.com/uploads/1/0/6/9/106923057/bdsc.pdf.
Dalton, D. R., Daily, C. M., Ellstrand, A. E., & Johnson, J. L. (1998). Meta-analytic reviews of board composition, leadership structure, and financial performance. Strategic Management Journal, 19(3), 269–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(199803)19:3%3c269:AID-SMJ950%3e3.0.CO;2-K.
Dixit, A. K. (2011). Lawlessness and economics: Alternative modes of governance. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Draho, J. (2004). The IPO decision: Why and how companies go public. Northampton: Edward Elgar.
Eisenberg, M. A. (1998). The conception that the corporation is a nexus of contracts, and the dual nature of the firm. Journal of Corporation Law, 24, 819. https://heinonline.org/HOL/Page?collection=journals&handle=hein.journals/jcorl24&id=827&men_tab=srchresults.
Fairfield, J. A. (2014). Smart contracts, Bitcoin bots, and consumer protection. Washington and Lee Law Review Online, 71(2), 36. https://scholarlycommons.law.wlu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=https://scholar.google.at/&httpsredir=1&article=1003&context=wlulr-online.
Fisch, C. (2019). Initial coin offerings (ICOs) to finance new ventures. Journal of Business Venturing, 34(1), 1–22.
Franke, N., Gruber, M., Harhoff, D., & Henkel, J. (2008). Venture capitalists’ evaluations of start-up teams: Trade-offs, knockout criteria, and the impact of VC experience. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 32(3), 459–483. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2008.00236.x.
Giudici, G. (2016). Equity crowdfunding of an entrepreneurial activity. In D. Audretsch, E. Lehmann, M. Meoli, & S. Vismara (Eds.), University evolution, entrepreneurial activity and regional competitiveness (pp. 415–425). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17713-7_20.
Giudici, G., Guerini, M., & Rossi Lamastra, C. (2013). Crowdfunding in Italy: State of the art and future prospects. Economia e Politica Industriale—Journal of Industrial and Business Economics, 40(4), 173–188.
Gompers, P. A., & Lerner, J. (2004). The venture capital cycle. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Hacker, P., & Thomale, C. (2018). Crypto-securities regulation: Icos, token sales and cryptocurrencies under EU financial law. European Company and Financial Law Review, 15(4), 645–696.
Hart, O. (1995). Corporate governance: Some theory and implications. The Economic Journal, 105(430), 678. https://doi.org/10.2307/2235027.
Hellmann, T., & Puri, M. (2000). The interaction between product market and financing strategy: The role of venture capital. The Review of Financial Studies, 13(4), 959–984. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/13.4.959.
Hoang, H., & Antoncic, B. (2003). Network-based research in entrepreneurship: A critical review. Journal of Business Venturing, 18, 165–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-9026(02)00081-2.
Huang, W., Meoli, M., & Vismara, S. (2019). The geography of initial coin offerings. Small Business Economics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-019-00135-y. (forthcoming).
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), 305–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-405X(76)90026-X.
Khan, W. A., & Vieito, J. P. (2013). Ceo gender and firm performance. Journal of Economics and Business, 67, 55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconbus.2013.01.003.
Kosba, A., Miller, A., Shi, E., Wen, Z., & Papamanthou, C. (2016). Hawk: The blockchain model of cryptography and privacy-preserving smart contracts. In 2016 IEEE symposium on security and privacy (SP) (pp. 839–858). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/SP.2016.55.
Koulu, R. (2016). Blockchains and online dispute resolution: Smart contracts as an alternative to enforcement. SCRIPTed: A Journal of Law, Technology and Society, 13. https://heinonline.org/HOL/Page?handle=hein.journals/scripted13&id=40&div=&collection=.
Lauslahti, K., Mattila, J., & Seppälä, T. (2017). Smart contracts—How will blockchain technology affect contractual practices? ETLA Reports, 68(68), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3154043.
Leland, H. E., & Pyle, D. H. (1977). Informational asymmetries, financial structure, and financial intermediation. The Journal of Finance, 32(2), 371–387. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2326770.
Luu, L., Chu, D.-H., Olickel, H., Saxena, P., & Hobor, A. (2016). Making smart contracts smarter. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC conference on computer and communications security—CCS’16 (pp. 254–269). New York, NY, USA: ACM Press. https://doi.org/10.1145/2976749.2978309.
McConnell, J. J., Servaes, H., & Lins, K. V. (2008). Changes in insider ownership and changes in the market value of the firm. Journal of Corporate Finance, 14(2), 92–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCORPFIN.2008.02.001.
McWaters, J., Bruno, G., Galaski, R., & Chatterjee, S. (2016). The future of financial infrastructure—An ambitious look at how blockchain can reshape financial services. An Industry Project of the Financial Services Community| Prepared in collaboration with Deloitte. In World Economic Forum. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_The_future_of_financial_infrastructure.pdf.
Nelson, M. W., Elliott, J. A., & Tarpley, R. L. (2002). Evidence from auditors about managers’ and auditors’ earnings management decisions. The Accounting Review, 77(s-1), 175–202. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.2002.77.s-1.175.
Peters, G. W., & Panayi, E. (2016). Understanding modern banking ledgers through blockchain technologies: Future of transaction processing and smart contracts on the internet of money (pp. 239–278). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42448-4_13.
Piva, E., & Rossi-Lamastra, C. (2018). Human capital signals and entrepreneurs’ success in equity crowdfunding. Small Business Economics, 51(3), 667–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9950-y.
Posner, R. A. (2014). Economic analysis of law. South Holland: Wolters Kluwer Law & Business.
Schwienbacher, A., & Hornuf, L. (2018). Initial coin offerings, information disclosure, and fraud cases. Working paper.
Shane, S., & Cable, D. (2002). Network ties, reputation, and the financing of new ventures. Management Science, 48(3), 364–381. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.48.3.364.7731.
Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. W. (1997). A survey of corporate governance. The Journal of Finance, 52(2), 737–783. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.1997.tb04820.x.
Stuart, T. E., Hoang, H., & Hybels, R. C. (1999). Interorganizational endorsements and the performance of entrepreneurial ventures. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44(2), 315–349. https://doi.org/10.2307/2666998.
Vismara, S. (2016). Equity retention and social network theory in equity crowdfunding. Small Business Economics, 46(4), 579–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-016-9710-4.
Watanabe, H., Fujimura, S., Nakadaira, A., Miyazaki, Y., Akutsu, A., & Kishigami, J. (2016). Blockchain contract: Securing a blockchain applied to smart contracts. In 2016 IEEE international conference on consumer electronics (ICCE) (pp. 467–468). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE.2016.7430693.
Wright, A., & De Filippi, P. (2015). Decentralized blockchain technology and the rise of lex cryptographia. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2580664.
Yermack, D. (2017). Corporate Governance and Blockchains. Review of Finance, 21(1), rfw074. https://doi.org/10.1093/rof/rfw074.
Yuan, Y., & Wang, F. Y. (2016). Blockchain: The state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 42(4), 481–494. http://www.aas.net.cn/EN/abstract/abstract18837.shtml.
Zetzsche, D. A., Buckley, R. P., Arner, D. W., & Föhr, L. (2017). The ICO gold rush: It’s a scam, it’s a bubble, it’s a super challenge for regulators. University of Luxembourg Law Working Paper, 11, 17–83. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3072298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giudici, G., Adhami, S. The impact of governance signals on ICO fundraising success. J. Ind. Bus. Econ. 46, 283–312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40812-019-00118-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40812-019-00118-w