Abstract
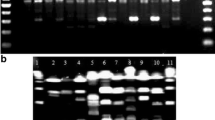
Three typing methods, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of the 16S-23S intergenic spacer region (ISR), PCR amplification of the enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC) and of the repetitive extragenic palindromic units (REP), were evaluated for typing 26 isolates of Aeromonas popoffii from different geographical origins. When the methods were independently studied, ERIC showed the highest discriminatory power. When the methods were combined, the best combination of two methods was ERIC with REP since strains showed a tendency to cluster according to their geographical origin. However, this tendency was reinforced with the addition of ISR-RFLP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borrell N., Acinas S.G., Figueras M.J. and Martínez-Murcia A. 1997. Identification of Aeromonas clinical isolates by restriction fragment length polymorphism of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35: 1671–1674.
Davin-Regli A., Bollet C., Chamorey E., Colonna D'istria V. and Cremieux A. 1998. A cluster cases of infections due to Aeromonas hydrophila revealed by combined RAPD and ERIC-PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 47: 499–504.
Demarta A., Tonolla M., Caminada A.-P., Ruggeri N. and Peduzzi R. 1999. Signature region within the 16S rDNA sequences of Aeromonas popoffii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 172: 239–246.
Demarta A., Tonolla M., Caminada A., Beretta M. and Peduzzi R. 2000. Epidemiological relationships between Aeromonas strains isolated from symptomatic children and household environments as determined by ribotyping. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 16: 447–453.
Figueras M.J., Soler L., Chacón M.R., Guarro J. and Martínez-Murcia A.J. 2000. Extended method for discrimination of Aeromonas spp. by 16S rDNA-RFLP. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 2069–2073.
Hulton C.S.J., Higgins C.F. and Sharp P.M. 1991. ERIC sequences: a novel family of repetitive elements in the genome of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and other enterobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 5: 825–834.
Huys G., Kampfer P., Altwegg M., Kersters I., Lamb A., Coopman R. et al. 1997. Aeromonas popoffii sp nov., a mesophilic bacterium isolated from drinking water production plants and reservoirs. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47: 1165–1171.
Janda J.M. and Abbott S.L. 1998. Envolving concepts regarding the genus Aeromonas: An expanding panorama of species, disease presentation, and unanswered questions. Clin. Infect. Dis. 27: 332–344.
Marshall S., Clark C.G., Wang G., Mulvey M., Kelly M.T. and Johnson W.M. 1999. Comparison of molecular methods for typing Vibrio parahemolyticus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37: 2473–2478.
Martínez-Murcia A.J., Borrell N. and Figueras M.J. 2000. Typing of clinical and environmental Aeromonas veronii strains based on the 16S-23S rDNA spacers. FEMS Immun. Med. Microbiol. 28: 225–232.
Maslow J.N., Mulligan M.E. and Arbeit R.D. 1993. Molecular epidemiology: application of contemporary techniques to the typing of microorganisms. Clin. Infect. Dis. 17: 153–164.
Metha A., Leite J.R.P. and Rosato Y.B. 2001. Assessment of the genetic diversity of Xylella fastidiosa isolated from citrus in Brazil by PCR-RFLP of the 16S rDNA and 16S-23S intergenic spacer and rep-PCR figerprinting. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 79: 53–59.
Sander A., Ruess M., Bereswill S., Schuppler M. and Steinbrueckner B. 1998. Comparison of different DNA fingerprinting techniques for molecular typing of Bartonella henselae isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36: 2973–2981.
Soler L., Figueras M.J., Chacón M.R., Vila J., Marco F., Martinez-Murcia A.J. et al. 2002. Potential virulence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas popoffii recovered from freshwater and seawater. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 32: 243–247.
Talon D., Mulin B. and Thouverez M. 1998. Clonal identification of Aeromonas hydrophila strains using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 14: 305–310.
Tyler K.D., Wang G., Tyler S.D. and Johnson W.M. 1997. Factors affecting reliability and reproducibility of amplification-based DNA fingerprinting of representative bacterial pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35: 339–346.
Versalovic J., Koeuth T. and Lupski J.R. 1991. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 19: 6823–6831.
Vila J., Marcos M.A. and Jimenez de Anta M.T. 1996. A comparative study of different PCR-based DNA fingerprinting techniques for typing of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-A. baumannii complex. J. Med. Microbiol. 44: 482–489.
Vinuesa P., Redemaker J.L.W., Bruijn F.J. and Werner D. 1998. Genotypic characterization of Bradyrhizobium strains nodulating endemic woody legumes of the Canary Islands by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of genes encoding 16S rRNA (16S rDNA) and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacers, repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR genomic fingerprinting, and partial 16S rDNA sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 2096–2104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soler, L., Figueras, M.J., Chacón, M.R. et al. Comparison of three molecular methods for typing Aeromonas popoffii isolates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 83, 341–349 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023312415276
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023312415276