Abstract
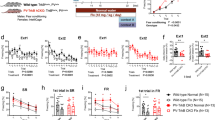
Recent hypotheses propose that one prerequisite to obtain a rapid antidepressant (AD) effect would reside in processes of synaptic reinforcement occurring within the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus independently from neurogenesis. However, to date no relationship has been established between an increased DG synaptic plasticity, and rapid AD-like action. To the best of our knowledge, this study shows for the first time that inducing a long-term potentiation (LTP) within the DG by stimulating the perforant pathway (PP) is sufficient to induce such effects. Thus, Sprague-Dawley rats having undergone a successful LTP displayed a significant reduction of immobility when passed acutely 3 days thereafter in the forced swimming test (FST). Further, in a longitudinal paradigm using the pseudo-depressed Wistar-Kyoto rat strain, LTP elicited a decrease of FST immobility after only 2 days, whereas the AD desipramine was not effective before 16 days. In both models, the influence of LTP was transient, as it was no more observed after 8–9 days. No effects were observed on the locomotor activity or on anxiety-related behavior. Theta-burst stimulation of a brain region anatomically adjacent to the PP remained ineffective in the FST. Immunoreactivity of DG cells for phosphorylated histone H3 and doublecortin were not modified three days after LTP, indicating a lack of effect on both cell proliferation and neurogenesis. Finally, depleting brain serotonin contents reduced the success rate of LTP but did not affect its subsequent AD-like effects. These results confirm the ‘plastic DG’ theory of rapid AD efficacy. Beyond, they point out stimulations of the entorhinal cortex, from which the PP originates, as putative new approaches in AD research.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Koretz D, Merikangas KR et al. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA 2003; 289: 3095–3105.
Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Bernert S, Bruffaerts R, Brugha TS, Bryson H et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in Europe: results from the European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders (ESEMeD) project. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2004; 420: 21–27.
Artigas F, Nutt DJ, Shelton R . Mechanism of action of antidepressants. Psychopharmacol Bull 2002; 36: 123–132.
Rush AJ, Warden D, Wisniewski SR, Fava M, Trivedi MH, Gaynes BN et al. STAR*D: revising conventional wisdom. CNS Drugs 2009; 23: 627–647.
Blier P, El Mansari M . Serotonin and beyond: therapeutics for major depression. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2013; 368: 20120536.
Blier P, de Montigny C . Serotonin and drug-induced therapeutic responses in major depression, obsessive-compulsive and panic disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999; 21: 91S–98S.
Berton O, Nestler EJ . New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006; 7: 137–151.
Duman RS, Li N . A neurotrophic hypothesis of depression: role of synaptogenesis in the actions of NMDA receptor antagonists. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2012; 367: 2475–2484.
Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS . Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 9104–9110.
Bambico FR, Belzung C . Novel insights into depression and antidepressants: a synergy between synaptogenesis and neurogenesis? Curr Top Behav Neurosci 2013; 15: 243–291.
Mateus-Pinheiro A, Patrício P, Bessa JM, Sousa N, Pinto L . Cell genesis and dendritic plasticity: a neuroplastic pas de deux in the onset and remission from depression. Mol Psychiatry 2013; 18: 748–750.
Duman RS . Neurobiology of stress, depression, and rapid acting antidepressants: remodeling synaptic connections. Depress Anxiety 2014; 31: 291–296.
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M et al. mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 2010; 329: 959–964.
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003; 301: 805–809.
Perera TD, Dwork AJ, Keegan KA, Thirumangalakudi L, Lipira CM, Joyce N et al. Necessity of hippocampal neurogenesis for the therapeutic action of antidepressants in adult nonhuman primates. PLoS One 2011; 6: e17600.
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL . A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993; 361: 31–39.
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL . Expression of NMDA receptor-dependent LTP in the hippocampus: bridging the divide. Mol Brain 2013; 6: 5.
Engert F, Bonhoeffer T . Dendritic spine changes associated with hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. Nature 1999; 399: 66–70.
Medvedev NI, Dallérac G, Popov VI, Rodriguez Arellano JJ, Davies HA, Kraev IV et al. Multiple spine boutons are formed after long-lasting LTP in the awake rat. Brain Struct Funct 2014; 219: 407–414.
Abraham WC, Mason-Parker SE, Williams J, Dragunow M . Analysis of the decremental nature of LTP in the dentate gyrus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1995; 30: 367–372.
Cryan JF, Markou A, Lucki I . Assessing antidepressant activity in rodents: recent developments and future needs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2002; 23: 238–245.
Cryan JF, Valentino RJ, Lucki I . Assessing substrates underlying the behavioral effects of antidepressants using the modified rat forced swimming test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2005; 29: 547–569.
Lahmame A, Armario A . Differential responsiveness of inbred strains of rats to antidepressants in the forced swimming test: are Wistar Kyoto rats an animal model of subsensitivity to antidepressants? Psychopharmacology 1996; 123: 191–198.
Lahmame A, del Arco C, Pazos A, Yritia M, Armario A . Are Wistar-Kyoto rats a genetic animal model of depression resistant to antidepressants? Eur J Pharmacol 1997; 337: 115–123.
López-Rubalcava C, Lucki I . Strain differences in the behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs in the rat forced swimming test. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; 22: 191–199.
Tejani-Butt S, Kluczynski J, Paré WP . Strain-dependent modification of behavior following antidepressant treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2003; 27: 7–14.
Hurley LL, Akinfiresoye L, Kalejaiye O, Tizabi Y . Antidepressant effects of resveratrol in an animal model of depression. Behav Brain Res 2014; 268: 1–7.
Paxinos G, Watson C . The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998.
Gilbert ME, Mack CM . Chronic lead exposure accelerates decay of long-term potentiation in rat dentate gyrus in vivo. Brain Res 1998; 789: 139–149.
Tizabi Y, Hauser SR, Tyler KY, Getachew B, Madani R, Sharma Y et al. Effects of nicotine on depressive-like behavior and hippocampal volume of female WKY rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2010; 34: 62–69.
Tizabi Y, Bhatti BH, Manaye KF, Das JR, Akinfiresoye L . Antidepressant-like effects of low ketamine dose is associated with increased hippocampal AMPA/NMDA receptor density ratio in female Wistar-Kyoto rats. Neuroscience 2012; 213: 72–80.
Tronel S, Lemaire V, Charrier V, Montaron MF, Abrous DN . Influence of ontogenetic age on the role of dentate granule neurons. Brain Struct Funct 2015; 220: 645–661.
Norwood BA, Bauer S, Wegner S, Hamer HM, Oertel WH, Sloviter RS et al. Electrical stimulation-induced seizures in rats: a "dose-response" study on resultant neurodegeneration. Epilepsia 2011; 52: e109–e112.
Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M . Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev 2005; 85: 523–569.
Lucas G, Rymar VV, Sadikot AF, Debonnel G . Further evidence for an antidepressant potential of the selective sigma1 agonist SA 4503: electrophysiological, morphological and behavioural studies. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2008; 11: 485–495.
Bruel-Jungerman E, Davis S, Rampon C, Laroche S . Long-term potentiation enhances neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 5888–5893.
Shakesby AC, Anwyl R, Rowan MJ . Overcoming the effects of stress on synaptic plasticity in the intact hippocampus: rapid actions of serotonergic and antidepressant agents. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 3638–3644.
Wang JW, David DJ, Monckton JE, Battaglia F, Hen R . Chronic fluoxetine stimulates maturation and synaptic plasticity of adult-born hippocampal granule cells. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 1374–1384.
Bessa JM, Ferreira D, Melo I, Marques F, Cerqueira JJ, Palha JA et al. The mood-improving actions of antidepressants do not depend on neurogenesis but are associated with neuronal remodeling. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 764–773.
Jeffery KJ, Abraham WC, Dragunow M, Mason SE . Induction of Fos-like immunoreactivity and the maintenance of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of unanesthetized rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1990; 8: 267–274.
Bambico FR, Nguyen NT, Gobbi G . Decline in serotonergic firing activity and desensitization of 5-HT1A autoreceptors after chronic unpredictable stress. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2009; 19: 215–228.
Bambico FR, Bregman T, Diwan M, Li J, Darvish-Ghane S, Li Z et al. Neuroplasticity-dependent and -independent mechanisms of chronic deep brain stimulation in stressed rats. Transl Psychiatry 2015; 5: e674.
Malberg JE, Duman RS . Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003; 28: 1562–1571.
Lucas G, Rymar VV, Du J, Mnie-Filali O, Bisgaard C, Manta S et al. Serotonin4 (5-HT4 receptor agonists are putative antidepressants with a rapid onset of action. Neuron 2007; 55: 712–725.
Alfarez DN, Joëls M, Krugers HJ . Chronic unpredictable stress impairs long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal CA1 area and dentate gyrus in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 17: 1928–1934.
Azmitia EC, Segal M . An autoradiographic analysis of the differential ascending projections of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol 1978; 179: 641–667.
Bliss TV, Goddard GV, Riives M . Reduction of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of the rat following selective depletion of monoamines. J Physiol 1983; 334: 475–491.
Alves SE, Hoskin E, Lee SJ, Brake WG, Ferguson D, Luine V et al. Serotonin mediates CA1 spine density but is not crucial for ovarian steroid regulation of synaptic plasticity in the adult rat dorsal hippocampus. Synapse 2002; 45: 143–151.
Page ME, Detke MJ, Dalvi A, Kirby LG, Lucki I . Serotonergic mediation of the effects of fluoxetine, but not desipramine, in the rat forced swimming test. Psychopharmacology 1999; 147: 162–167.
Sanberg CD, Jones FL, Do VH, Dieguez D Jr, Derrick BE . 5-HT1a receptor antagonists block perforant path-dentate LTP induced in novel, but not familiar, environments. Learn Mem 2006; 13: 52–62.
Abraham WC, Mason SE, Demmer J, Williams JM, Richardson CL, Tate WP et al. Correlations between immediate early gene induction and the persistence of long-term potentiation. Neuroscience 1993; 56: 717–727.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by grants from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR Spade 2009-MNPS-026.01 and MemoNeuro 2010-BLAN-1408.01), as well as by financial supports from the INSERM, the Bordeaux and Lyon 1 Universities, and the Région Aquitaine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanzari, A., Bourcier-Lucas, C., Freyssin, A. et al. Inducing a long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus is sufficient to produce rapid antidepressant-like effects. Mol Psychiatry 23, 587–596 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.94
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.94
This article is cited by
-
2-Pentadecyl-2-oxazoline ameliorates memory impairment and depression-like behaviour in neuropathic mice: possible role of adrenergic alpha2- and H3 histamine autoreceptors
Molecular Brain (2021)
-
Activation of the p11/SMARCA3/Neurensin-2 pathway in parvalbumin interneurons mediates the response to chronic antidepressants
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Ketamine and its metabolite, (2R,6R)-HNK, restore hippocampal LTP and long-term spatial memory in the Wistar-Kyoto rat model of depression
Molecular Brain (2020)