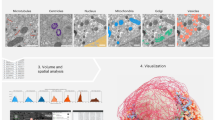
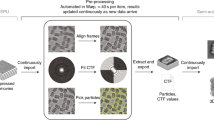
Abstract
Today’s volume electron microscopy techniques produce large image datasets on the order of thousands of gigabytes. The vast amount of data makes manual analysis almost infeasible, and data storing and processing challenging. Specialized infrastructure and software was therefore developed during the last decade to address these problems, ranging from distributed and versioned 3D image stores to deep neural network architectures optimized for the segmentation of objects of interest. Illustrated by the example of connectomics, the reconstruction of neural circuitry from 3D images of brain tissue, the most common approaches and solutions are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggman KL, Helmstaedter M, Denk W (2011) Wiring specificity in the direction-selectivity circuit of the retina. Nature 471:183–188
Ohyama T, Schneider-Mizell CM, Fetter RD et al (2015) A multilevel multimodal circuit enhances action selection in Drosophila. Nature 520:633–639
Takemura S-Y, Bharioke A, Lu Z et al (2013) A visual motion detection circuit suggested by Drosophila connectomics. Nature 500:175–181
Morgan JL, Berger DR, Wetzel AW, Lichtman JW (2016) The fuzzy logic of network connectivity in mouse visual thalamus. Cell 165:192–206
Kasthuri N, Hayworth KJ, Berger DR et al (2015) Saturated reconstruction of a volume of neocortex. Cell 162:648–661
Lee W-CA, Bonin V, Reed M et al (2016) Anatomy and function of an excitatory network in the visual cortex. Nature 532:370–374
Kornfeld J, Benezra SE, Narayanan RT et al (2017) EM connectomics reveals axonal target variation in a sequence-generating network. eLife 6
Helmstaedter M, Briggman KL, Turaga SC et al (2013) Connectomic reconstruction of the inner plexiform layer in the mouse retina. Nature 500:168–174
Kim JS, Greene MJ, Zlateski A et al (2014) Space-time wiring specificity supports direction selectivity in the retina. Nature 509:331–336
Wanner AA, Genoud C, Masudi T et al (2016) Dense EM-based reconstruction of the interglomerular projectome in the zebrafish olfactory bulb. Nat Neurosci 19:816–825
Schmidt H, Gour A, Straehle J et al (2017) Axonal synapse sorting in medial entorhinal cortex. Nature 549:469–475
Zheng Z, Lauritzen JS, Perlman E et al (2018) A complete electron microscopy volume of the brain of adult Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 174:730–743.e22
Bock DD, Lee W-CA, Kerlin AM et al (2011) Network anatomy and in vivo physiology of visual cortical neurons. Nature 471:177–182
Svara FN, Kornfeld J, Denk W, Bollmann JH (2018) Volume EM reconstruction of spinal cord reveals wiring specificity in speed-related motor circuits. Cell Rep 23:2942–2954
Vishwanathan A, Daie K, Ramirez AD et al (2017) Electron microscopic reconstruction of functionally identified cells in a neural integrator. Curr Biol 27:2137–2147.e3
Wanner AA, Kirschmann MA, Genoud C (2015) Challenges of microtome-based serial block-face scanning electron microscopy in neuroscience. J Microsc 259:137–142
Kornfeld J, Denk W (2018) Progress and remaining challenges in high-throughput volume electron microscopy. Curr Opin Neurobiol 50:261–267
Denk W, Horstmann H (2004) Serial block-face scanning electron microscopy to reconstruct three-dimensional tissue nanostructure. PLoS Biol 2:e329
Briggman KL, Bock DD (2012) Volume electron microscopy for neuronal circuit reconstruction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 22:154–161
Marr B (2018) How much data do we create every day? The mind-blowing stats everyone should read. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2018/05/21/how-much-data-do-we-create-every-day-the-mind-blowing-stats-everyone-should-read/. Accessed 15 Sep 2018
Cardona A, Saalfeld S, Schindelin J et al (2012) TrakEM2 software for neural circuit reconstruction. PLoS One 7:e38011
Saalfeld S, Cardona A, Hartenstein V, Tomancak P (2009) CATMAID: collaborative annotation toolkit for massive amounts of image data. Bioinformatics 25:1984–1986
The HDF5® library & file format – the HDF Group. The HDF Group. https://www.hdfgroup.org/solutions/hdf5/. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
HDF5 plugin for ImageJ. https://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/resources/opensource/imagej_plugins/hdf5.html. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
Dorkenwald S, Schubert PJ, Killinger MF et al (2017) Automated synaptic connectivity inference for volume electron microscopy. Nat Methods 14:435–442
ELEKTRONN – Convolutional neural network toolkit in python. Fast GPU acceleration and easy usage. http://elektronn.org. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
Katz WT, Plaza SM (2019) DVID: distributed versioned image-oriented dataservice. Front Neural Circuits 13:5
Kleissas D, Hider R, Pryor D et al (2017) The block object storage service (bossDB): a cloud-native approach for petascale neuroscience discovery. bioRxiv 2017:217745
Burns R, Perlman E, Baden A et al (2018) A community-developed open-source computational ecosystem for big neuro data. Nat Methods 15(11):846–847
Berger DR, Seung HS, Lichtman JW (2018) VAST (volume annotation and segmentation tool): efficient manual and semi-automatic labeling of large 3D image stacks. Front Neural Circuits 12:88
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2008) Digital image processing. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Pizer SM, Philip Amburn E, Austin JD et al (1987) Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 39:355–368
Heinrich L, Bogovic JA, Saalfeld S (2017) Deep learning for isotropic super-resolution from non-isotropic 3D electron microscopy. Lect Notes Comput Sci 2017:135–143
Jain V (2017) Adversarial image alignment and interpolation. arXiv:1707.00067
Hanslovsky P, Bogovic JA, Saalfeld S (2017) Image-based correction of continuous and discontinuous non-planar axial distortion in serial section microscopy. Bioinformatics 33:1379–1386
Buniatyan D, Macrina T, Ih D et al (2017) Deep learning improves template matching by normalized cross correlation. arXiv:1705.08593
Lowe DG (1999) Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: Proceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference on computer vision
SRI International. Artificial Intelligence Center, Fischler MA, Bolles RC (1980) Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun ACM 24(6):381–395
Sun C, Beare R, Hilsenstein V, Jackway P (2006) Mosaicing of microscope images with global geometric and radiometric corrections. J Microsc 224:158–165
Saalfeld S, Fetter R, Cardona A, Tomancak P (2012) Elastic volume reconstruction from series of ultra-thin microscopy sections. Nat Methods 9:717–720
Kaynig V, Fischer B, Müller E, Buhmann JM (2010) Fully automatic stitching and distortion correction of transmission electron microscope images. J Struct Biol 171:163–173
TrakEM2. ImageJ. https://imagej.net/TrakEM2. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
Image Transformation Web Services. https://www.janelia.org/image-transformation-web-services. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
Helmstaedter M, Briggman KL, Denk W (2011) High-accuracy neurite reconstruction for high-throughput neuroanatomy. Nat Neurosci 14:1081–1088
Boergens KM, Berning M, Bocklisch T et al (2017) webKnossos: efficient online 3D data annotation for connectomics. Nat Methods 14:691–694
Sommer C, Straehle C, Kothe U, Hamprecht FA (2011) Ilastik: interactive learning and segmentation toolkit. In: 2011 IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: from nano to macro
Turaga SC, Murray JF, Jain V et al (2010) Convolutional networks can learn to generate affinity graphs for image segmentation. Neural Comput 22:511–538
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv [cs.CV]. arXiv:1505.04597
Ciresan D, Giusti A, Gambardella LM (2012) Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2012:1–9
SNEMI3D. http://brainiac2.mit.edu/SNEMI3D/. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
CREMI. https://cremi.org/. Accessed 3 Mar 2019
Beier T, Pape C, Rahaman N et al (2017) Multicut brings automated neurite segmentation closer to human performance. Nat Methods 14:101
Berning M, Boergens KM, Helmstaedter M (2015) SegEM: efficient image analysis for high-resolution connectomics. Neuron 87:1193–1206
Nunez-Iglesias J, Kennedy R, Parag T et al (2013) Machine learning of hierarchical clustering to segment 2D and 3D images. PLoS One 8:e71715
Pape C, Beier T, Li P et al (2017) Solving large multicut problems for connectomics via domain decomposition. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCVW)
Januszewski M, Kornfeld J, Li PH et al (2018) High-precision automated reconstruction of neurons with flood-filling networks. Nat Methods 15(8):605–610
Meirovitch Y, Matveev A, Saribekyan H et al (2016) A multi-pass approach to large-scale connectomics. arXiv [q-bio.QM]
Januszewski M, Maitin-Shepard J, Li P et al (2016) Flood-filling networks. arXiv [cs.CV]
Kreshuk A, Straehle CN, Sommer C et al (2011) Automated detection and segmentation of synaptic contacts in nearly isotropic serial electron microscopy images. PLoS One 6:e24899
Kreshuk A, Koethe U, Pax E et al (2014) Automated detection of synapses in serial section transmission electron microscopy image stacks. PLoS One 9:e87351
Roncal WG, Pekala M, Kaynig-Fittkau V et al (2015) VESICLE: volumetric evaluation of synaptic interfaces using computer vision at large scale. Proceedings of the British machine vision conference 2015
Staffler B, Berning M, Boergens KM et al (2017) SynEM, automated synapse detection for connectomics. eLife 6:e26414
Schubert P, Dorkenwald S, Januszewski M et al (2019) Learning cellular morphology with neural networks. Nat Commun 10:2736
Zung J, Tartavull I, Lee K, Seung HS (2017) An error detection and correction framework for connectomics. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2018)
Rolnick D, Meirovitch Y, Parag T et al (2017) Morphological error detection in 3D segmentations. arXiv:1705.10882
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the authors of the software packages listed in Table 1 for providing details on their software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kornfeld, J., Svara, F., Wanner, A.A. (2020). Image Processing for Volume Electron Microscopy. In: Wacker, I., Hummel, E., Burgold, S., Schröder, R. (eds) Volume Microscopy . Neuromethods, vol 155. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0691-9_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0691-9_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0690-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0691-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols