Abstract
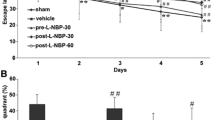
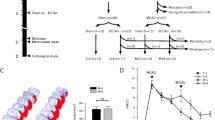
Rationale for Pharmacotherapy of Remacemide in 4-VO Model: Studies have reported memory impairment (25) and a selective and delayed onset of CA1 pyramidal cell necrosis in man after global ischemia (18). Memory tests demonstrated anterograde amnesia in a patient (R.B.) who developed circumscribed memory impairment following an ischemic episode. Prior to death, R.B. showed no signs of cognitive impairments other than memory loss. Histological evaluations revealed selective and bilateral CA1 pyramidal cell loss (28). The 4-VO model is widely used for studying the phenomenon of “selectively vulnerable, delayed onset” pathophysiology of hippocampal CAl neurons in global ischemia (19,20). Post-ischemic pharmacological treatments may modify the functional and morphological outcome of global ischemia in the hippocampus, involving ischemically compromised but possibly still “viable” CA1 neurons (20). There is credible evidence for a critical role of the hippocampus in a specific type of spatial, representational, or episodic memory (23,24,28). Circumscribed memory impairment with selective CA1 cell necrosis has been reported in the 4-VO model (15,26). Protection of hippocampal CA1 cell damage may represent a valid “neural endpoint”, or target for drug intervention (20).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchan, A.M. (1990) Do NMDA antagonists protect against cerebral ischemia: are clinical trials warranted? Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 2:1–26.
Buchan, A.M., Li, H., Cho, S., and Pulsinelli, W.A. (1991) Blockade of the AMPA receptor prevents CA1 hippocampal injury following severe but transient forebrain ischemia in adult rats. Submitted: J. Neurosci.
Busto, R., Dietrich, W.O., Globus, M.Y.-T., and Ginsberg, M.D. (1989) The importance of brain temperature of cerebral ischemic injury. Stroke. 20:1113–1114.
Choi, D.W. (1990) Cerebral hypoxia: some new approaches and unanswered questions. J. Neurosci. 10:2493–2501.
Cotman, C.W., and Monaghan, D.T. (1988) Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission: NMDA receptors and Hebb-type synaptic plasticity. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 11:61–80.
Cotman, C.W., Monaghan, D.T., Ottersen, O.P., and Storm-Mathisen, J. (1987) Anatomical organization of excitatory amino acid receptors and their pathways. TINS. 10(7):273–280.
Diemer, N.H., Johansen, F.F., Sheardown, M., Honore, T., and Jorgensen, M.B. (1990) The role of excitatory mechanisms for the development of ischemia-induced damage in rat hippocampus. In: Krieglstein, J., and Oberpichler, H., eds. Pharmacology of Cerebral Ischemia. Wiss. Ver1.Gis. pp. 113–116.
Ginsberg, M.D., and Busto, R. (1989) Rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 20:1627–1642.
Ginsberg, M.D., and Dietrich, W.O. (1989) Preface/Introduction. In: Ginsberg, M.D., and Dietrich, W.O., eds. Cerebrovascular Diseases. New York: Raven Press, pp. v–vii.
Hollmann, M., Hartley, M., and Heinemann, S. (1991) Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA-gated receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 252:851–853.
Keith, J.R., and Rudy, J.W. (1990) Why NMDA-receptor-dependent long-term potentiation may not be a mechanism of learning and memory: reappraisal of the NMDA-receptor blockade stragety. Psychobiology. 18:251–257.
Meldrum, B. (1989) Excitotoxicity in ischemia: an overview. In: Ginsberg, M.D., and Dietrich, W.D., eds. Cerebrovascular Diseases. New York: Raven Press, pp. 47–60.
Morris, R.G.M. (1989) Synaptic plasticity and learning: selective impairment of learning in rats and blockade of long-term potentiation in vivo by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist AP5. J. Neurosci. 9:3040–3057.
Nellgard, B., and Wieloch, T. (1991) Post-ischemic blockade of AMPA but not NMDA receptors mitigate neuronal damage in the rat brain following transient but severe cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. (in press).
Ordy, J.M., Thomas, G.J., Volpe, B.T., Dunlap, W.P., and Colombo, P.M. (1988) An animal model of human-type memory loss based on aging, lesion, forebrain ischemia, and drug studies with the rat. Neurobiol. Aging. 9:667–683.
Ordy, J.M., Wengenack, T.M., Bialobok, P., Coleman, P.D., Rodier, P., Baggs, R.B., Dunlap, W.P., and Kates, B. (1991) Selective vulnerability, early progression of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell degeneration and GFAP-positive astrocyte reactivity in the rat 4–VO model of transient global ischemia. Exp. Neurol. (in press).
Palmer, G.C., Stagnitto, M.L., Ordy, J.M., Griffith, R.C., Napier, J.J., Gentile, R.J., Woodhead, J.H., and Swinyard, E.A. (1991) Preclinical profile of stereoisomers of the anticonvulsant remacemide in mice. Epilepsy Res. 8:36–48.
Petito, C.K., Feldmann, E., Pulsinelli, W.A., and Plum, F. (1987) Delayed hippocampal damage in humans following cardiorespiratory arrest. Neurology. 37:1281–1286.
Pulsinelli, W.A., and Buchan, A.M. (1988) The 4-vessel occlusion rat model: method for complete occlusion of the vertebral arteries and control of the collateral circulation. Stroke. 19:913–914.
Pulsinelli, W.A., and Buchan, A.M. (1990) The NMDA receptor/ion channel its importance to in vivo ischemic injury to selectively vulnerable neurons. In: Krieglstein, J., and Oberpichler, H., eds. Pharmacology of Cerebral Ischemia. Wiss. Verl.-Ges. pp. 169–175.
Ross, D.T., and Graham, D.I. (1991) Selective loss and selective sparinl of neurons in the thalamic reticular nucleus following human cardiac arrest. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Abstr. 11(suppl 2):S855.
Sheardown, M.J., Nielsen, E.O., Hansen, A.J., Jacobsen, P., and Honore, T. (1990) 2,3–Dihydroxy–6–nitro–7–sulfamoyl–benzo(F)quinoxaline: a neuroprotectant for cerebral ischemia. Science. 247:571–574.
Squire, L.R. (1986) Mechanisms of memory. Science. 232:1612–1619.
Thomas, G.J., and Ordy, J.M. (1991) Memory: a behavioristic and neuroscience approach. In: Squire, L.R., and Butters, N., eds. Neuropsychology of Memory. New York: Guilford Press, (in press).
Volpe, B.T., and Petito, C.K. (1985) Dementia with bilateral medial temporal lobe ischemia. Neurology. 35:1793–1797
Volpe, B.T., and Davis, H.P. (1989) An approach to the functional nalysis of an animal model of ischemic injury. In: Ginsberg, M.D., and Dietrich, W.D., eds. Cerebrovascular Diseases. New York: Raven Press, pp. 335–340
Willets, J., Balster, R.L., and Leander, J.D. (1990) The behavioral pharmacology of NMDA receptor antagonists. TIPS. 11(10):423–428.
Zola-Morgan, S., Squire, L.R., and Amaral, D.G. (1986) Human amnesia an the medial temporal region: enduring memory impairment following a bilateral lesion limited to field CA1 of the hippocampus. J. Neurosci 6:2950–2967.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ordy, J.M. et al. (1992). Pharmacological Effects of Remacemide and MK-801 on Memory and Hippocampal CA1 Damage in the Rat Four-Vessel Occlusion (4-VO) Model of Global Ischemia. In: Globus, M.YT., Dietrich, W.D. (eds) The Role of Neurotransmitters in Brain Injury. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3452-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3452-5_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6528-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3452-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive