Abstract
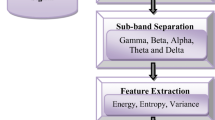
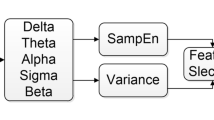
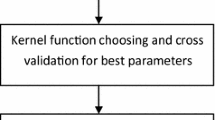
Sleep apnea syndrome is one the most prevalent sleep disorders. The accurate diagnosis and treatment of apnea by physicians can help to avoid its destructive effects in the long term. Electroencephalogram (EEG) records activity of the brain from different areas of scalp and can be an appropriate method to diagnose sleep apnea. In this work, we proposed a Computer Aided Diagnosis System (CADS) for sleep apnea based on complexity features of EEG. At first, EEG time series of 20 participants were decomposed into six frequency bands (delta, theta, alpha, sigma, beta, and gamma) by using bandpass Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filters. Then, complexity features such as fractals, Lempel-Ziv Complexity (LZC), entropies, and generalized Hurst exponent that was used for the first time to detect sleep apnea from EEG signals, were extracted from each frequency band. The minimum-redundancy maximum-relevance (mRMR) algorithm was applied to sort 120 features of three EEG channels. Finally, two popular classifiers, Support Vector Machine (SVM) and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), were used to detect sleep apnea. \( 99.33\%\) accuracy was obtained using the SVM classifier and generalized hurst exponent had an effective contribution to detect apnea.
Supported by organization x.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alqassim, S., et al.: Sleep apnea monitoring using mobile phones. In: International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom). IEEE (2012)
Azim, Md.R., et al.: Analysis of EEG and EMG signals for detection of sleep disordered breathing events. In: International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (2010)
Bhattacharjee, A., et al.: Sleep apnea detection based on Rician modeling of feature variation in multiband EEG signal. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 23(3), 1066–81074 (2018)
Bello, S.A., Alqasemi, U.: Computer Aided Detection of Obstructive Sleep Apnea from EEG Signals. SSRN 3890660 (2021)
Devuyst, S., Dutoit, T., Kerkhofs, M.: The DREAMS databases and assessment algorithm. Zenodo, Genève (2005)
Gutta, S., et al.: Cardiorespiratory model-based data-driven approach for sleep apnea detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 22(4), 1036–1045 (2017)
Gaurav, G., Anand, R.S., Kumar, V.: EEG based cognitive task classification using multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis. Cogn. Neurodyn. 15(6), 999–1013 (2021)
Jayaraj, R., Mohan, J.: Classification of sleep apnea based on sub-band decomposition of EEG signals. Diagnostics 11(9) (2021)
Kandel, E.R., et al.: Principles of Neural Science, vol. 3. McGraw-Hill, New York (2000)
Kang, J., et al.: EEG entropy analysis in autistic children. J. Clin. Neurosci. 62, 199–206 (2019)
Karegar, F.P., Fallah, A., Rashidi, S.: ECG based human authentication with using Generalized Hurst Exponent. In: Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE) (2017)
Kannathal, N., et al.: Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 80(3), 187–194 (2005)
Lin, S.-Y., et al.: EEG signal analysis of patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) using power spectrum and fuzzy entropy. In: International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD) (2017)
Li, X., Ouyang, G., Richards, D.A.: Predictability analysis of absence seizures with permutation entropy. Epilepsy Res. 77(1), 70–74 (2007)
Liu, D., Pang, Z., Lloyd, S.R.: A neural network method for detection of obstructive sleep apnea and narcolepsy based on pupil size and EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 19(2), 308–318 (2008)
Li, Y., et al.: Interhemispheric brain switching correlates with severity of sleep-disordered breathing for obstructive sleep apnea patients. Appl. Sci. 9(8), 1568 (2019)
Lahmiri, S.: Generalized Hurst exponent estimates differentiate EEG signals of healthy and epileptic patients. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 490, 378–385 (2018)
Gorriz, J.M., et al.: Artificial intelligence within the interplay between natural and artificial computation: advances in data science, trends and applications. Neurocomputing 410, 237–270 (2020)
Subha, D.P., et al.: EEG signal analysis: a survey. J. Med. Syst. 34(2), 195–212 (2010)
Sharma, A., Amarnath, M., Kankar, P.K.: Feature extraction and fault severity classification in ball bearings. J. Vibr. Control 22(1), 176–192 (2016)
Saha, S., et al.: An approach for automatic sleep apnea detection based on entropy of multi-band EEG signal. In: IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON) (2016)
Senaratna, C.V., et al.: Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in the general population: a systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 34, 70–81 (2017)
Shahnaz, C., Minhaz, A.T., Ahamed, S.T.: Sub-frame based apnea detection exploiting delta band power ratio extracted from EEG signals. In: IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON) (2016)
Schluter, T., Conrad, S.: An approach for automatic sleep stage scoring and apnea-hypopnea detection. Front. Comput. Sci. 6(2), 230–241 (2012)
Tibdewal, M.N., et al.: Multiple entropies performance measure for detection and localization of multi-channel epileptic EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 38, 158–167 (2017)
Taran, S., Bajaj, V.: Sleep apnea detection using artificial bee colony optimize Hermite basis functions for EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69(2), 608–616 (2019)
Taran, S., et al.: Detection of sleep apnea events using electroencephalogram signals. Appl. Acoust. 181, 108–137 (2021)
Uthayakumar, R.: Fractal dimension in Epileptic EEG signal analysis. In: Banerjee, S., Rondoni, L. (eds.) Applications of Chaos and Nonlinear Dynamics in Science and Engineering-Vol. 3, pp. 103–157. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34017-8_4
Ubeyli, E.D., et al.: Analysis of sleep EEG activity during hypopnoea episodes by least squares support vector machine employing AR coefficients. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(6), 4463–4467 (2010)
Wang, H., Guo, Z., Du, W.: Diagnosis of rolling element bearing based on multifractal detrended fluctuation analyses and continuous hidden Markov model. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 35(8), 3313–3322 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-021-0705-y
Wang, Y., et al.: An efficient method to detect sleep hypopnea-apnea events based on EEG signals. IEEE Access 9, 641–650 (2020)
Wang, Y., et al.: A Robust Sleep Apnea-hypopnea Syndrome Automated Detection Method Based on Fuzzy Entropy Using Single Lead-EEG Signals (2021)
Xin, X., Yaru, Z., Sanli, Y., et al.: A New Method for Detecting Sleep Apnea. Research Square (2022)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 100, 9–34 (1999)
Zhao, X., et al.: Classification of sleep apnea based on EEG sub-band signal characteristics. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–11 (2021)
Zhou, J., Wu, X., Zeng, W.: Automatic detection of sleep apnea based on EEG detrended fluctuation analysis and support vector machine. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 29(6), 767–772 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-015-9664-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gholami, B., Behboudi, M.H., Khadem, A., Shoeibi, A., Gorriz, J.M. (2022). Sleep Apnea Diagnosis Using Complexity Features of EEG Signals. In: Ferrández Vicente, J.M., Álvarez-Sánchez, J.R., de la Paz López, F., Adeli, H. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Neuroscience: Affective Analysis and Health Applications. IWINAC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13258. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06242-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06242-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06241-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06242-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)