Abstract
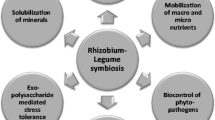
Rhizobia are a diverse group of nodule-forming bacteria known for inhabiting the soil and establishing functional symbiotic associations with legume plants. Rhizobial inoculants are widely employed in agricultural practices to reduce nitrogen fertilizer inputs on legume crops due to rhizobial ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. Here we argue that rhizobia should also be considered an alternative method to agricultural pesticides use in plant disease management. Several rhizobial strains have been reported leading to disease resistance, while also promoting plant yield and biomass increases. The biocontrol properties of rhizobia could be associated with lytic enzymes and antimicrobial secondary metabolite production, especially when regarding diseases affecting root systems of plants. Aside from the action of antifungal molecules, suppression of plant diseases could be related to rhizobial plant growth promotion and/or symbiotic efficiency. Moreover, rhizobia have been found to induce systemic resistance to immunize plants, which is a valuable process, considering foliar and viral diseases. This review will focus on rhizobial mechanisms and efficacy to biocontrol diseases caused by different classes of pathogens affecting leguminous and even non-leguminous plants.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Ghaffar MH, Abo-El Maaty SA, Mahmoud SY (2011) Identification and detectability of broad bean stain virus in broad bean seeds and effects on nodulation. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 44:390–403. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235400903092925
Abu-Irmaileh B (1998) Present status of Orobanche control in the Near East. In: Current problems in Orobanche researches. Proceedings of the 4th International Orobanche Workshop September 23–26, 1998 Albena, Bulgaria, pp 425–430
Aguilar JAP, Andreu V, Campo J, Picó Y, Masiá A (2017) Pesticide occurrence in the waters of Júcar River, Spain from different farming landscapes. Sci Total Environ 607:752–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.176
Ahn IP, Park K, Kim CH (2002) Rhizobacteria-induced resistance perturbs viral disease progress and triggers defense-related gene expression. Mol Cells 13:302–308
Akhtar MS, Shakeel U, Siddiqui ZA (2010) Biocontrol of Fusarium wilt by Bacillus pumilus, Pseudomonas alcaligenes and Rhizobium sp. on lentil. Turk J Biol 34:1–7
Amarger N, Macheret V, Laguerre G (1997) Rhizobium gallicum sp. nov. and Rhizobium giardinii sp. nov., from Phaseolus vulgaris nodules. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 47:996–1006
Antoun H, Beauchamp CJ, Goussard N, Chabot R, Lalande R (1998) Potential of Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium species as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on non-legumes: effect on radishes (Raphanus sativus L.). In: Molecular microbial ecology of the soil. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 57–67
Ardley JK, Parker MA, De Meyer SE, Trengove RD, O’Hara GW, Reeve WG, Yates RJ, Dil-worth MJ, Willems A, Howieson JG (2012) Microvirga lupini sp. nov., Microvirga lotononidis sp. nov. and Microvirga zambiensis sp. nov. are alphaproteobacterial root-nodule bacteria that specifically nodulate and fix nitrogen with geographically and taxonomically separate legume hosts. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2579–2588. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.035097-0
Arora N, Kang S, Maheshwari D (2001) Isolation of siderophore-producing strains of Rhizobium meliloti and their biocontrol potential against Macrophomina phaseolina that causes charcoal rot of groundnut. Curr Sci 81:673–677
Ashoub A, Amara M (2010) Biocontrol activity of some bacterial genera against root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. J Am Sci 6:321–328
Ballhorn DJ, Reisdorff C, Pfanz H (2011) Quantitative effects of enhanced CO2 on jasmonic acid induced plant volatiles of lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.). J Appl Bot Food Qual 84:65–71
Ballhorn DJ, Kautz S, Schädler M (2013) Induced plant defense via volatile production is dependent on rhizobial symbiosis. Oecologia 172:833–846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-012-2539-x
Baraúna AC, Rouws LFM, Simoes-Araujo JL, dos Reis Junior FB, Iannetta PPM, Maluk M, Goi SR, Reis VM, James EK, Zilli JE (2016) Rhizobium altiplani sp. nov., isolated from effective nodules on Mimosa pudica growing in untypically alkaline soil in central Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4118–4124. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001322
Bardin M, Ajouz S, Comby M, Lopez-Ferber M, Graillot B, Siegwart M, Nicot PC (2015) Is the efficacy of biological control against plant diseases likely to be more durable than that of chemical pesticides? Front Plant Sci 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00566
Bass C, Denholm I, Williamson MS, Nauen R (2015) The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides. Pestic Biochem Physiol 121:78–87
Bautista VV, Monsalud RG, Yokota A (2010) Devosia yakushimensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.011254-0
Bhagat D, Sharma P, Sirari A, Kumawat K (2014) Screening of Mesorhizobium spp. for control of Fusarium wilt in chickpea in vitro conditions. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3:923–930
Bird DM, Koltai H (2000) Plant parasitic nematodes: habitats, hormones, and horizontally-acquired genes. J Plant Growth Regul 19:183–194
Blankson G, Osei-Fosu P, Adeendze E, Ashie D (2016) Contamination levels of organophosphorus and synthetic pyrethroid pesticides in vegetables marketed in Accra, Ghana. Food Control 68:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.03.045
Bouraoui M, Abbes Z, Abdi N, Hmissi I, Sifi B (2012) Evaluation of efficient Rhizobium isolates as biological control agents of Orobanche foetida Poir. parasitizing Vicia faba L. minor in Tunisia. Bulg J Agric Sci 18:557–564
Bournaud C, Moulin L, Cnockaert M, de Faria S, Prin Y, Severac D, Vandamme P (2017) Paraburkholderia piptadeniae sp. nov. and Paraburkholderia ribeironis sp. nov., two root-nodulating symbiotic species of Piptadenia gonoacantha in Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001648
Brevik E, Cerdà A, Mataix-Solera J, Pereg L, Quinton J, Six J, Van Oost K (2015) The interdisciplinary nature of SOIL. Soil 1:117–129. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-1-117-2015
Cerri MR, Frances L, Kelner A, Fournier J, Middleton PH, Auriac M-C, Mysore KS, Wen J, Erard M, Barker DG, Oldroyd GE, de Carvalho-Niebel F (2016) The symbiosis-related ERN transcription factors act in concert to coordinate rhizobial host root infection. Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00230
Chakraborty U, Purkayastha R (1984) Role of rhizobitoxine in protecting soybean roots from Macrophomina phaseolina infection. Can J Microbiol 30:285–289
Chandra S, Choure K, Dubey RC, Maheshwari DK (2007) Rhizosphere competent Mesorhizobiumloti MP6 induces root hair curling, inhibits Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and enhances growth of Indian mustard (Brassica campestris). Braz J Microbiol 38:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822007000100026
Chen WM, James EK, Coenye T, Chou J-H, Barrios E, de Faria SM, Elliott GN, Sheu S-Y, Sprent JI, Vandamme P (2006) Burkholderia mimosarum sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa spp. from Taiwan and South America. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1847–1185. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64325-0
Chowdhury J, Srivastava R, Singh R (1987) Effect of common bean mosaic virus infection on nitrogenase activity in root nodules of mung bean. J Plant Dis Protect 94:126–129
Crowley DE (2006) Microbial siderophores in the plant rhizosphere. In: Iron nutrition in plants and rhizospheric microorganisms. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 169–198
Dall’Agnol RF, Ribeiro RA, Delamuta JRN, Ormeño-Orrillo E, Rogel MA, Andrade DS, Mar-tínez-Romero E, Hungria M (2014) Rhizobium paranaense sp. nov., an effective N2-fixing symbiont of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) with broad geographical distribution in Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3222–3229. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.064543-0
Dall’Agnol RF, Plotegher F, Souza RC, Mendes IC, dos Reis Junior FB, Béna G, Moulin L, Hungria M (2016) Paraburkholderia nodosa is the main N2-fixing species trapped by promiscuous common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in the Brazilian ‘Cerradão’. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw108
Datta B, Chakrabartty PK (2014) Siderophore biosynthesis genes of Rhizobium sp. isolated from Cicer arietinum L. 3 Biotech 4:391–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-013-0164-y
De Bruijn FJ (2015) Biological nitrogen fixation. In: Principles of plant-microbe interactions. Springer, Leiden, pp 215–224
Desbrosses GJ, Stougaard J (2011) Root nodulation: a paradigm for how plant-microbe symbiosis influences host developmental pathways. Cell Host Microbe 10:348–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2011.09.005
Deshwal V, Dubey R, Maheshwari D (2003) Isolation of plant growth-promoting strains of Bradyrhizobium (Arachis) sp. with biocontrol potential against Macrophomina phaseolina causing charcoal rot of peanut. Curr Sci:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2011.09.005
Dreyfus B, Garcia J-L, Gillis M (1988) Characterization of Azorhizobium caulinodans gen. nov., sp. nov., a stem-nodulating nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from Sesbania rostrate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 38:89–98
Dubey P, Gupta G, Dubey R (2012) Culture filtrates of plant growth promoting Bradyrhizobium sp. (Vigna) strains VR1 and VR2 inhibit growth and sclerotia germination of Macrophomina phaseolina in vitro. New York Sci J 5:1–9
Elbadry M, Taha R, Eldougdoug KA, Gamal-Eldin H (2006) Induction of systemic resistance in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) to bean yellow mosaic potyvirus (BYMV) via seed bacterization with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. J Plant Dis Protect 113:247–251
Elsharkawy M, Shimizu M, Takahashi H, Hyakumachi M (2013) Induction of systemic resistance against Cucumber mosaic virus by Penicillium simplicissimum GP17-2 in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant Pathol 61:964–976. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.SI.07.2012.01
Figueredo MS, Tonelli ML, Ibáñez F, Morla F, Cerioni G, del Carmen Tordable M, Fabra A (2017) Induced systemic resistance and symbiotic performance of peanut plants challenged with fungal pathogens and co-inoculated with the biocontrol agent Bacillus sp. CHEP5 and Bradyrhizobium sp. SEMIA6144. Microbiol Res 197:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.01.002
Fox JE, Gulledge J, Engelhaupt E, Burow ME, McLachlan JA (2007) Pesticides reduce symbiotic efficiency of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia and host plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:10282–10287. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611710104
Franco-Andreu L, Gómez I, Parrado J, García C, Hernández T, Tejada M (2016) Behavior of two pesticides in a soil subjected to severe drought. Effects on soil biology. Appl Soil Ecol 105:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.04.001
Fuhrmann J (1990) Symbiotic effectiveness of indigenous soybean bradyrhizobia as related to serological, morphological, rhizobitoxine, and hydrogenase phenotypes. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:224–229
Ganesan S, Kuppusamy RG, Sekar R (2007) Integrated management of stem rot disease (Sclerotium rolfsii) of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) using Rhizobium and Trichoderma harzianum (ITCC-4572). Turk J Agric For 31:103–108
Ghosh PK, Kumar De T, Maiti TK (2015) Production and metabolism of indole acetic acid in root nodules and symbiont (Rhizobium undicola) isolated from root nodule of aquatic me-dicinal legume Neptunia oleracea Lour. J Bot 2015:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/575067
Gleadow R, Foley W, Woodrow I (1998) Enhanced CO2 alters the relationship between photosynthesis and defence in cyanogenic Eucalyptus cladocalyx F. Muell. Plant Cell Environ 21:12–22
Glick BR (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica. https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/963401
Grobelak A, Hiller J (2017) Bacterial siderophores promote plant growth: screening of catechol and hydroxamate siderophores. Int J Phytoremediation 19:825–833. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1290581
Heil M (2004) Direct defense or ecological costs: responses of herbivorous beetles to volatiles released by wild lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus). J Chem Ecol 30:1289–1295
Herridge DF, Peoples MB, Boddey RM (2008) Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9668-3
Horiuchi J, Prithiviraj B, Bais HP, Kimball BA, Vivanco JM (2005) Soil nematodes mediate positive interactions between legume plants and rhizobium bacteria. Planta 222:848–857
Huang JS (2001) Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and the effects of diseases on nodulation and nitrogen fixation. In: Plant pathogenesis and resistance. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 175–236
Hungria M, Franchini JC, Campo RJ, Crispino CC, Moraes JZ, Sibaldelli RNR, Mendes IC, Arihara J (2006) Nitrogen nutrition of soybean in Brazil: contributions of biological N2 fixation and N fertilizer to grain yield. Can J Plant Sci 86:927–939
Hungria M, Nogueira MA, Araujo RS (2013) Co-inoculation of soybeans and common beans with rhizobia and azospirilla: strategies to improve sustainability. Biol Fertil Soils 49:791–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0771-5
Jensen CE, Percich J, Graham P (2002) Integrated management strategies of bean root rot with Bacillus subtilis and Rhizobium in Minnesota. Field Crops Res 74:107–115
Jiao YS, Yan H, Jil HJ, Liu YH, Sui XH, Zhang XX, Wang ET, Chen WX, Chen WF (2015) Phyllobacterium sophorae sp. nov., a symbiotic bacterium isolated from root nodules of Sophora flavescens. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.067017-0
Jones KM, Sharopova N, Lohar DP, Zhang JQ, VandenBosch KA, Walker GC (2008) Differential response of the plant Medicago truncatula to its symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti or an exopolysaccharide-deficient mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:704–709. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709338105
Jordan D (1982) Transfer of Rhizobium japonicum Buchanan 1980 to Bradyrhizobium gen. nov., a genus of slow-growing, root nodule bacteria from leguminous plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 32:136–139
Jourand P, Giraud E, Béna G, Sy A, Willems A, Gillis M, Dreyfus B, de Lajudie P (2004) Methylobacterium nodulans sp. nov., for a group of aerobic, facultatively methylotrophic, legume root-nodule-forming and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2269–2273. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02902-0
Kandan A, Ramiah M, Vasanthi V, Radjacommare R, Nandakumar R, Ramanathan A, Samiyappan R (2005) Use of Pseudomonas fluorescens-based formulations for management of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) and enhanced yield in tomato. Biocontrol Sci Technol 15:553–569
Kavino M, Harish S, Kumar N, Saravanakumar D, Samiyappan R (2008) Induction of systemic resistance in banana (Musa spp.) against Banana bunchy top virus (BBTV) by combining chitin with root-colonizing Pseudomonas fluorescens strain CHA0. Eur J Plant Pathol 120:353–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9223-8
Kelemu S, Thomas RJ, Moreno CX, Ocampo GI (1995) Strains of Bradyrhizobium from tropical forage legumes inhibit Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 in vitro. Australas Plant Pathol 24:168–172
Kempel A, Brandl R, Schädler M (2009) Symbiotic soil microorganisms as players in aboveground plant–herbivore interactions–the role of rhizobia. Oikos 118:634–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2009.17418.x
Knudsen IMG, Hockenhull J, Funck Jensen D, Gerhardson B, Hökeberg M, Tahvonen R, Teperi E, Sundheim L (1997) Selection of biological control agents for controlling soil and seed-borne diseases in the field. Eur J Plant Pathol 103:775–784
Kumar H, Dubey R, Maheshwari D (2011) Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobia on seed germination, growth promotion and suppression of Fusarium wilt of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Crop Prot 30:1396–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2011.05.001
Li QQ, Wang ET, Chang YL, Zhang YZ, Zhang YM, Sui XH, Chen WF, Chen WX (2011) Ensifer sojae sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Glycine max grown in saline-alkaline soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1981–1988. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.025049-0
Li YH, Wang R, Zhang XX, Young JPW, Wang ET, Sui XH, Chen WX (2015) Bradyrhizobium guangdongense sp. nov. and Bradyrhizobium guangxiense sp. nov., isolated from effective nodules of peanut. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4655–4661. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000629
Lindström K, Martinez-Romero M (2005) International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes; Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Agrobacterium and Rhizobium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1383–1383
Lu YL, Chen WF, Wang ET, Han LL, Zhang XX, Chen WX, Han SZ (2009) Mesorhizobium shangrilense sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Caragana species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3012–3018. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.007393-0
Mabrouk Y, Zourgui L, Sifi B, Belhadj O (2007a) The potential of Rhizobium strains for biological control of Orobanche crenata. Biologia 62:139–143
Mabrouk Y, Zourgui L, Sifi B, Delavault P, Simier P, Belhadj O (2007b) Some compatible Rhizobium leguminosarum strains in peas decrease infections when parasitised by Orobanche crenata. Weed Res 47:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.2007.00548.x
Mabrouk Y, Mejri S, Hemissi I, Simier P, Delavault P, Saidi M, Belhadj O (2010) Bioprotection mechanisms of pea plant by Rhizobium leguminosarum against Orobanche crenata. Afr J Microbiol Res 4:2570–2575
Martínez-Romero E, Segovia L, Mercante FM, Franco AA, Graham P, Pardo MA (1991) Rhizobium tropici, a novel species nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris L. beans and Leucaena sp. Trees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 41:417–426
Martínez-Viveros O, Jorquera M, Crowley D, Gajardo G, Mora M (2010) Mechanisms and practical considerations involved in plant growth promotion by rhizobacteria. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 10:293–319. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162010000100006
Masson-Boivin C, Giraud E, Perret X, Batut J (2009) Establishing nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with legumes: how many rhizobium recipes? Trends Microbiol 17:458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2009.07.004
Maurhofer M, Hase C, Meuwly P, Metraux J-P, Defago G (1994) Induction of systemic resistance of tobacco to tobacco necrosis virus by the root-colonizing Pseudomonas fluorescens strain CHA0: Influence of the gacA gene and of pyoverdine production. Phytopathology 84:139–147
Mercante FM, Otsubo AA, Brito OR (2017) New native rhizobia strains for inoculation of common bean in the Brazilian savanna. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 41. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20150120
Miller RE, Woodrow IE (2008) Resource availability and the abundance of an N-based defense in Australian tropical rain forests. Ecology 89:1503–1509
Mitra S, Mukherjee A, Wiley-Kalil A, Das S, Owen H, Reddy PM, Ané J-M, James EK, Gya-neshwar P (2016) A rhamnose deficient lipopolysaccharide mutant of Rhizobium sp. IRBG74 is defective in root colonization and beneficial interactions with its flooding-tolerant hosts Sesbania cannabina and wetland rice. J Exp Bot 67:5869–5884. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw354
Mourad K, Fadhila K, Chahinez M, Meriem R, Philippe DL, Abdelkader B (2009) Antimicrobial activities of Rhizobium sp. strains against Pseudomonas savastanoi, the agent responsible for the olive knot disease in Algeria. Grasas y Aceites 60:139–146
Omar S, Abd-Alla M (1998) Biocontrol of fungal root rot diseases of crop plants by the use of rhizobia and bradyrhizobia. Folia Microbiolo 43:431–437
Orellana R, Fan F (1978) Nodule infection by bean yellow mosaic virus in Phaseolus vulgaris. Appl Environ Microbiol 36:814–818
Orellana R, Fan F, Sloger C (1978) Tobacco ringspot virus and Rhizobium interactions in soybean: impairment of leghemoglobin accumulation and nitrogen fixation. Phytopathology 68:577–582
Orellana R, Weber D, Cregan P (1980) N2-fixing competence of Rhizobium japonicum strains in soybean infected with tobacco ringspot virus. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 17:381–388
Osdaghi E, Shams-Bakhsh M, Alizadeh A, Mr L, Hatami Maleki H (2011) Induction of resistance in common bean by Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli and decrease of common bacterial blight. Phytopathol Mediterr 50:45–54. https://doi.org/10.14601/Phytopathol_Mediterr-8524
Owens LD, Thompson JF, Pitcher R, Williams T (1972) Structure of rhizobitoxine, an antimetabolic enol-ether amino-acid from Rhizobium japonicum. J Chem Soc Chem Commun:714–714
Pang Y, Liu X, Ma Y, Chernin L, Berg G, Gao K (2009) Induction of systemic resistance, root colonisation and biocontrol activities of the rhizospheric strain of Serratia plymuthica are dependent on N-acyl homoserine lactones. Eur J Plant Pathol 124:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9411-1
Piccoli C, Cremonese C, Koifman RJ, Koifman S, Freire C (2016) Pesticide exposure and thyroid function in an agricultural population in Brazil. Environ Res 151:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.011
Poole P, Ramachandran V, Terpolilli J (2018) Rhizobia: from saprophytes to endosymbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:29–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.171
Radl V, Simões-Araújo JL, Leite J, Passos SR, Martins LMV, Xavier GR, Rumjanek NG, Bal-dani JI, Zilli JE (2014) Microvirga vignae sp. nov., a root nodule symbiotic bacterium isolated from cowpea grown in semi-arid Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.053082-0
Reitz M, Rudolph K, Schröder I, Hoffmann-Hergarten S, Hallmann J, Sikora R (2000) Lipopolysaccharides of Rhizobium etli strain G12 act in potato roots as an inducing agent of systemic resistance to infection by the cyst nematode Globodera pallida. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3515–3518
Rivas R, Willems A, Subba-Rao NS, Mateos PF, Dazzo FB, Kroppenstedt RM, Martínez-Molina E, Gillis M, Velázquez E (2003) Description of Devosia neptuniae sp. nov. that nodulates and fixes nitrogen in symbiosis with Neptunia natans, an aquatic legume from India. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:47–53
Rivera-Becerril F, van Tuinen D, Chatagnier O, Rouard N, Béguet J, Kuszala C, Soulas G, Gia-ninazzi-Pearson V, Martin-Laurent F (2017) Impact of a pesticide cocktail (fenhexamid, folpel, deltamethrin) on the abundance of Glomeromycota in two agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 577:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.098
Rome S, Fernandez MP, Brunel B, Normand P, Cleyet-Marel JC (1996) Sinorhizobium medicae sp. nov., isolated from annual Medicago spp. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 46:972–980
Roy N, Chakrabartty PK (2000) Effect of aluminum on the production of siderophore by Rhizobium sp.(Cicer arietinum). Curr Microbiol 41:5–10
Rubiales D, Pérez-de-Luque A, Cubero J, Sillero J (2003) Crenate broomrape (Orobanche crenata) infection in field pea cultivars. Crop Prot 22:865–872
Rubiales D, Moreno M, Sillero J (2005) Search for resistance to crenate broomrape (Orobanche crenata Forsk.) in pea germplasm. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:853–861
Samavat S, Besharati H, Behboudi K (2011) Interactions of rhizobia cultural filtrates with Pseudomonas fluorescens on bean damping-off control. J Agric Sci Technol 13:965–976
Sankoh AI, Whittle R, Semple KT, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ (2016) An assessment of the impacts of pesticide use on the environment and health of rice farmers in Sierra Leone. Environ Int 94:458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.05.034
Siddiqui ZA, Baghel G, Akhtar M (2007) Biocontrol of Meloidogyne javanica by Rhizobium and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on lentil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9244-z
Silva K, Florentino LA, Silva KB, De Brandt E, Vandamme P, de Souza Moreira FM (2012) Cupriavidus necator isolates are able to fix nitrogen in symbiosis with different legume species. Syst Appl Microbiol 35:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2011.10.005
Singh R, Srivastava R (1983) Effect of nitrogen nutrition and Rhizobium on multiplication and symptom expression of common bean mosaic virus in mung bean. J Plant Dis Prot 207:212
Singh PK, Singh M, Vyas D (2010) Biocontrol of Fusarium wilt of chickpea using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobium leguminosorum Biovar. Caryologia 63:349–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2010.10589745
Soto MJ, Sanjuan J, Olivares J (2006) Rhizobia and plant-pathogenic bacteria: common infection weapons. Microbiology 152:3167–3174. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.29112-0
Soto M, Nogales J, Pérez-Mendoza D, Gallegos M-T, Olivares J, Sanjuán J (2011) Pathogenic and mutualistic plant-bacteria interactions: ever increasing similarities. Open Life Sci 6:911–917. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-011-0069-x
Souza Moreira FM et al (2006) Azorhizobium doebereinerae sp. nov. microsymbiont of Sesbania virgata (Caz.) Pers. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2005.09.004
Stajković O, Kuzmanović D, Miličić B (2010) Nodulation and N2 fixation effectiveness of Bradyrhizobium strains in symbiosis with Adzuki Bean, Vigna angularis. Braz Arch Biol Technol 53:293–299. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132010000200007
Taha K, Berraho EB, El Attar I, Dekkiche S, Aurag J, Béna G (2018) Rhizobium laguerreae is the main nitrogen-fixing symbiont of cultivated lentil (Lens culinaris) in Morocco. Syst Appl Microbiol 41:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2017.09.008
Thamer S, Schädler M, Bonte D, Ballhorn DJ (2011) Dual benefit from a belowground symbiosis: nitrogen fixing rhizobia promote growth and defense against a specialist herbivore in a cyanogenic plant. Plant Soil 341:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0635-4
Tonelli ML, Furlan A, Taurian T, Castro S, Fabra A (2011) Peanut priming induced by biocontrol agents. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 75:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2010.11.001
Trujillo ME, Willems A, Abril A, Planchuelo A-M, Rivas R, Ludeña D, Mateos PF, Martínez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2005) Nodulation of Lupinus albus by strains of Ochrobactrum lupini sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1318–1327. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.3.1318-1327.2005
Tu JC (1978) Protection of soybean from severe Phytophthora root rot by Rhizobium. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 12:233–240
Tu J, Ford R, Grau C (1970) Some factors affecting the nodulation and nodule efficiency in soybeans infected by soybean mosaic virus. Phytopathology 60:1653–1656
Valverde A, Velázquez E, Fernández-Santos F, Vizcaíno N, Rivas R, Mateos PF, Martínez-Molina E, Igual JM, Willems A (2005) Phyllobacterium trifolii sp. nov., nodulating Trifolium and Lupinus in Spanish soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1985–1989. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63551-0
Vandamme P, Goris J, Chen W-M, De Vos P, Willems A (2002) Burkholderia tuberum sp. nov. and Burkholderia phymatum sp. nov., nodulate the roots of tropical. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1078/07232020260517634
Vargas LK, Volpiano CG, Lisboa BB, Giongo A, Beneduzi A, Passaglia LMP (2017) Potential of rhizobia as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. In: Microbes for legume improvement. Springer, Vienna, pp 153–174
Volpiano CG, Lisboa BB, São José JFB, de Oliveira AMR, Beneduzi A, Passaglia LMP, Vargas LK (2018) Rhizobium strains in the biological control of the phytopathogenic fungi Sclerotium (Athelia) rolfsii on the common bean. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3799-y
Wang ET, Chen WF, Sui XH, Zhang XX, Liu HC, Chen WX (2011) Rhizobium herbae sp. nov. and Rhizobium giardinii-related bacteria, minor microsymbionts of various wild legumes in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1912–1920. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.024943-0
Westhoek A, Field E, Rehling F, Mulley G, Webb I, Poole PS, Turnbull LA (2017) Policing the legume-Rhizobium symbiosis: a critical test of partner choice. Sci Rep 7:1419. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01634-2
Williamson VM, Hussey RS (1996) Nematode pathogenesis and resistance in plants. Plant Cell 8:1735
Winter TR, Rostás M (2010) Nitrogen deficiency affects bottom-up cascade without disrupting indirect plant defense. J Chem Ecol 36:642–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9797-z
Wood CW, Pilkington BL, Vaidya P, Biel C, Stinchcombe JR (2018) Genetic conflict with a parasitic nematode disrupts the legume–rhizobia mutualism. Evol Lett 2:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1002/evl3.51
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Syed JH, Cheng Z, Li J, Zhang G, Jones KC (2015) Current status of persistent organic pesticides residues in air, water, and soil, and their possible effect on neighboring countries: A comprehensive review of India. Sci Total Environ 511:123–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.041
Yan J, Li Y, Han XZ, Chen WF, Zou WX, Xie Z, Li M (2017a) Agrobacterium deltaense sp. nov., an endophytic bacteria isolated from nodule of Sesbania cannabina. Arch Microbiol 199:1003–1009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1367-0
Yan J, Li Y, Yan H, Chen WF, Zhang X, Wang ET, Han XZ, Xie ZH (2017b) Agrobacterium salinitolerans sp. nov., a saline alkaline tolerant bacterium isolated from root nodule of Sesbania cannabina. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1906–1911. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001885
Yokota K, Fukai E, Madsen LH, Jurkiewicz A, Rueda P, Radutoiu S, Held M, Hossain MS, Szczyglowski K, Morieri G, Oldroyd GED, Downie JA, Nielsen MW, Rusek AM, Sato S, Tabata S, James EK, Oyaizu H, Sandal N, Stougaard J (2009) Rearrangement of actin cytoskeleton mediates invasion of Lotus japonicus roots by Mesorhizobium loti. Plant Cell 21:267–284. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.063693
Yuhashi KI, Ichikawa N, Ezura H, Akao S, Minakawa Y, Nukui N, Yasuta T, Minamisawa K (2000) Rhizobitoxine production by Bradyrhizobium elkanii enhances nodulation and competitiveness on Macroptilium atropurpureum. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2658–2663
Yuttavanichakul W, Lawongsa P, Wongkaew S, Teaumroong N, Boonkerd N, Nomura N, Tittabutr P (2012) Improvement of peanut rhizobial inoculant by incorporation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as biocontrol against the seed borne fungus, Aspergillus niger. Biol Control 63:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2012.06.008
Zhou PF, Chen WM, Wei GH (2010) Mesorhizobium robiniae sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Robinia pseudoacacia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2552–2556. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.019356-0
Zilli JÉ, Valicheski RR, Rumjanek NG, Simões-Araújo JL, Freire Filho FR, Neves MCP (2006) Eficiência simbiótica de estirpes de Bradyrhizobium isoladas de solo do Cerrado em caupi. PAB 41:811–818
Zurdo-Piñeiro JL, Rivas R, Trujillo ME, Vizcaíno N, Carrasco JA, Chamber M, Palomares A, Mateos PF, Martínez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2007) Ochrobactrum cytisi sp. nov., isolated from nodules of Cytisus scoparius in Spain. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:784–788. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64613-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Volpiano, C.G. et al. (2019). Rhizobia for Biological Control of Plant Diseases. In: Kumar, V., Prasad, R., Kumar, M., Choudhary, D. (eds) Microbiome in Plant Health and Disease. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8495-0_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8495-0_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-8494-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-8495-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)