Abstract
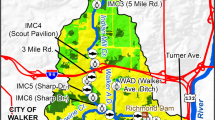
The invertebrate fauna of a small northern stream was examined within Edmonton, Alberta. Many invertebrates that were common upstream of the city were absent or rare within the city. In contrast, some tubificids and chironomids were very abundant within the city. Diversity and richness (number of taxa) of the fauna were much lower within Edmonton than upstream, while the total density was much higher within the city. These changes in the urban invertebrate fauna were apparently caused by the discharge of organic materials and silt from storm sewer runoff.
Chemical analysis of routinely-collected water samples did not show significant differences between urban and non-urban sites. This was probably due to the sporadic nature of storm sewer runoff. Peak levels of contaminants in the stream were usually missed because of the routine nature of sampling. Aquatic invertebrates, which exhibit long-term responses to sporadic runoff incidents, provided a better indication of stream water quality than did routine chemical monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggus, R., 1971. Summer benthos in newly flooded areas of Beaver Reservoir during the second and third years of filling, 1965–1966. In: Hall, G. E. (Ed.) Reservoir Fisheries and Limnology. Am. Fish. Soc. Special Publication 8, Washington, D.C.: 139–152.
Aston, R. J., 1973. Tubificids and water quality: a review. Envir. Pollut. 5: 1–10.
Barton, B. A., 1977. Short term effects of highway construction on the limnology of a small stream in southern Ontario. Freshwat. Biol. 7: 99–108.
Brinkhurst, R. O., 1965. Observations on the recovery of a British river from gross organic pollution. Hydrobiologia 25: 9–51.
Brinkhurst, R. O., 1966. The Tubificidae (Oligochaeta) of polluted waters. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 16: 854–859.
Brinkhurst, R. O. & Kennedy, C. R., 1965. Studies on the biology of the Tubificidae (Annelida, Oligochaeta) in a polluted stream. J. anim. Ecol. 34: 429–443.
Brković-Popović, I. & Popović, M., 1977. Effects of heavy metals on survival and respiration rate of tubificid worms. I. Effects on survival. Envir. Pollut. 13: 65–72.
Bryan, H., 1972. Quality of stormwater drainage from urban land. Wat. Resour. Bull., La. 8: 578–588.
Butcher, R. W., 1955. Relation between the biology and the polluted condition of the Trent. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 12: 823–827.
Field, R., 1975. Coping with urban runoff in the U.S.A. Wat. Res. 9: 499–506.
Hawkes, H. A. & Davies, L. J., 1970. Some effects of organic enrichment on benthic invertebrate communities in stream riffles. In: Duffey, E. & Watt A. S. (Eds.) The Scientific Management of Plant and Animal Communities for Conservation. Brit. Ecol. Soc. Symp. 11: 271–293.
Langford, T. E. & Bray, E. S., 1969. The distribution of Plecoptera and Ephemeroptera in a lowland region of Britain (Lincolnshire). Hydrobiologia 34: 243–271.
Learner, M. A., Williams, R., Harcup, M. & Huges, B. D., 1971. A survey of the macrofauna of the River Cynon, a polluted tributary of the River Taff (South Wales). Freshwat. Biol. 1: 339–367.
Nuttall, P. M., 1972. The effects of sand deposition upon the macroinvertebrate fauna of the River Camel, Cornwall. Freshwat. Biol. 2: 181–186.
Nuttall, P. M. & Purves, J. B., 1974. Numerical indices applied to the results of a survey of the macroinvertebrate fauna of the Tamar catchment (Southwest England). Freshwat. Biol. 4: 213–222.
Paine, G. H. & Gaufin, A. R., 1956. Aquatic Diptera as indicators of pollution in a midwestern stream. Ohio J. Sci. 56: 291–304.
Sartor, J. D., Boyd, G. B. & Agardy, F. J., 1974. Water pollution aspects of street surface contaminants. J. Wat. Poll. Control Fed. 46: 458–467.
Simpson, E. H., 1949. Measurement of diversity. Nature 163: 688.
Surber, E. W., 1953. Biological effects of pollution in Michigan waters. Sewage ind. Wastes 25: 79–86.
Wanielista, M. R., Yousef, Y. A. & McLellon, W. M., 1977. Nonpoint source effects on water quality. J. Wat. Poll. Control Fed. 49: 441–451.
Weibel, S. R., Anderson, R. J. & Woodward, R. L., 1964. Urban land runoff as a factor in stream pollution. J. Wat. Poll. Control Fed. 36: 914–924.
Weibel, S. R., Weidner, R. B., Cohen, J. M. & Christianson, A. G., 1966. Pesticides and other contiminants in rainfall and runoff. J. am. Wat. Wks Ass. 58: 1075–1084.
Whitely, L. S., 1968. The resistance of tubificid worms to three common pollutants. Hydrobiologia 32: 193–205.
Whitten, B. K. & Goodnight, C. G., 1966. Toxicity of some common insecticides to tubificids. J. Wat. Poll. Control Fed. 38: 227–235.
Wilhm, J. L. & Dorris, T. C., 1968. Biological parameters for water quality criteria. Bioscience 18: 477–481.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whiting, E.R., Clifford, H.F. Invertebrates and urban runoff in a small northern stream, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Hydrobiologia 102, 73–80 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006052
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006052