Abstract
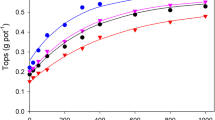
The effect of low root medium pH on growth and proton release of field beans (Vicia faba L. cv. Kristall) was studied in soil and nutrient solution experiments. Decrease of soil pH due to proton release by roots strongly depended on the proton buffer capacity of 8 different soil types tested in a pot experiment. Whereas in soils of high proton buffer capacity no pH decrease during the growth period was detectable, in soils of low buffer capacity pH in the bulk soil dropped from about pH 7.3 to 6.5, 6.3 or 5.8 during growth until maturity. This decrease in pH was closely correlated with an inhibition of plant dry weight production (Y=1.06×+3.33, r=0.94***). Growth reduction was not due to direct inhibition of nitrogen fixation. In short term experiments vegetative growth and proton release were inhibited at pH<6. At pH 5 or lower proton uptake was observed in 1 mM CaSO4. Low pH (4.0 relative to pH 7.0) decreased uptake of all major ions except for Cl the exclusion of which was disturbed. It is concluded that the sensitivity of field beans to low pH is related to a lack of capability to release protons by ATPase activity. This sets limits to nutrient uptake and possibly cytoplasmic pH regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan S and Raven J A 1987 Intracellular pH regulation in Ricinus communis grown witl. ammonium or nitrate as N source: The role of long distance transport. J. Exp. Bot. 38, 580–596.
Andrew C S 1976 Effect of calcium, pH and nitrogen on the growth and chemical composition of some tropical and temperate pasture legumes. I. Nodulation and growth. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 27, 611–623.
Andrew C S and Johnson A D 1976 Effect of calcium, pH and nitrogen on the growth and chemical composition of some tropical and temperate pasture legumes. II. Chemical composition (calcium, nitrogen, potassium, magnesium, sodium, and phosphorus). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 27, 625–636.
Bertl A and Felle H 1985 Cytoplasmic pH of root hair cells of Sinapis alba recorded by a pH-sensitive micro-electrode. J. Exp. Bot. 36, 1142–1149.
Briskin D P 1986 Plasma membrane H+-transporting ATPase: Role in potassium ion transport? Physiol. Plant. 68, 159–163.
Felle H 1988 Short-term pH regulation in plants. Physiol. Plant. 74, 583–591.
Hauter R and Mengel K 1988 Measurement of pH at the root surface of red clover (Trifolium pratense) grown in soils differing in proton buffer capacity. Biol. Fert. Soils 5, 295–298.
Hauter R and Steffens D 1985 Einfluß einer mineralischen und symbiontischen Stickstoffernährung auf Protonenabgabe der Wurzeln, Phosphat Aufnahme und Wurzelent-wicklung von Rotklee. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 148, 633–646.
Jarvis S C and Robson A D 1983 A comparison of the cation/anion balance of ten cultivars of Trifolium subterraneum L., and their effects on soil acidity. Plant and Soil 75, 235–243.
Läuchli A 1984 Salt exclusion: An adaptation of legumes for crops and pastures under saline conditions. In Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Strategies for Crop Improvement. Eds. R C Staples and G H Toennissen. pp 171–187. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Leonard R T 1984 Membrane-associated ATPase and nutrient absorption by roots. In Advances in Plant Nutrition. Vol. 1. Eds. P B Tinker and A Läuchli. pp 209–240. Praeger, New York.
Lin W 1981 Inhibition of anion transport in corn root protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 68, 435–438.
Mahler R L and McDole R E 1987 Effect of soil pH on crop yield in Northern Idaho. Agron. J. 79, 751–755.
Marschner H, Römheld V, Horst W J and Martin P 1986 Root-induced changes in the rhizosphere: Importance for the mineral nutrition of plants. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 149, 441–456.
Mengel K and Schubert S 1985 Active extrusion of protons into deionized water by roots of intact maize plants. Plant Physiol. 79, 344–348.
Mengel K and Steffens S 1982 Beziehung zwischen Kationen/Anionen-Aufnahme von Rotklee und Protonenab-scheidung der Wurzeln. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 145, 229–236.
Moore D P 1974 Physiological effects of pH on roots. In The Plant Root and Its Environment. Ed. E W Carson. pp 135–151. University Press of Virginia, Charlotteville, VA.
Moritsugu M, Suzuki T and Kawasaki T 1983 Effect of nitrogen source on growth and mineral uptake in plants under constant pH and conventional culture conditions. Ber. Ohara Inst. Landw. Biol. Okayama Univ. 18, 125–144.
Munns D N 1978 Soil acidity and nodulation. In Mineral Nutrition of Legumes in Tropical and Subtropical Soils. Eds. C S Andrew and E J Kamprath. pp 243–263. CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia.
Munns D N 1986 Acid soil tolerance in legumes and rhizobia. In Advances in Plant Nutrition. Vol. 2. Eds. B Tinker and A Läuchli. pp 63–91. Praeger, New York.
Prenzel J 1985 Verlauf und Ursachen der Bodenversauerung. Z. Deutsch. Geol. Ges. 136, 293–302.
Raven J A and Smith F A 1976 Nitrogen assimilation and transport in vascular land plants in relation to intracellular pH regulation. New Phytol. 76, 415–431.
Schaller G and Fischer W R 1985 pH-Anderungen in der Rhizosphäre von Mais- und Erdnußwurzeln. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 148, 306–320.
Schubert S 1987 Plant nutrition and H+ extrustion by plant roots. Plant Physiol. (Life Sci. Adv.) 6, 29–33.
Schubert S and Läuchli A 1986 Na+ exclusion, H+ release, and growth of two different maize cultivars under NaCl salinity. J. Plant Physiol. 126, 145–154.
Schubert S and Mengel K 1989 Important factors of nutrient availability: Root morphology and physiology. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 152, 169–174.
Singh L, Pal U R and Arora Y 1987 Direct and residual effect of liming on yield and nutrient uptake of maize (Zea mays L.) in moderately acid soils in the savanna zone of Nigeria. Fert. Res. 12, 11–20.
Ullrich-Eberius C I, Novacky A, Fischer E and Lüttge U 1981 Relationship between energy-dependent phosphate uptake and the electrical membrane potential in Lemna gibba G 1. Plant Physiol 67, 797–801.
Van Beusichem M L 1982 Nutrient absorption by pea plants during dinitrogen fixation. 2. Effects of ambient acidity and temperature. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 30, 85–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schubert, S., Schubert, E. & Mengel, K. Effect of low pH of the root medium on proton release, growth, and nutrient uptake of field beans (Vicia faba). Plant Soil 124, 239–244 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009266
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009266