Abstract
Pasture swards containing perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) alone or with one of five different white clover (Trifolium repens L.) cultivars were examined for production and transfer of fixed nitrogen (N) to grass under dairy cow grazing. Grass-only swards produced 21% less than mixed clover-grass swards during the second year after sowing. Production from grass-only plots under a mowing and clipping removal regime was 44% less than from grass-only plots under grazing. Much of this difference could be attributed to N transfer. In swards without clover, the ryegrass component also decreased in favour of other grasses.
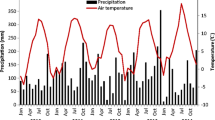
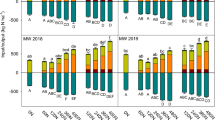
The average amount of fixed N in herbage from all clover cultivars was 269 kg N ha−1 yr−1. Above-ground transfer of fixed N to grasses (via cow excreta) was estimated at 60 kg N ha−1 yr−1. Below-ground transfer of fixed N to grasses was estimated at 70 kg N ha−1 yr−1 by 15N dilution and was similar for all clover cultivars. Thus, about 50% of grass N was met by transfer of fixed N from white clover during the measurement year. Short-term measurements using a 15N foliar-labelling method indicated that below-ground N transfer was largest during dry summer conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball P R and Keeney D R 1981 Nitrogen losses from urine-affected areas of a New Zealand pasture under contrasting seasonal conditions. Proc. XIV Int. Grassl. Cong. 342–344.
Boller B C and Nosberger J 1987 Symbiotically fixed nitrogen from field-grown white and red clover mixed with ryegrasses at low levels of 15N-fertilisation. Plant and Soil 104, 219–226.
Bremner J M and Keeney D R 1965 Steam distillation methods for determination of ammonium, nitrate and nitrite. Anal. Chim. Acta 32, 485–495.
Broadbent F E, Nakashima T and Chang G Y 1982 Estimation of nitrogen fixation by isotope dilution in field and greenhouse experiments. Agron. J 74, 625–628.
Brophy L S, Heichel G H and Russelle M P 1987 Nitrogen transfer from forage legumes to grass in a systematic planting design. Crop Sci. 27, 753–758.
Butler G W, Greenwood R W and Soper K 1959 Effects of shading and defoliation on the turnover of root and nodule tissue of plants of Trifolium repens, Trifolium pratense, and Lotus uliginosus. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 2, 415–426.
Field T R O and Ball P R 1982 Nitrogen balance in an intensively utilised dairy farm system. Proc. N.Z. Grassl. Assoc. 44, 64–69.
Henzell E F and Ross P J 1973 The nitrogen cycle of pasture ecosystems. In Chemistry and Biochemistry of Herbage 2. Eds. G W Butler and R W Bailey. pp 227–246. Academic Press. New York.
Hoglund J H, Crush J R, Brock J L, Ball R and Carran R A 1979 Nitrogen fixation in pasture. XII. General discussion. N.Z. J. Exp. Agric. 7, 45–51.
Jagusch K T 1973 Livestock production from pasture. In Pastures and Pasture plants. Ed. R H M Langer. pp 229–242. A H & A W Reed, London.
Johansen C and Kerridge P C 1979 Nitrogen fixation and transfer in tropical legume-grass swards in south-eastern Queensland. Trop. Grassl. 13, 165–170.
Ladd J N, Amato M, Jackson R B and Butler J H A 1983 Utilisation by wheat crops of nitrogen from legume residues decomposing in soils in the field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 15, 213–238.
Ledgard S F 1989 Nutrition, moisture and rhizobial strain influence isotopic fractionation during N2 fixation in pasture legumes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 21, 61–68.
Ledgard S F, Steele K W and Saunders W M H 1982 Effects of cow urine and its major constituents on pasture properties. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 225, 61–68.
Ledgard S F, Freney J R and Simpson J R 1985 Assessing nitrogen transfer from legumes to associated grasses. Soil Biol. Biochem. 17, 575–577.
Ledgard S F, Brier G J and Littler R A 1987 Legume production and nitrogen fixation in hill pasture communities. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 30, 413–421.
Ledgard S F, Brier G J and Upsdell M P 1990 Effect of clover cultivar on production and nitrogen fixation in clover-ryegrass swards under dairy cow grazing. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 33, 243–249.
Masterton C L and Murphy P M 1976 Application of the acetylene reduction technique to the study of nitrogen fixation by white clover in the field. In Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Plants. Ed. P S Nutman. pp 299–316. Cambridge University Press, U.K.
Muller M M and Sundman V 1988 The fate of nitrogen (15N) released from different plant materials during decomposition under field conditions. Plant and Soil 105, 133–139.
Simpson J R 1976 Transfer of nitrogen from three pasture legumes under periodic defoliation in a field environment. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 16, 863–869.
Steele K W 1982 Nitrogen in grassland soils. In Nitrogen Fertilisers in N.Z. Agriculture. Ed. P B Lynch. pp 29–44. N.Z. Institute of Agric. Science, NZ.
Ta T C and Faris M A 1987 Effects of alfalfa proportions and clipping frequencies on timothy-alfalfa mixtures. II. Nitrogen fixation and transfer. Agron. J. 79, 820–824.
Ta T C, Macdowall F D H and Faris M A 1986 Excretion of assimilated N fixed by nodules of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Can. J. Bot. 64, 2063–2067.
Vallis I, Haydock K P, Ross P J and Henzell E F 1967 Isotope studies on the uptake of nitrogen by pasture plants. III. The uptake of small additions of 15N-labelled fertiliser by Rhodes grass and Townsville lucerne. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 18, 865–877.
Vallis I, Henzell E F and Evans T R 1977 Uptake of soil nitrogen by legumes in mixed swards. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 28, 413–425.
Virtanen A I, vonHausen S and Laine T 1937 Investigations on the root nodule bacteria of leguminous plants. XX. Excretion of nitrogen in associated culture of legumes and non-legumes. J. Agric. Sci. 27, 584–610.
Waring S A and Bremner J M 1964 Ammonium production in soil under waterlogged conditions as an index of nitrogen availability. Nature 201, 951–952.
Wedin W F 1985 Recent advances in pasture management and utilisation. Proc. Forage Grassl. Conf., 26–32.
Wilman D 1989 The growth of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) in field swards in Wales: A review. Proc. Int. Grassl. Congr. 16, 1039–1040.
Wolton K M 1978 Dung and urine as agents of sward change: A review. In Changes in Sward Composition and Productivity. Eds. A H Charles and R J Haggar. pp 131–135. British Grassl. Soc. Occasional Symposium No. 10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ledgard, S.F. Transfer of fixed nitrogen from white clover to associated grasses in swards grazed by dairy cows, estimated using 15N methods. Plant Soil 131, 215–223 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009451
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009451