Abstract
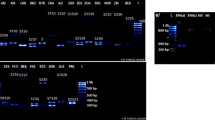
Differential screening of a Brassica napus genomic library led to the isolation of the clone named Bp 19 containing a gene which is highly expressed during microspore development. The accumulation of Bp 19 mRNA starts in uninucleate microspores, increases during development reaching a peak in the late stages but declines considerably in mature pollen. The nucleotide sequence of the entire coding region and of extended portions of the 5′ and 3′ flanking regions was determined. Several homologous cDNA clones were also isolated and sequenced. The Bp 19 gene contains a single intron of 137 bp and gives origin to a mRNA of ca. 1.9 kb which codes for a polypeptide of 584 amino acids. Bp 19 protein has an estimated molecular weight of 63 kilodaltons and has a highly hydrophobic amino terminal region which shows features of a signal peptide. The carboxy half of the Bp 19 protein, starting at amino acid 269, has striking sequence similarity to the pectin esterases of tomato and of the plant pathogen Erwinia chrysanthemi. Four short domains are extremely well conserved in all the three proteins and therefore could represent catalytic sites responsible for enzyme activity. Comparison of the 5′ flanking region of the Bp 19 gene with the sequence of other pollen-specific promoters revealed the presence of several conserved regions. These short promoter sequences could correspond to regulatory elements responsible for pollen-specific gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albani D, Robert LS, Donaldson PA, Altosaar I, Arnison PG, Fabijanski SF: Characerization of a pollen-specific gene family from Brassica napus which is activated during early microspore development. Plant Mol Biol 15: 605–622 (1990).
Breathnach R, Chambon P: Organization and expression of eukaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Ann Rev Biochem 50: 349–384 (1981).
Brown SM, Crouch ML: Characterization of a gene family abundantly expressed in Oenothera organensis pollen that shows sequence similarity to polygalacturonase. Plant Cell 2: 263–274 (1990).
Chen EY, Seeburg PH: Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA 4: 165–170 (1985).
Collmer A, Keen NT: The role of pectic enzymes in plant pathogenesis. Ann Rev Phytopath 24: 383–409 (1986).
Dean C, Tamaki S, Dunsmuir P, Favreau M, Katayama C, Dooner H, Bedbrook J: mRNA transcripts of several plant genes are polyadenylated at multiple sites in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 14: 2229–2240 (1986).
Ebert RA, Ha SB, An G: Identification of an essential upstream element in the nopaline synthase promoter by stable and transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 5745–5749 (1987).
Gubler U, Hoffmann BJ: A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene 25: 263–269 (1983).
Hanson DD, Hamilton DA, Travis JL, Bashe DM, Mascarenhas JP: Characterization of a pollen-specific cDNA clone from Zea mays and its expression. Plant Cell 1: 173–179 (1989).
Henikoff S: Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene 28: 351–359 (1984).
Joshi CP: An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translational start site in 79 plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 6643–6653 (1987).
Kozak M: Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell 44: 283–292 (1986).
Kyte J, Doolittle RF: A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157: 105–132 (1982).
Lam E, Benfey PN, Gilmartin PM, Fang R-X: Chua N-H: Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 7890–7894 (1989).
Lutcke HA, Chow KC, Mickel FS, Moss KA, Kern HF, Scheele GA: Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J 6: 43–48 (1987).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1982).
Mascarenhas JP: The biochemistry of angiosperm pollen development. Bot Rev 41: 259–314 (1975).
Mascarenhas JP: The male gametophyte of flowering plants. Plant Cell 1: 657–664 (1989).
Messing J, Geragthy D, Heidecker G, Hu N-T, Kridl J, Rubenstein I: Plant gene structure. In: Kosuge T, Meredith CP, Hollaender A (eds) Genetic Engineering of Plants, pp. 211–227. Plenum, New York. (1983).
Mikami K, Sakamoto A, Takase H, Tabata T, Iwabuchi M: Wheat nuclear protein HBP-1 binds to the hexameric sequence in the promoter of various plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 9707–9717 (1989).
Pearson W, Lipman DJ: Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2444–2448 (1988).
Plastow GS: Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the pectin methyl esterase gene of Erwinia chrysanthemi B374. Mol Microbiol 2: 247–254 (1988).
Pressey R, Reger BJ: Polygalacturonase in pollen from corn and other grasses. Plant Sci 59: 57–62 (1988).
Ray J, Knapp J, Grierson D, Bird C, Schuch W: Identification and sequence determination of a cDNA clone for tomato pectin esterase. Eur J Biochem 174: 119–124 (1988).
Robert LS, Donaldson PA, Ladaique C, Altosaar I, Arnison PG, Fabijanski SF: Antisense RNA inhibition of β-glucuronidase gene expression in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 13: 399–409 (1989).
Tanksley SD, Zamir D, Rick CM: Evidence for extensive overlap of sporophytic and gametophytic gene expression in Lycopersicon esculentum. Science 213: 453–455 (1981).
Twell D, Wing R, Yamaguchi J, McCormick S: Isolation and expression of an anther-specific gene from tomato. Mol Gen Genet 217: 240–245 (1989).
van Tunen AJ, Hartman SA, Mur LA, Mol JNM: Regulation of chalcone flavanone isomerase (CHI) gene expression in Petunia hybrida: the use of alternative promoters in corolla, anthers and pollen. Plant Mol Biol 12: 539–551 (1989).
von Heijne G: Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem 133: 17–21 (1983).
Willing RP, Bashe D, Mascarenhas JP: An analysis of the quantity and diversity of messenger RNAs from pollen and shoots of Zea mays. Theor Appl Genet 75: 751–753 (1988).
Wing RA, Yamaguchi J, Larabell SK, Ursin VM, McCormick S: Molecular and genetic characterization of two pollen-expressed genes that have sequence similarity to pectate lyases of the plant pathogen Erwinia. Plant Mol Biol 14: 17–28 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albani, D., Altosaar, I., Arnison, P.G. et al. A gene showing sequence similarity to pectin esterase is specifically expressed in developing pollen of Brassica napus. Sequences in its 5′ flanking region are conserved in other pollen-specific promoters. Plant Mol Biol 16, 501–513 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023417
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023417