Abstract
A pot experiment was conducted to measure the effect of silicon on phosphorus uptake and on the growth of rice at different P levels. Rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Akebono) was cultured in Kimura B nutrient solution without and with silicon (1.66 mM Si) and with three phosphorus levels (0.014 mM P, low; 0.21 mM, medium; and 0.70 mM, high).
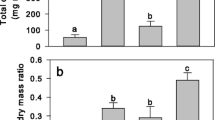
Shoot dry weight with Si (+Si) in solution increased with increasing P level, while shoot weight without Si (−Si) was maximum at 0.21 mM P, suggesting that +Si raised the optimum P level for rice. +Si increased shoot weight more when P was low or high than when P was medium.
The concentration and amount of inorganic P in shoots increased with increasing P level. +Si did not significantly decrease P uptake by rice at 0.014 mM P, however, uptake at 0.21 and 0.70 mM P was 27 and 30 percent less than uptake with −Si, respectively. In −Si with 0.21 and 0.70 mM P, inorganic P in shoots was more than double the concentration in shoots grown in +Si solutions.
The Si concentration in shoots decreased slightly with increasing P level, although Si uptake was not significantly affected by P. +Si decreased the uptake of Fe and Mn by an average of 20 and 50 percent, respectively, thus P/Mn and P/Fe ratios increased in the shoot when P was low.
From the results above, the beneficial effect of Si on the growth of rice was clearly shown when P was low or high. This effect may have resulted from decreased Mn and Fe uptake, and thus increased P availability within P deficient plants, or from reduced P uptake when P was high.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biddulph O 1953 Translocation of radioactive mineral nutrients in plant. Kan. Agric. Exp. Sta. Rep. 4, 48–58.
Bortner C E 1933 Toxicity of manganese to Turkish tobacco in acid Kentucky soils. Soil Sci. 39, 15–33.
Brenchley W E, Maskell E J and Warington K 1927 The inter-relation between silicon and other elements in plant nutrition. Ann. Appl. Biol. XIV, 45–82.
Committee on the methods of crop analysis 1982 Methods of phosphate analysis. In Methods of Cultured Plant Analysis. pp 344–348. Yokendo Publishers, Tokyo, Japan.
Gile P L and Smith J G 1925 Colloidal silica and efficiency of phosphorus. J. Agric. Res. XXXI, 247–260.
Hall A D and Morison C G T 1906 On the function of silica in the nutrtion of cereals, Part I. Proc. Roy. Soc. 77, 455–477.
Lemmermann O and Wiessmann H 1922 Die ertragssteigernde Wirkung der Kieselsäure bei unzureichender Phosphorsäurernäbrung der Pflanzen. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Düng. (A) 1, 186–255.
Ma J F and Takahashi E 1989 Effect of silicic acid on phosphorus uptake by rice plant. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 35, 227–234.
Noda M and Komai Y 1958 Effect of silicate materials on the availability of inorganic phosphate in the soil. In Studies on Maximizing the Yield of Agricultural Products by the Application of Silicate Material. pp 100–115. Monbusho, Tokyo, Japan.
Okuda A and Takahashi E 1961 Studies on the physiological role of silicon in crop plants (Part 1); Discussion on the silicon deficient culture method. J. Sci. Soil Manure, Japan 32, 475–480.
Okuda A and Takahashi E 1962 Studies on the physiological role of silicon in crop plants (Part 6). Effect of silicon on iron uptake by rice plant and oxidation power of root. J. Sci. Soil Manure, Japan 33, 59–64.
Roy A C, Ali M Y, Fox R L and Silva J A 1971 Influence of calcium silicate on phosphate solubility and availability in Hawaiian Latosols. Proc. Int. Symp Fert. Eval. (New Delhi) 1, 757–765.
Smyth J T and Sanchez P A 1980 Effects of lime, silicate, and phosphorus sorption on ion retention. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 500–505.
Syouji K 1981 Application effect of calcium silicate, rice straw and citrate on availability of phosphorus in soil. J. Sci. Soil Manure, Japan 52, 253–259.
Tanaka K and Takahashi E 1980 Comparative Studies on Silicon Nutrition. MSc Thesis, Kyoto University, Japan.
Toth S J 1939 The stimulating effects of silicates on plant yields in relation to anion displacement. Soil Sci. 47, 123–141.
Yoneyama T 1988 Problems on phosphorus fertility in upland soil. 5. Uptake and metabolism of phosphorus of plant. Agric. Hortic. 63, 16–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Takahashi, E. Effect of silicon on the growth and phosphorus uptake of rice. Plant Soil 126, 115–119 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041376
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041376