Abstract
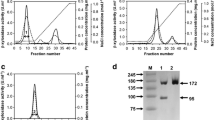
Bacillus stearothermophilus L1 was isolated by enrichment culture using an alkaline extract of pulp as the carbon source at 65°C and pH 9.0. The bacterium produced extracellular xylanase and α-l-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55). The xylanase activity was high when the cells were grown in the presence of d-xylose, whereas the arabinofuranosidase activity was high when grown in media containing l-arabinose. The arabinofuranosidase was purified 59-fold with an 80% yield by DEAE Sephacel and Sephadex G-100 chromatography. The purified enzyme had an apparent molecular mass of 110 000 kDa and consisted of two subunits of 52 500 kDa and 57 500 kDa. Using p-nitrophenyl-α-l-arabinofuranosidase as the substrate, the enzyme had a Michaelis constant (K m) of 2.2 × 10−4 m, maximum reaction velocity (Vmax) of 11o μmol min−1 mg−1, temperature optimum of 70°C and pH optimum of 7.0 (50% activity at pH 8.0). The enzyme was specific for the furanoside configuration. The purified enzyme partially delignified softwood Kraft pulp. Treatment of the pulp with 38 units ml−1 of α-l-arabinofuranosidase at 65°C for 2 h at pH 8.0 and 9.0 led to lignin releases of 2.3% and 2.1%, respectively. The enzyme acted synergistically with a thermophilic xylanase in the delignification process, yielding a 19.2% release of lignin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Hiroi T, Eriksson KE (1976) Microbiological degradation of lignin. Part 1. Influence of cellulose on the degradation of lignins by white-rot fungus Pleorotus ostreatus. Sven Papperstidn 79:157–161
Kirkpatrick N, Reid ID, Ziomek E, Ho C, Paice MG (1989) Relationship between fungal biomass production and the brigthening of hardwood Kraft pulp by Coriolus versicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1147–1152
Laemmli U (1980) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T-4. Nature 227:680–685
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Paice MG, Bernier R, Jurasek L (1988) Viscosity-enhancing bleaching of hardwood Kraft pulp with xylanase from cloned gene. Biotechnol Bioeng 32:235–239
Presnell TL, Fukui H, Joyce TW, Chang H (1992) Bleach plant effluent influence enzyme production by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:184–189
Ratto M, Poutanen K, Viikari L (1992) Production of xylanolytic enzymes by an alkali tolerant Bacillus circulans strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37:470–473
Ross NW, Jonson KG, Braum C, Mackenzie CR, Scheinder H (1992) Enzymatic hydrolysis of water-soluble lignin-carbohydrate complexes from Populus deltoiedes: effect of combinations of β-mannanases and acetyl xylan esterase. Enzyme Microbiol Biotechnol 14:90–95
Senior DJ, Mayer PR, Miller D, Sutcliffe R, Tan L, Saddler JN (1988) Selective solubilization of xylan in pulp using a purified xylanase from Trichoderma harazianum. Biotechnol Lett 10:907–912
Senior DF, Mayer PR, Saddler JN (1991) The interaction of xylanase with commercial pulps. Biotechnol Bioeng 37:274–279
Shoham YY, Zosim Z, Rosenberg E (1993) Partial decolorization of Kraft pulp at high temperature and at high pH values with an extracellular xylanase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biotechnol (in press)
Talbot G, Sygusch J (1990) Purification and characterization of thermostable β-mannanase and α-galactosidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3505–3510
Viikari L, Ranua M, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1986) Application of enzymes in bleaching. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry, Stockholm, June 16–19, 1986. pp 66–69
Viikari L, Ranua M, Kantelinen A, Linko M, Sundquist J (1987) Application of enzymes in bleaching. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Wood and Pulping Chemistry, Paris, April 27–30, 1987, vol 1. pp 151–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: Eugene Rosenberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezalel, L., Shoham, Y. & Rosenberg, E. Characterization and delignification activity of a thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 57–62 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170429
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170429