Summary
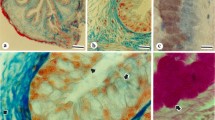
Precise localization of xanthine oxidase activity might elucidate physiological functions of the enzyme, which have not been established so far. Because xanthine oxidase is sensitive to chemical (aldehyde) fixation, we have localized its activity in unfixed cryostat sections of rat duodenum, oesophagus and tongue mounted on a semipermeable membrane. Previous studies had shown that this procedure enables the exact localization of activities of peroxisomal oxidases with maintenance of acceptable ultrastructure. Moreover, leakage and/or diffusion of enzyme molecules was prevented with this method. The incubation medium to detect xanthine oxidase activity contained hypoxanthine as substrate and cerium ions as capturing agent for hydrogen peroxide. After incubation, reaction product in the sections was either visualized for light microscopy or sections were fixed immediately and processed for electron microscopy. At the ultrastructural level, crystalline reaction product specifically formed by xanthine oxidase activity was found to be present in the cytoplasmic matrix of enterocytes and goblet cells and in mucus of duodenum. Moderate activity was found in the cytoplasm of apical cell layers of epithelia of oesophagus and tongue, with highest activity in the cornified layer. Moreover, large amounts of reaction product were found to surround bacteria present between cell remnants of the cornified layer of the oesophagus. Many bacteria surrounded by the enzyme showed signs of destruction and/or cell death. The intracellular localization of xanthine oxidase activity in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells as well as the extracellular localization suggest that the enzyme plays a role in the lumen of the digestive tract, for instance in the defence against microorganisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaya, Y., Yamazaki, K-I., Sato, M., Noda, K., Nishino, T. & Nishino, T. (1990) Proteolytic conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase from the NAD-dependent type to the O2-dependent type. Amino acid sequence of rat liver xanthine dehydrogenase and identification of the cleavage sites of the enzyme protein during irreversible conversion by trypsin. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 14170–5.
Angermüller, S. (1989) Peroxisomal oxidases: cytochemical localization and biological relevance. Progr. Histochem. Cytochem. 20, 1–63.
Angermüller, S. & Fahimi, H. D. (1988) Light microscopic visualization of the reaction product of cerium used for localization of peroxisomal oxidases. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36, 23–8.
Angermüller, S., Bruder, G., Völkl, A., Wesch, H. & Fahimi, H. D. (1987) Localization of xanthine oxidase in crystalline cores of peroxisomes. A cytochemical and biochemical study. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 45, 137–44.
Arborgh, B., Ericsson, J. L. E. & Helminen, H. (1971) Inhibition of renal acid phosphatase and aryl sulfatase activity by glutaraldehyde fixation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 19, 449–51.
Becker, B. F. (1993) Towards a physiological function of uric acid. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 14, 615–31.
Becker, B. F., Reinholz, N., Özçelik, T., Leipert, B. & Gerlach, E. (1989) Uric acid as radical scavenger and antioxidant in the heart. Pflügers Arch. 415, 127–35.
Björk, L. & Cleasson, O. (1979) Xanthine oxidase as a source of hydrogen peroxide for the lactoperoxidase system in milk. J. Diary Sci. 62, 1211–5.
Briggs, R. T., Drath, D. B., Karnovsky, M. L. & Karnovsky, M. J. (1975) Localization of NADH oxidase on the surface of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by a new cytochemical method. J. Cell Biol. 67, 566–86.
Chalmers, G. R. & Edgerton, V. R. (1989) Marked and variable inhibition by chemical fixation of cytochrome oxidase and succinate dehydrogenase in single motoneurons. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37, 899–901.
Dikov, A., Alexandrov, I., Russinova, A. & Boya-Djieva-Michailova, A. (1988) Ultracytochemical detection of enzymes by reduction of potassium ferricyanide. I. A method for detection of xanthine oxidase. Acta Histochem. 83, 107–15.
Engerson, T. D., Mckelvey, T. G., Rhyne, D. B., Boggio, E. B., Snyder, S. J. & Jones, H. P. (1987) Conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to oxidase in ischemic rat tissues. J. Clin. Invest. 79, 1564–70.
Frederiks, W. M. & Marx, F. (1993) A histochemical procedure for light microscopic demonstration of xanthine oxidase activity in unfixed cryostat sections using cerium ions and a semipermeable membrane technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 41, 667–70.
Frederiks, W. M., Kooij, A. & Marx, F. (1993) The effect of ischemia on xanthine oxidase activity in rat intestine and liver. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 74, 21–6.
Frederiks, W. M., Bosch, K. S., van DenMunckhof, R. J. M. & vanNoorden, C. J. F. (1994) A quantitative histochemical study on xanthine oxidase activity in rat liver using the cerium capture method in the presence of polyvinyl alcohol. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 42, 1091–7.
Gossrau, R., vanNoorden, C. J. F. & Frederiks, W. M. (1989) Enhanced light microscopic visualization of oxidase activity with the cerium capture method. Histochemistry 92, 349–53.
Gossrau, R., Frederiks, W. M. & vanNoorden, C. J. F. (1990) Histochemistry of reactive oxygenspecies (ROS)-generating oxidases in cutaneous and mucous epithelia of laboratory rodents with special reference to xanthine oxidase. Histochemistry 94, 539–44.
Granger, D. N., Höllwarth, M. E. & Parks, D. A. (1986) Ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of oxygen-derived free radicals. Acta Physiol. Scand. 126 (Suppl. 548), 47–63.
Granger, D. N., Rutili, G. & Mccord, J. M. (1981) Superoxide radicals in feline intestinal ischemia. Gastroenterology 81, 22–9.
Hopwood, D. (1991) Fixation of tissue for histochemistry. In Histochemical and Immunocytochemical Techniques. Applications to Pharmacology and Toxicology (edited by Bach, P. H. & Baker, J. R. J.), pp. 147–65. London: Chapman & Hall.
Ichikawa, M., Nishino, T., Nishino, T. & Ichikawa, A. (1992) Subcellular localization of xanthine oxidase in rat hepatocytes: high resolution immunoelectron microscopic study combined with biochemical analysis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 40, 1097–1103.
Jarasch, E.-D., Grund, C., Bruder, G., Heid, H. W., Keenan, T. W. & Franke, W. W. (1981) Localization of xanthine oxidase in mammary-gland epithelium and capillary endothelium. Cell 25, 67–82.
kooij, A. (1994) A re-evaluation of the tissue distribution and physiology of xanthine oxidoreductase. Histochem. J. 26, 889–915.
Kooij, A., Schiller, H. J., Schijns, M., vanNoorden, C. J. F. & Frederiks, W. M. (1994) Conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase into xanthine oxidase in rat liver and plasma at the onset of reper-fusion after ischemia. Hepatology 19, 1488–95.
Kooij, A., Bosch, K. S., Frederiks, W. M. & vanNoorden, C. J. F. (1992) High levels of xanthine oxidoreductase in rat endothelial, epithelial and connective tissue cells. Virchows Archiv. B. Cell. Pathol. 62, 143–50.
Kooij, A., Frederiks, W. M., Gossrau, R. & vanNoorden, C. J. F. (1991) Localization of xanthine oxidoreductase activity using the tissue protectant polyvinyl alcohol and final electron acceptor tetranitro BT. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39, 87–93.
Massey, V., Komai, H., Palmer, G. & Elion, G. B. (1970) On the mechanism of inactivation of xanthine oxidase by allopurinol and other pyrazolo [3,4-d] pyrimidines. J. Biol Chem. 245, 2837–44.
Mcmillan, P. J. (1967) Differential demonstration of muscle and heart type lactic dehydrogenase of rat muscle and kidney. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 21–31.
Meijer, A. E. F. H. (1972) Semipermeable membranes for improving the histochemical demonstration of enzyme activities in tissue sections. Histochemie 30, 31–9.
Meijer, A. E. F. H. (1980) Semipermeable membrane techniques in quantitative enzyme histochemistry. In Trends in Enzyme Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. Ciba Foundation Symposium 73, pp. 103–20. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica.
Patel, H. R. H., Frederiks, W. M., Marx, F., Best, A. J. & vanNoorden, C. J. F. (1991) A quantitative histochemical study of d-amino acid oxidase activity in rat liver in relationship with feeding conditions. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39, 81–6.
Peden, D. B., Hohman, R., Brown, M. E., Mason, R. T., Berkebile, C., Fales, H. M. & Kaliner, M. A. (1990) Uric acid is a major antioxidant in human nasal airway secretions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 7638–42.
Richardson, K. C., Jarrett, L. & Finke, E. H. (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 35, 313–23.
Sackler, M. L. (1966) Xanthine oxidase from liver and duodenum of the rat: histochemical localization and electrophoretic heterogeneity. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 326–33.
Schellens, J. P. M., Frederiks, W. M., vanNoorden, C. J. F., Vreeling Sindelárová, H., Marx, F. & Mcmillan, P. J. (1992) The use of unfixed cryostat sections for electron microscopic study of d-amino acid oxidase activity in rat liver. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 40, 1975–9.
Terao, J. & Nagao, A. (1991) Antioxidative effect of human saliva on lipid peroxidation. Agric. Biol. Chem. 55, 869–72.
Tubaro, E., Lotti, B., Cavallo, G., Croce, C. & Borelli, G. (1980a) Liver xanthine oxidase increase in mice in three pathological models. A possible defence mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 29, 1939–43.
Tubaro, E., Lotti, B., Santiangeli, C. & Cavallo, G. (1980b) Xanthine oxidase increase in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages in mice in three pathological situations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 29, 1945–8.
van DenMunckhof, R. J. M., Vreeling-sindelárová, H., Schellens, J. P. M. & Frederiks, W. M. (1994) Localization of uric acid oxidase activity in core and matrix of peroxisomes as detected in unfixed cryostat sections of rat liver. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 42, 177–83.
vanNoorden, C. J. F. & Frederiks, W. M. (1992) Enzyme Histochemistry: a Laboratory Manual of Current Methods. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
vanNoorden, C. J. F. & Frederiks, W. M. (1993) Cerium methods for light and electron microscopical histochemistry. J. Microsc. 171, 3–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Den Munckhof, R.J.M., Vreeling-Sindelárová, H., Schellens, J.P.M. et al. Ultrastructural localization of xanthine oxidase activity in the digestive tract of the rat. Histochem J 27, 897–905 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173844
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173844