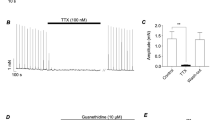
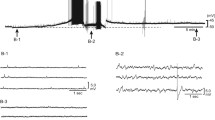
Summary
Excitatory junction potentials (e j.ps; intracellular electrodes) and excitatory junction currents (e.j.cs; extracellular electrodes) elicited by stimulation (20 pulses at 1 Hz every minute) of the hypogastric nerve trunk were recorded from guinea-pig isolated vas deferens.
Intracellular recording. At a variety of stimulation intensities, bath-applied yohimbine (0.1–1 μmol/l) did not change the first one to three e j.ps in a train but increased the amplitude of subsequent e j.ps. The effect of yohimbine was abolished in tissues from reserpinepretreated guinea pigs. Bath-applied desipramine (0.1 μmol/l) diminished the amplitude of all but the first one to three e j.ps in a train. - Extracellular recording. Yohimbine (0.1–1 μmol/l), when applied locally through the recording suction electrode, increased the number of e.j.cs per given number of stimuli, i. e., enhanced the probability of occurrence of e.j.cs. When desipramine (0.1 μmol/l) was present both in the bath and in the recording electrode, the probability of the occurrence of e.j.cs was decreased. In the presence of desipramine, yohimbine (0.1–1 μmol/l) increased the number of e j.cs even more markedly. Neither the nerve terminal impulse nor the number of spontaneous e j.cs was changed by yohimbine. A mixture of tetraethylammonium (2 mmol/l) and 4-aminopyridine (0.2 mmol/l), when applied locally, both increased the number of e.j.cs and changed markedly the shape of the nerve terminal impulse.
These experiments demonstrate presynaptic α2-autoinhibition at a high degree of resolution, i. e., when the intermittent release of transmitter from only a few varicosities along a single terminal axon is monitored by the e j.c. α2-Autoinhibition is not due to a depression of impulse conduction but to a depression of stimulus-secretion coupling in varicosities reached by the impulse. Taken together with the low probability of transmitter release at the level of individual varicosities, the results support the idea of lateral inhibition by noradrenaline released from distant varicosities rather than inhibition due to noradrenaline released from the same varicosity. The mode of action of yohimbine differs from that of K+ channel blocking agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allcorn RJ, Cunnane TC, Kirkpatrick K (1986) Actions of α, β-methylene ATP and 6-hydroxydopamine on sympathetic neurotransmission in the vas deferens of the guinea-pig, rat and mouse: support for co-transmission. Br J Pharmacol 89:647–659
Bennett MR (1973) An electrophysiological analysis of the uptake of noradrenaline at sympathetic nerve terminals. J Physiol (Lond) 229:533–546
Bennett MR, Middleton J (1975) An electrophysiological analysis of the effects of amine-uptake blockers and α-adrenoceptor blockers on adrenergic neuromuscular transmission. Br J Pharmacol 55:87–95
Blakeley AGH, Cunnane TC (1979) The packeted release of transmitter from the sympathetic nerves of the guinea-pig vas deferens: an electrophysiological study. J Physiol (Lond) 296:85–96
Blakeley AGH, Cunnane TC, Petersen SA (1981) An electropharmacological analysis of the effects of some drugs on neuromuscular transmission in the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. J Auton Pharmacol 1:367–375
Blakeley AGH, Cunnane TC, Petersen SA (1982) Local regulation of transmitter release from rodent sympathetic nerve terminals? J Physiol (Lond) 325:93–109
Bönisch H (1984) The transport of (+)-amphetamine by the neuronal noradrenaline carrier. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 327:267–272
Brock JA, Cunnane TC (1987) Relationship between the nerve action potential and transmitter release from sympathetic postganglionic nerve terminals. Nature 326:605–607
Brock JA, Cunnane TC (1988a) Electrical activity at the sympathetic neuroeffector junction in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol (Lond) 399:607–632
Brock JA, Cunnane TC (1988b) Studies on the mode of action of bretylium and guanethidine in post-ganglionic sympathetic nerve fibres. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338: 504–509
Cunnane TC, Manchanda R (1989) Simultaneous intracellular and focal extracellular recording of junction potentials and currents, and the time course of quantal transmitter action in rodent vas deferens. Neuroscience 30:563–575
Illes P, Starke K (1983) An electrophysiological study of presynaptic α-adrenoceptors in the vas deferens of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol 78:365–373
Kalsner S (1983) Yohimbine and prolongation of stimulation pulse duration alter similarly 3H-transmitter efflux in heart: an alternative to the negative feedback hypothesis. Br J Pharmacol 79:985–992
Langer SZ (1977) Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol 60:481–497
Langer SZ (1981) Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev 32:337–362
Limberger N, Starke K (1984) Further study of prerequisites for the enhancement by α-adrenoceptor antagonist of the release of noradrenaline. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 325:240–246
Limberger, Mayer A, Zier G, Valenta B, Starke K, Singer EA (1989) Estimation of pA2 values at presynaptic α2-autoreceptors in rabbit and rat brain cortex in the absence of autoinhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:639–647
Mayer A, Limberger N, Starke K (1988) Transmitter release patterns of noradrenergic, dopaminergic and cholinergic axons in rabbit brain slices during short pulse trains, and the operation of presynaptic autoreceptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338:632–643
Meldrum LA, Burnstock G (1983) Evidence that ATP acts as a cotransmitter with noradrenaline in sympathetic nerves supplying the guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 92:161–163
Sneddon P, Westfall DP (1984) Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol (Lond) 347:561–580
Starke K (1977) Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 77:1–124
Starke K (1987) Presynaptic α-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 107:73–146
Starke K, Göthert M, Kilbinger H (1989) Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol Rev 69:864–989
Stjärne L (1989) Basic mechanisms and local modulation of nerve impulse-induced secretion of neurotransmitters from individual sympathetic nerve varicosities. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 112:1–137
Story DF, McCulloch MW, Rand MJ, Standford-Starr CA (1981) Conditions required for the inhibitory feedback loop in noradrenergic transmission. Nature 293:62–65
Westfall DP, Stitzel RE, Rowe JN (1978) The postjunctional effects and neural release of purine compounds in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 50:27–38
Zier G, Drobny H, Valenta B, Singer EA (1988) Evidence against a functional link between noradrenaline uptake mechanisms and presynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:118–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to K. Starke at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brock, J.A., Cunnane, T.C., Starke, K. et al. α2-Adrenoceptor-mediated autoinhibition of sympathetic transmitter release in guinea-pig vas deferens studied by intracellular and focal extracellular recording of junction potentials and currents. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342, 45–52 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178971
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178971