Summary
-
1.
The binding characteristics of [3H]ICS 205-930, a potent and selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, were investigated in membranes prepared from murine neuroblastoma-glioma NG 108-15 cells.
-
2.
[3H]ICS 205-930 bound rapidly, reversibly and stereoselectively to a homogeneous population of high affinity recognition sites: B max = 58 ± 3 fmol/mg protein, pK D = 9.01 ± 0.08 (n = 11). Non linear regression and Scatchard analysis of saturation data suggested the existence of a single class of [3H]ICS 205-930 recognition sites on NG 108-15 cells. The binding was rapid, stable and reversible. The affinity of [3H]ICS 205-930 determined in kinetic studies was in agreement with that obtained under equilibrium conditions.
-
3.
Competition studies performed with a variety of agonists and antagonists also suggested the presence of a homogeneous population of [3H]ICS 205-930 recognition sites. All competition curves were steep and monophasic and were best fit by a 1 receptor site model. [3H]ICS 205-930 binding sites displayed the pharmacological profile of a 5-HT3 receptor. Potent 5-HT3 receptor antagonists showed nanomolar affinities for [3H]ICS 205–930 binding sites with the following rank order of potency: SDZ 206-830 > ICS 205-930 > SDZ 206-792 > BRL 43694 > quipazine > BRL 24924 > SDZ 210-204 > MDL 72222 > SDZ 210-205. Metoclopramide, mCPP and mianserin showed submicromolar affinity. The rank order of potency of agonists was: 5-HT = 2-methyl-5-HT > phenylbiguanide ≫ 8-OH-DPAT > 5-carboxamidotryptamine. Drugs acting at 5-HT1, 5-HT2, dopamine receptors, α- and β-adrenoceptors, (methysergide, ketanserin, pindolol, spiperone, SCH 23390) showed very low affinities for [3H]ICS 205-930 recognition sites.
-
4.
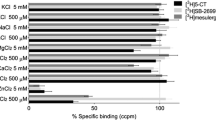
The binding of [3H]ICS 205-930 was not affected by quanine or adenine nucleotides (GTP, GppNHp and ATP) at 1 mmol/l. Moreover, these nucleotides did not affect the binding of agonists suggesting that 5-HT3 recognition sites are not coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins.
-
5.
The interactions of agonists and antagonists with [3H]ICS 205-930 recognition sites were competitive in nature, as demonstrated by saturation experiments carried out with [3H]ICS 205-930 in the presence and the absence of unlabelled compounds: apparent B max values were not reduced whereas apparent K D values were increased in the presence of competing ligands. There was a good agreement between apparent K B values determined in saturation experiments with agonists and antagonists and their K D values determined in competition experiments.
-
6.
These findings are consistent with [3H]ICS 205-930 labelling 5-HT3 receptors on NG 108-15 cells. The pharmacological profile of the sites labelled by [3H]ICS 205-930 on NG 108-15 cells is very similar to that of the 5-HT3 sites identified on neuroblastoma NlE-115 cells (Hoyer and Neijt 1988a, b).
-
7.
The present data demonstrate that [3H]ICS 205-930 is a suitable ligand for the identification of 5-HT3 recognition sites in membrane preparations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GR 38032F:
-
(1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-9-methyl-3[(2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-4-one)
- Hepes:
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine ethane sulfonic acid
- Tris:
-
Tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane
- G proteins:
-
guanine nucleotide regulatory binding proteins
- GTP:
-
guanosine-5′-triphosphate
- ATP:
-
adenosine-5′-triphosphate
- GppNHp:
-
guanyl-5′-yl-imidodiphosphate
References
Amano T, Richelson E, Nirenberg M (1972) Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:258–263
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bradley PB, Engel G, Feniuk W, Fozard JR, Humphrey PPA, Middlemiss DN, Mylecharane EJ, Richardson BP, Saxena PR (1986) Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology 25:563–576
Brittain RT, Butler A, Coates IH, Fortune DH, Hagan R, Hill JM, Humber DC, Humphrey PPA, Ireland SJ, Jack D, Jordan CC, Oxford A, Straughan DW, Tyers MB (1987) GR 38032F, A novel selective 5HT3 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 90: 87P
Costall B, Domeney AM, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ, Tyers MB (1987) The antipsychotic potential of GR 38032F, a selective antagonist of 5HT3 receptors in the central nervous system. Br J Pharmacol 90:89P
Dawson G, McLawhon RW, Scheideler MA (1983) In: Pfeiffer SE (ed) Neuroscience approached through cell culture, vol 2. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 89–114
De Lean A (1979) SCTFIT. A computer program for simultaneous analysis of saturation and competition curves. Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Duke University, Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27720
Fake CS, King FD, Sanger GJ (1987) BRL 43694: A potent and novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 91:335P
Fozard JR (1984a) MDL 72222, a potent and highly selective antagonist at neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. NaunynSchmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 326: 36–44
Fozard JR (1984b) Neuronal 5-HT receptors in the periphery. Neuropharmacology 23:1473–1486
Hagan RM, Butler A, Hill JM, Jordan CC, Ireland SJ, Tyers MB (1987) Effect of 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, GR 38032F, on responses to injection of a neurokinin agonist into the ventral tegmental area of the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 138:303–305
Hoyer D, Neijt HC (1987) Identification of serotonin 5-HT3 recognition sites by radioligand binding in NG 108–15 neuroblastoma-glioma cells. Eur J Pharmacol 143:291–292
Hoyer D, Neijt HC (1988a) Identification of 5-HT3 recognition sites in NIE-115 neuroblastoma cells with [3H]ICS 205-930. Br J Pharmacol 93:97P
Hoyer D, Neijt HC (1988b) Identification of scrotonin 5-HT3 recognition sites in membranes of NIE-115 neuroblastoma cells by radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol 33:303–309
Ireland SJ, Tyers MB (1987) Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced depolarization of the rat isolated vagus nerve. Br J Pharmacol 90:229–238
Kilpatrick GJ, Jones BJ, Tyers MB (1987) The identification and distribution of 5-HT3 receptors in rat brain using radioligand binding. Nature 330:746–748
Neijt HC, Vijverberg HPM, Van den Berken J (1986) The dopamine response in mouse neuroblastoma cells is mediated by serotonin 5HT receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 127:271–274
Neijt HC, te Duits IJ, Vijverberg HPM (1988) Pharmacological characterization of serotonin 5-HT3 receptor-mediated electrical response in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Neuropharmacology 27:301–307
Richardson BP, Engel G (1986) The pharmacology and function of the 5-HT3 receptors. Trends Neurosci 9:424–428
Richardson BP, Engel G, Donatsch P, Stadler PA (1985) Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature (London) 316:126–131
Rodbard D (1974) Statistical quality control and routine data processing for radioimmunoassay and immunoradiometric assays. Clin Chem 20:1255–1270
Round A, Wallis DI (1986) The depolarizing action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on rabbit vagal afferent and sympathetic neurones in vitro and its selective blockade by ICS 205–930. Br J Pharmacol 88:485–494
Round A, Wallis DI (1987) Further studies on the blockade of 5-HT depolarizations of rabbit vagal afferent and sympathetic ganglion cells by MDL 72222 and other antagonists. Neuropharmacology 26:39–48
Scatchard G (1949) Attraction of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann NY Acad Sci 51:660–679
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send of print requests to D. Hoyer at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neijt, H.C., Karpf, A., Schoeffter, P. et al. Characterisation of 5-HT3 recognition sites in membranes of NG 108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma cells with [3H]ICS 205-930. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337, 493–499 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182721
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182721