Summary
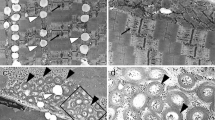
A basic problem in genetic counseling of families with Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy (DMD/BMD) concerns the carrier status of female relatives of an affected male. In about 60% of these patients, deletions of one or more exons of the dystrophin gene can be identified. These deletions preferentially include exon 45, which can be detected by multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Southern blot analysis of genomic cosmid clones that map to this critical region. As a new approach for definitive carrier detection, we have performed chromosomal in situ suppression (CISS) hybridization with these cosmid clones in female relatives of four unrelated patients. In normal females, most metaphases showed signals on both×chromosomes, whereas only one×chromosome was labeled in carriers. Our results demonstrate that CISS hybridization can define the carrier status in female relatives of DMD patients exhibiting a deletion in the dystrophin gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahata K, Hoffman EP, Kunkel LM, Ishiura S, Tsukahara T, Ishihara T, Sunohara N, Nonaka I, Ozawa E, Sugita H (1989) Dystrophin diagnosis: comparison of dystrophin abnormalities by immunofluorescence and immunoblot analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7154–7158
Bakker E, Bonten EJ, De Lange LF, Veenema H, Majoor-Krakauer D, Hofker MH, Ommen GJB van, Pearson PL (1986) DNA probe analysis for carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a standard diagnostic procedure. J Med Genet 23:573–580
Bakker E, Veenema H, Den Dunnen JT, Broeckhoven C van, Grootscholten PM, Bonten EJ, Ommen GJB van, Pearson PL (1989) Germinal mosaicism increases the recurrence risk for “new” Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. J Med Genet 26:553–559
Blonden LAJ, Den Dunnen JT, Paasen HMB van, Wapenaar MC, Grootscholten PM, Ginjaar HB, Bakker E, Pearson PL, Ommen GJB van (1989) High resolution deletion breakpoint mapping in the DMD gene by whole cosmid hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res 17:5611–5621
Bonilla E, Samitt CE, Miranda AF, Hays AP, Salviati G, DiMauro S, Kunkel LM, Hoffman EP, Rowland LP (1988) Duchenne muscular dystrophy: deficiency of dystrophin at the muscle cell surface. Cell 54:447–452
Chamberlain JS, Gibbs RA, Ranier JE, Caskey CT (1989) Multiplex PCR for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In: Innis M, Gelfand D, Sninski J, White T (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 272–281
Chen J, Denton MJ, Morgan G, Pearn JH, Mackinlay AG (1988) The use of field-inversion gel electrophoresis for deletion detection in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet 42:777–780
Cherif D, Bernard O, Berger R (1989) Detection of single-copy genes by nonisotopic in situ hybridization on human chromosomes. Hum Genet 81:358–362
Cremer T, Lichter P, Manuelidis L, Ward DC (1988) Detection of chromosome aberrations in metaphase and interphase tumor cells by in situ hybridization using chromosome-specific library probes. Hum Genet 80:235–246
Darras BT, Blattner P, Harper JF, Spiro AJ, Alter S, Francke U (1988) Intragenic deletions in 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)/Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) families studied with the dystrophin cDNA: location of breakpoints on HindIII and BglI exon-containing fragment maps, meiotic and mitotic origin of the mutation. Am J Hum Genet 43:620–629
Davie AM, Emery AH (1978) Estimation of proportion of new mutants among cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet 15:339–345
Den Dunnen JT, Grootscholten PM, Bakker E, Blonden LAJ, Ginjaar HB, Wapenaar MC, Paassen HMB van, Broeckhoven C van, Pearson PL, Ommen GJB van (1989) Topography of the DMD gene: FIGE and cDNA analysis of 194 cases reveals 115 deletions and 13 duplications. Am J Hum Genet 45:835–847
Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Kunkel LM (1987) Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 51:919–928
Kievits T, Dauwerse JG, Devilee P, Breuning MH, Cornelisse CJ, Ommen GJB van, Pearson PL (1990) Rapid sub-chromosomal localization of cosmids by non-radioactive in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 53:134–136
Koenig M, Monaco AP, Kunkel LM (1988) The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell 53:219–288
Koenig M, et al (1989) The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet 45:498–506
Landegent JE, Jansen in de Wal N, Dirks RW, Baas F, Van der Ploeg M (1987) Use of whole cosmid cloned genomic sequences for chromosomal localization by non-radioactive in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 73:354–357
Langer PR, Waldrop AA, Ward DC (1981) Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:6633–6637
Lichter P, Cremer T, Tang C-JC, Watkins PC, Manuelidis L, Ward DC (1988) Rapid detection of human chromosome 21 aberrations by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:9664–9668
Lichter P, Tang C-JC, Call K, Hermanson G, Evans GA, Housman D, Ward DC (1990) High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science 247:64–69
Love DR, Davis KE (1989) Duchenne muscular dystrophy: the gene and the protein. Mol Biol Med 6:7–17
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (eds) (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Mao Y, Cremer M (1989) Detection of Duchenne muscular carriers by dosage analysis using the DMD cDNA clone 8. Hum Genet 81:193–195
Miranda AF, Francke U, Bonilla E, Martucci G, Schmidt B, Salviati G, Rubin M (1989) Dystrophin immunocytochemistry in muscle culture: detection of a carrier of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Genet 32:268–273
Moser H (1984) Duchenne muscular dystrophy: pathogenetic aspects and genetic prevention. Hum Genet 66:17–40
Nederlof PM, Van der Flier S, Wiegant J, Raap AK, Tanke HJ, Loem JS, Van der Ploeg M (1990) Multiple fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytometry 11:126–131
Pinkel D, Gray JW, Trask B, Van den Engh G, Fuscoe J, Van Dekken H (1986) Cytogenetic analysis with fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 51:151–157
Shapira F, Dreyfus JC, Shapira G, Démos J (1960) Etudes de l'aldolase et de la créatine kinase du sérum chez les méres de myopathes. Rev Fr Etudes Clin Biol 5:990–994
Speer A, Rosenthal A, Billwitz H, Hanke R, Forrest SM, Love D, Davies KE, Coutelle C (1989) DNA amplification of a further exon of DMD locus increases possibilities for deletion screening. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4892
Wapenaar MC, Kievits T, Hart KA, Abbs S, Blonden LAJ, Den Dunnen JT, Grootscholten PM, Bakker E, Verellen-Dumoulin C, Bobrow M, Ommen GJB van, Pearson PL (1988) A deletion hot spot in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Genomics 2:101–108
Yang T, Hansen S, Oishi K, Ryder O, Hamkalo B (1982) Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X-chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6593–6597
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ried, T., Mahler, V., Vogt, P. et al. Direct carrier detection by in situ suppression hybridization with cosmid clones of the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy locus. Hum Genet 85, 581–586 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193578
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193578