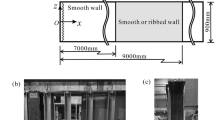
Abstract
In this paper we address the effectiveness of riblets on skin friction reduction under the influence of an adverse pressure gradient. The measurements were taken in a wind tunnel. Skin friction was observed with a drag balance which has a reproducibility of better than 1%. The accuracy of the balance is estimated to be less than 1% for the case of zero-pressure gradient and at most 3% for a pressure gradient. The data on skin friction reduction at zero pressure gradient were consistent with previous results and amount to 5% at dimensionless riblet width of s + = 13. We find that at all adverse pressure gradients the skin friction reduction by riblets persists. At moderate pressure gradients the reduction increases somewhat to 7%. The velocity profile which is also measured, exhibits the characteristic shape for a boundary layer with an adverse pressure gradient and agrees well with theory. From the velocity profiles measured at two stations we estimated with the help of a momentum balance the skin friction and skin friction reduction. The results differ from the drag-balance data. Due to the poor accuracy of the momentum balance method which we estimate in our case, we conclude that the results obtained with this method are less reliable than those obtained with the drag balance. This throws some doubt on previous results on drag reduction under the influence of a pressure gradient which were based on the momentum balance method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechert, B. W.; Bartenwerfer, M. 1989: The viscous flow on surfaces with longitudinal ribs. J. Fluid Mech. 206, 105–129
Bradshaw, P. 1967: The turbulent structure of equilibrium boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 29, 4, 625–645
Choi, K.-S. 1990: Effects of longitudinal pressure gradients on turbulent drag reduction with riblets. Turbulence Control by Passive Means (ed. E. Coustols), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Clauser, F. H. 1954: Turbulent boundary layers in adverse pressure gradients. J. Aero. Sci., 21, 91–108
Coustols, E.; Savill, A. M. 1992: Turbulent skin-friction drag reduction by active and passive means; Parts 1 and 2. Special Course on Skin-Friction Drag Reduction. Agard Report 786, 8-1–8-80
Frei, D.; Thomann, H. 1980: Direct measurements of skin friction in a turbulent boundary layer with strong adverse pressure gradient. J. Fluid Mech. 101, 79–95
Luchini, P.; Manzo, F.; Pozzi, A. 1991: Resistance of a groove surface to a parallel flow and cross-flow. J. Fluid Mech. 228, 87–109
Ludweig, H.; Tillmann, W. 1949: Untersuchungen über die Wandschubspannung in turbulente Reibungsschichten. Ing.- Arch 17, 288–299
Mellor, G. L.; Gibson, D. M. 1966: Equilibrium turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech., 24, 2, 225–253
Robinson, S. K. 1991: Coherent motions in the turbulent boundary layer. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 23, 601–639
Tardu, S.; Pulvin, P.; Truong T. V. 1991: Fine structure of the turbulence in a boundary layer manipulated by internal devices. 1st European Turbulence Conference, Cambridge, 16–20 September
Townsend, A. A. 1976: The structure of turbulent shear flow (second edition), London: Cambridge Univ. Press
Schlichting, H. 1968: Boundary-layer theory. New York: McGraw-Hill
Schofield, W. H. 1981: Equilibrium boundary layers in moderate to strong adverse pressure gradients. J. Fluid Mech. 113, 91–122
Schwarz-van Manen, A. D.; Hoogsteen, R.; Stouthart, J. C.; Krishna Prasad, K.; Nieuwstadt, F. T. M. 1991: Coherent structures over a smooth and triangular riblet drag reducing surface. Recent development in turbulence management (ed. K.-S. Choi), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Squire, L. C.; Savill, A. M. 1989: Drag measurements on planar riblet surfaces at high subsonic speeds. Appl. Sci. Res. 46, 229–244
Truong, T. V.; Pulvin, Ph. 1989: Influence of wall riblets on diffuser flow. Appl. Sci. Res. 46, 217–228
Van den Berg, B. 1988: Drag reducing potentials of turbulent manipulation in adverse pressure gradient flow. AIAA J 26, 367–368
Walsh, M. J, 1990. Riblets. In: Viscous drag reduction in boundary layers (eds. Bushnell, D. M. Heffner, J. W.), Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, 203–261
Walsh, M. J.; Anders, J. B. 1989: Riblet/LEBU research at NASA Langley. Appl. Sci. Res., 46, 255–262
White, F. M. 1991: Viscous Fluid Flow (second edition). New York: McGraw-Hill
Yaglom, A. M. 1979: Similarity laws for constant pressure and pressure gradient turbulent wall flows. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 11, 505–540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieuwstadt, F.T.M., Wolthers, W., Leijdens, H. et al. The reduction of skin friction by riblets under the influence of an adverse pressure gradient. Experiments in Fluids 15, 17–26 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195591
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195591