Abstract
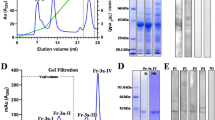
The major birch (Betula alba L.) pollen allergen, Bet v 1, has been shown to be homologous to pathogenesis-related proteins in a number of plants. Recently, it was demonstrated that a ginseng protein with high homology to an intracellular pathogenesis-related protein of parsley and to Bet v 1 is a ribonuclease (RNase). Birch pollen extract was separated in an RNase activity gel. Four major RNase bands were excised from the gel, reseparated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and identified by Western blotting with a specific Bet v 1 monoclonal antibody and patient's serum. Thus the monomer and the dimer of Bet v 1 showed RNase activity. Purified recombinant Bet v 1 was shown to degrade plant RNA. The RNase activity of recombinant Bet v 1 was 180 units · mg−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IPR:
-
intracellular pathogenesis-related (protein)
- PR:
-
pathogenesis related
- RNasin:
-
RNase inhibitor
References
Breiteneder H, Pettenburger K, Bito A, Valenta R, Kraft D, Rumpold H, Scheiner O, Breitenbach M (1989) The gene coding for the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 is highly homologous to a pea disease resistance response gene. EMBO J 8: 1935–1938
Bufe A, Becker W-M, Schramm G, Petersen A, Mamat U, Schlaak M (1994) Major allergen Phl p Va (timothy grass) bears at least two different IgE-reactive epitopes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94: 173–181
Bufe A, Schramm G, Keown MB, Schlaak M, Becker W-M (1995) Major allergen Phl p Vb is a novel pollen RNase. FEBS Lett 363: 6–12
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Larsen J, Stroman P, Ipsen H (1992) PCR based cloning and sequencing of isogenes encoding the tree pollen major allergen Car b 1 from Carpinus betulus, hornbeam, Mol Immunol 29: 703–711
Moiseyev GP, Beintema JJ, Fedoreyeva LI, Yakovlev GI (1994) High sequence similarity between a ribonuclease from ginseng calluses and fungus-elicited proteins from parsley indicates that intracellular pathogenesis-related proteins are ribonucleases. Planta 193: 470–472
Petersen A, Becker W-M, Schlaak M (1993) Comparison of four grass pollen species concerning their allergens of grass group V by 2D immunoblotting and microsequencing. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 374: 855–861
Scheiner O (1992) Recombinant allergens: biological, immunological and practical aspects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 98: 93–96
Somssich IE, Schmelzer E, Kawalleck P, Hahlbrock K (1988) Gene structure and in situ transcript localization of pathogenesis-related protein 1 in parsley. Mol Gen Genet 213: 93–98
Yen Y, Green PJ (1991) Identification and properties of the major ribonucleases of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 97: 1487–1493
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We thank Daniela Warneke for her excellent technical assistance and Oliver Cromwell (Allergopharma, Reinbek, Germany) for carefully reading the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bufe, A., Spangfort, M.D., Kahlert, H. et al. The major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, shows ribonuclease activity. Planta 199, 413–415 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195733
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195733