Summary
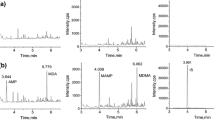
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of methamphetamine and amphetamine in biologic materials was carried out by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. A deuterium-labeled methamphetamine was employed as an internal standard with a detection limit of 50 pg and absolute stability and reproducibility. Blood was found to be the best material for estimation of the toxicity of the stimulant drug. It can be replaced by muscle which contains methamphetamine concentrations close to those of blood. The authors' classification of the toxic blood levels of methamphetamine from therapeutic to fatal doses was confirmed by additional data obtained from new case studies.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurden qualitative und quantitative Analysen von Methamphetamin und Amphetamin aus biologischem Material mittels Gaschromatographie/Massenspektrometrie durchgeführt. Als interner Standart wurde Deuterium-markiertes Methamphetamin mit einer Nachweisgrenze von 50 pg bei hoher Stabilität und Reproduzierbarkeit verwendet. Blut erwies sich als das beste Ausgangsmaterial zur toxikologischen Untersuchung dieses stimulierenden Arzneimittels. Es kann jedoch auch durch Muskulatur ersetzt werden, in der Methamphetamin-Konzentrationen ähnlich denen im Blut nachweisbar sind. Die vom Autor vorgenommene Klassifizierung von toxischen Methamphetamin-Blutkonzentrationen nach therapeutischen und tödlichen Dosen wurde durch weitere Daten aus neuen Fällen bestätigt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagata T, Hara K, Kageura M (1979) Medico-legal demonstration of wake amines — Detection of amines from biological materials and signification of determined values on practical cases. Proc Jpn Soc Med Mass Spectrom 4:95–102 (in Japanese)
Lindeke B, Cho AK (1972) Specifically deuterated 1-phenyl-1-isopropylamines — Synthesis of deuterium-labelled (±)-amphetamine, (±)-p-methoxyamphetamine and (±)-α-methyltyramine. Acta Pharm Suec 9:363–372
Kamei K, Murata M, Ishii K, Namekata M, Momose A (1973) Detection of amphetamine and related amines in urine by gas chromatography and combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 21:1996–2003
Nagata T, Hara K, Kageura M, Totoki K, Takamoto M (1977) Demonstration of amphetamine, methamphetamine, and ephedrine in blood by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Jpn J Legal Med 31:146–150 (in Japanese)
Kojima T, Une I, Yashiki M (1983) CI-mass fragmentographic analysis of methamphetamine and emphetamine in human autopsy tissues after acute methamphetamine poisoning. Forensic Sci Int 21:253–258
Suzuki O, Hattori H, Asano M (1984) Detection of methamphetamine and emphetamine in a single human hair by gas chromatography/chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J Forensic Sci 29:611–617
Nagata T (1983) Signification of metamphetamine concentration in body fluids and tissues. Jpn J Legal Med 37:513–518 (in Japanese)
Bruce RB, Maynard WR Jr (1969) Determination of amphetamine and related amines in blood by gas chromatography. Anal Chem 41:977–979
Gaffney TE, Hammar C-G, Holmstedt B, McMahon RE (1971) Ion specific detection of internal standards labelled with stable isotopes. Anal Chem 43:307–310
Cho AK, Lindeke B, Hodshon BJ, Jenden DJ (1973) Deuterium substituted amphetamine as an internal standard in gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric (GC-MS) assay for amphetamine. Anal Chem 45:570–574
Matin SB, Wan SH, Knight JB (1977) Quantitative determination of isomers of amphetamine in human plasma and saliva using chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrom 4:118–121
Kreuz DS, Axelrod J (1974) Amphetamine in human plasma: a sensitive and specific enzymatic assay. Science 183:420–421
Broughton A, Ross DL (1975) Drug screening by enzymatic immunoassay with the centrifugal analyzer. Clin Chem 21:186–189
Faraj BA, Israili ZH, Kight NE, Smissman EE, Pazdernik TJ (1976) Specificity of an antibody directed against d-methamphetamine — studies with rigid and nonrigid analogs. J Med Chem 19:20–25
Tamaki Y, Fukuda M, Kishida T, Takahashi N (1983) Solid-phase micro ELISA for methamphetamine. Jpn J Legal Med 37:417–420
O'Brien JE, Zazulak W, Abbey V, Hinsvark O (1972) Determination of amphetamine and phentermine in biological fluids. J Chromatogr Sci 10:336–341
Mizoi Y (1982) Methamphetamine concentrations in blood and organs of intoxicated cases. In: Nanikawa R (ed) Detection of poisons and drugs in biological specimen. Jpn J Legal Med 36:513–526 (in Japanese)
Une I (1983) A study on the metabolism of methamphetamine in its abusers. Jpn J Legal Med 37:814–822 (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant-in-aid for scientific research in 1983/1984 from the Japanese Ministry of Education
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, K., Nagata, T. & Kimura, K. Forensic toxicologic analysis of methamphetamine and amphetamine in body materials by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Z Rechtsmed 96, 93–104 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198625
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198625
Key words
- Methamphetamine, toxicological analysis in biological material
- Amphetamine, in body material
- Toxicology, Methamphetamine, amphetamine